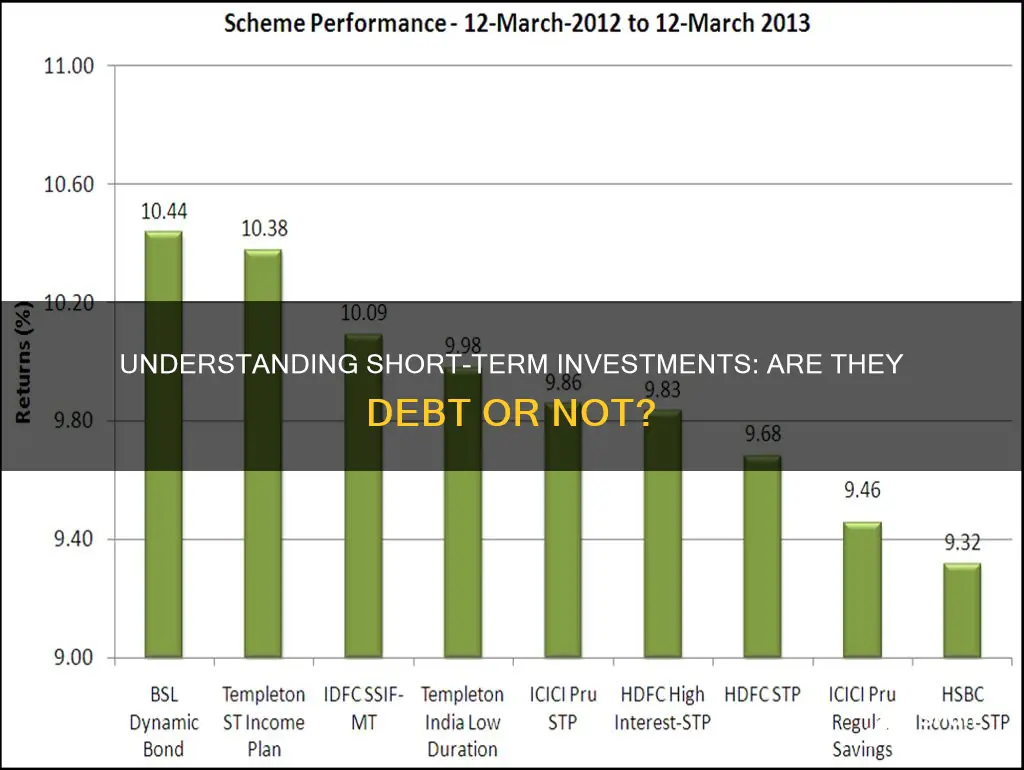
Short-term investments are a crucial aspect of financial planning, and understanding their nature is essential for investors. When considering whether short-term investments are debt, it's important to recognize that they are typically classified as non-debt financial instruments. These investments are designed to be held for a relatively short period, often less than a year, and they do not involve borrowing or lending money with interest. Instead, they are used to generate returns through various strategies, such as trading securities, derivatives, or money market instruments. While short-term investments can be considered more liquid and less risky compared to long-term investments, they are not debt obligations and do not carry the same financial commitments as borrowing.
What You'll Learn
- Definition: Short-term investments in debt are financial assets with a maturity of less than one year
- Types: Examples include money market funds, treasury bills, and commercial paper
- Risk: These investments carry lower risk compared to long-term debt
- Liquidity: They offer quick access to funds without significant loss of value
- Taxation: Short-term debt investments may be taxed differently from long-term holdings

Definition: Short-term investments in debt are financial assets with a maturity of less than one year
Short-term investments in debt, often referred to as money market instruments, are a crucial component of financial markets and play a vital role in the global economy. These investments are characterized by their short-term nature, typically maturing in less than one year. This definition is essential to understand as it highlights the liquidity and flexibility associated with these financial assets.
When we talk about short-term investments in debt, we are referring to various financial instruments that are designed to be held for a brief period. These can include treasury bills, certificates of deposit (CDs), and commercial paper. Each of these instruments has a unique feature that makes it suitable for short-term investment strategies. For instance, treasury bills are issued by governments and offer a low-risk investment option with a maturity period ranging from a few days to a year. CDs, on the other hand, are issued by banks and provide a fixed rate of return over a specified period, often with a penalty for early withdrawal.
The key aspect of these short-term investments is their ability to provide liquidity to investors. Given their short maturity, these assets can be easily converted into cash without significant loss of value. This liquidity is particularly attractive to investors who seek to manage their cash flow effectively or those who prefer a more dynamic investment approach. For instance, a business might use short-term debt investments to quickly access funds for operational expenses or to take advantage of short-term market opportunities.
In the context of personal finance, short-term investments in debt can be a strategic tool for individuals looking to grow their savings or manage their cash reserves. These investments offer a balance between safety and potential growth, making them an attractive option for risk-averse investors. Moreover, the short-term nature of these investments allows individuals to access their funds quickly if needed, providing a level of flexibility that is not always available with longer-term investments.
Understanding the definition of short-term investments in debt is crucial for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers alike. It enables a clearer picture of the financial landscape, helping to manage risks, allocate resources efficiently, and make informed decisions. By recognizing the characteristics and benefits of these short-term financial assets, stakeholders can navigate the complex world of finance with greater confidence and precision.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: A Brainly Guide
You may want to see also

Types: Examples include money market funds, treasury bills, and commercial paper
Short-term investments are a crucial component of financial portfolios, offering liquidity and the potential for capital growth over a relatively brief period. These investments are typically characterized by their low-risk nature and the ability to be quickly converted into cash without significant loss of value. One of the most common types of short-term investments is money market funds. These funds are designed to provide a safe and liquid investment option, often used by individuals and institutions as a place to park their cash temporarily. Money market funds invest in a diversified portfolio of short-term, high-quality securities, such as government bonds, certificates of deposit, and commercial paper. They offer a competitive interest rate while maintaining a stable net asset value, making them an attractive choice for risk-averse investors.
Treasury bills are another essential example of short-term investments. These are issued by governments and represent a loan made by an investor to the government for a specified period, typically ranging from a few days to a year. Treasury bills are considered one of the safest investments due to their low risk and high liquidity. They are often used by governments to manage their cash flow and are a popular choice for investors seeking a secure and stable return. The interest earned on treasury bills is usually paid at maturity, providing a fixed income stream for investors.
Commercial paper is a unique short-term investment instrument that is primarily used by corporations. It is a promissory note issued by a company, promising to pay the holder the face value on a specified maturity date. Commercial paper is typically used for short-term financing, such as covering operational costs or managing cash flow. Investors purchase this paper, essentially lending money to the issuing company, and are repaid with interest upon maturity. This investment is considered low-risk, especially when issued by large, creditworthy corporations, making it an attractive option for conservative investors.
In summary, short-term investments play a vital role in financial planning, offering a balance between liquidity and potential returns. Money market funds, treasury bills, and commercial paper are prime examples of such investments, each serving a specific purpose in the financial market. These instruments cater to various investor needs, providing safe havens for cash management and offering competitive returns for those seeking short-term capital growth. Understanding these types of investments is essential for anyone looking to optimize their financial portfolio and make informed decisions regarding their short-term financial goals.
Debt vs. Equity: Long-Term Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

Risk: These investments carry lower risk compared to long-term debt
Short-term investments, often referred to as money market instruments, are indeed a type of debt investment, but they differ significantly in terms of risk and liquidity compared to long-term debt. These short-term investments are typically considered to carry lower risk, making them an attractive option for investors seeking a balance between safety and potential returns.
The primary reason for this lower risk is the short duration of these investments. Short-term investments, such as treasury bills, certificates of deposit (CDs), and money market funds, are designed to mature within a year or less. This short-term nature means that the principal amount is less likely to be affected by market fluctuations and economic downturns. For instance, if an investor purchases a 90-day CD, the investment is secure until maturity, and the principal is guaranteed to be returned. This level of security is a stark contrast to long-term debt, which can be subject to various market risks and economic uncertainties over an extended period.
Additionally, short-term investments are highly liquid, allowing investors to access their funds quickly without incurring significant losses. This liquidity is particularly important for investors who need to maintain a certain level of cash flow or who may require their capital in case of unexpected expenses. In contrast, long-term debt often involves a longer commitment, making it less liquid and potentially more challenging to convert into cash without a loss.
Another factor contributing to the lower risk is the creditworthiness of the issuing entities. Short-term investments are often backed by government entities or highly rated financial institutions, ensuring a higher level of security. For example, US Treasury bills are considered one of the safest investments due to their backing by the US government. This level of creditworthiness further reduces the risk associated with these short-term investments.
In summary, short-term investments are a safer option compared to long-term debt due to their short duration, high liquidity, and the creditworthiness of the issuing entities. These factors make them an ideal choice for investors who prioritize capital preservation and quick access to funds while still seeking some level of return. Understanding the risk profile of short-term investments is crucial for investors to make informed decisions about their portfolios.
Debt Securities: Unlocking the Investment-Finance Connection
You may want to see also

Liquidity: They offer quick access to funds without significant loss of value
Short-term investments, often referred to as liquid assets or near-cash equivalents, are financial instruments that provide investors with a high level of liquidity. This means they can be quickly converted into cash with minimal impact on their value. These investments are crucial for individuals and businesses seeking to maintain financial flexibility and ensure they have access to funds when needed.
One of the key advantages of short-term investments is their ability to offer liquidity without compromising on the potential for growth. These investments typically have a short maturity period, ranging from a few days to a year, which allows investors to access their funds relatively soon after purchase. For example, money market funds, which are a common type of short-term investment, provide investors with a safe and liquid option to park their money while still earning a modest return.
In the context of personal finance, short-term investments can be essential for emergency funds, short-term goals, or even as a means to bridge the gap between savings and larger investments. For instance, a person might invest in a 90-day T-bill, a type of short-term debt instrument, to have immediate access to funds without tying up their money for an extended period. This ensures that they can quickly respond to financial obligations or take advantage of unexpected investment opportunities.
Businesses also benefit significantly from short-term investments. Companies often use these investments to manage their cash flow, ensuring they have the necessary funds to cover short-term expenses and obligations. For example, a business might invest in commercial paper, which is a short-term debt instrument, to finance day-to-day operations or bridge the gap between accounts payable and receivable. This allows businesses to maintain a healthy cash flow and avoid potential financial strain.
Additionally, short-term investments can be a strategic tool for risk management. Investors can diversify their portfolios by including liquid assets, which can act as a safety net during market downturns or economic uncertainties. By having a portion of their investments in highly liquid assets, investors can quickly respond to changing market conditions and protect their capital. This strategic approach to liquidity management is a critical aspect of financial planning and risk mitigation.
Unlocking Long-Term Wealth: ETFs as a Strategic Investment Strategy
You may want to see also

Taxation: Short-term debt investments may be taxed differently from long-term holdings
The classification of short-term investments as debt can have significant implications for taxation, often leading to different treatment compared to long-term holdings. When an individual or entity holds an investment for a short period, typically less than a year, it is generally considered a short-term capital gain or ordinary income. This distinction is crucial for tax purposes as it determines the applicable tax rates and rules.
In many jurisdictions, short-term capital gains are taxed at a higher rate than long-term gains. This is because short-term investments are often seen as more speculative and volatile, and the tax system aims to discourage frequent trading and short-term market manipulation. As a result, investors may be incentivized to hold investments for longer periods to benefit from lower tax rates on capital gains.
For example, in the United States, short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income, which can be up to 37% for high-income earners. In contrast, long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate, ranging from 0% to 20%, depending on the taxpayer's income level. This significant difference in tax treatment encourages investors to consider the duration of their holdings when making investment decisions.
Additionally, the classification of short-term investments as debt can impact the timing of tax payments. Short-term debt investments may be subject to immediate taxation when sold, whereas long-term investments might allow for a more gradual tax liability over time. This difference can affect an investor's cash flow and financial planning, especially for those with substantial short-term gains or losses.
Understanding the tax implications of short-term investments is essential for investors to make informed decisions and manage their tax obligations effectively. It highlights the importance of considering the investment horizon and the potential tax consequences when evaluating different investment opportunities. Proper tax planning can help investors optimize their financial strategies and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Long-Term Investments: Separating Fact from Fiction
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Short-term investments are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or sold within one year or the business's operating cycle, whichever is longer. These investments are typically low-risk and liquid, providing an opportunity to generate returns while maintaining easy access to the funds.
The primary distinction lies in the time horizon. Short-term investments are for the near future, often used to meet upcoming financial obligations or take advantage of short-term market opportunities. Long-term investments, on the other hand, are held for an extended period, typically years, and are often more aggressive in nature to achieve higher returns.
No, short-term investments are generally not classified as debt. They are a form of investment or financial asset. Debt, in contrast, represents a liability or obligation to repay a loan or borrowings. Short-term investments are used to generate returns or provide liquidity, not to finance long-term projects or operations.
Common short-term investments include money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), treasury bills, and short-term bonds. These instruments offer low to moderate risk and provide a safe haven for investors seeking quick access to their funds without compromising on returns.
Short-term investments are reported in the current assets section of a company's balance sheet. They are valued at fair value, and any changes in value are reflected in the income statement as investment income or loss. This classification helps investors understand the liquidity and short-term financial health of a business.