Magic Formula Investing is a unique and innovative approach to stock selection and portfolio management, offering a systematic way to identify undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and growth potential. This method, developed by Joel Greenblatt, combines two powerful financial ratios, the Magic Formula Score and the Quality Ratio, to rank companies based on their financial health and growth prospects. By applying these ratios, investors can uncover hidden gems in the market, providing an edge in building a robust and profitable investment portfolio. This strategy has gained popularity among value investors seeking a disciplined and data-driven approach to stock picking.
What You'll Learn
- Magic Formula: A quantitative approach to stock selection, using financial ratios
- Screening Criteria: Investors use specific ratios and metrics to filter stocks
- Value and Momentum: The formula combines value and momentum strategies for stock picks
- Backtesting: Historical performance validation of the Magic Formula strategy
- Portfolio Construction: Building a diversified portfolio using the selected stocks

Magic Formula: A quantitative approach to stock selection, using financial ratios
The Magic Formula is a quantitative investment strategy that aims to identify undervalued stocks by using a combination of financial ratios and a specific formula. This approach was popularized by Joel Greenblatt, a renowned investor and professor, who introduced the concept in his book "The Little Book of Common Sense Investing." The Magic Formula is designed to be a simple and systematic way to find companies with strong financial fundamentals and attractive valuation metrics.
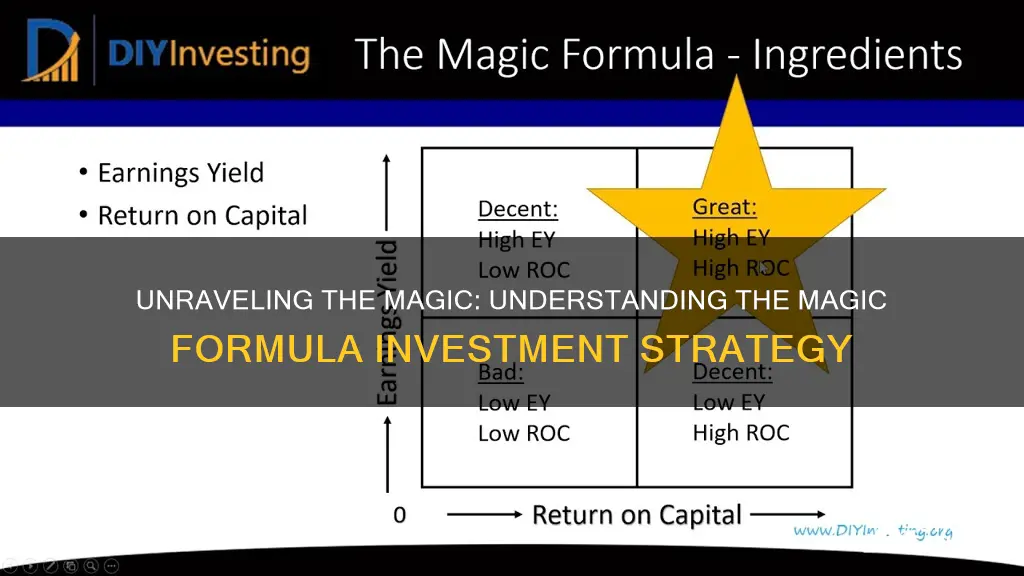
At its core, the Magic Formula involves calculating two key ratios: the Return on Capital (ROC) and the Equity Multiples (EM). The ROC measures a company's ability to generate returns from its capital investments, while EM assesses the efficiency of equity financing. These ratios are then combined using a specific formula to rank companies based on their potential for profitability and financial health.
Here's a breakdown of the process: First, you would calculate the ROC, which is determined by dividing a company's net operating profit (NOP) by the sum of its invested capital (IC). NOP represents the company's earnings before interest and taxes, while IC includes assets like property, plant, and equipment, as well as long-term debt. A higher ROC indicates better efficiency in generating returns from capital investments.
Next, the Equity Multiples (EM) ratio is calculated by dividing a company's market value of equity (MVE) by its book value of equity (BVE). MVE represents the company's total market value, while BVE is the value of shareholders' equity as per the company's balance sheet. A lower EM suggests that the company's equity is being utilized more efficiently.
The Magic Formula then combines these two ratios. Companies with a high ROC and a low EM are considered the best candidates for investment. The formula ranks companies based on these combined scores, providing a quantitative ranking system for stock selection.
This approach is particularly appealing to investors who prefer a systematic and data-driven method of stock picking. By focusing on financial ratios and a specific formula, the Magic Formula aims to eliminate emotional biases and provide a more objective evaluation of companies. It allows investors to identify stocks that are potentially undervalued and have strong financial fundamentals, offering the potential for long-term capital appreciation.
The Homeowner's Dilemma: Is Buying a House Truly a Smart Investment?
You may want to see also

Screening Criteria: Investors use specific ratios and metrics to filter stocks
Investors employing the Magic Formula approach to stock selection utilize a systematic method to identify undervalued companies with strong growth potential. This strategy relies heavily on a set of screening criteria, which are specific ratios and metrics designed to evaluate a company's financial health, efficiency, and potential for long-term growth. These criteria act as filters, allowing investors to narrow down their search from the vast universe of stocks to a more manageable and potentially profitable group.
One of the key screening criteria is the Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio, which compares a company's market value to its book value. A low P/B ratio indicates that the stock might be undervalued, suggesting that the market has not fully recognized the company's intrinsic worth. Investors often set a threshold for this ratio, such as a P/B of 1 or lower, to identify potential bargains. For instance, a tech startup with a P/B ratio of 0.5 might be considered an attractive investment opportunity.
Another important metric is the Return on Equity (ROE), which measures a company's profitability in relation to the amount of equity invested by shareholders. A consistently high ROE over several years is a strong indicator of a well-managed business with a history of generating substantial profits. Investors might target companies with an ROE of 20% or higher, as this suggests efficient use of shareholders' capital and a potential for continued growth.
Additionally, the Magic Formula approach often incorporates the concept of 'Quality of Earnings,' which assesses the sustainability and quality of a company's earnings. This can be evaluated through metrics like Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) margin and the consistency of earnings growth over time. A company with high and consistent EBIT margins and steady earnings growth is likely to be a more reliable investment.
By applying these screening criteria, investors can systematically evaluate and compare companies across various sectors and industries. This approach helps to eliminate the influence of emotional decision-making and provides a more objective basis for stock selection. The Magic Formula strategy emphasizes the importance of fundamental analysis, ensuring that investments are made based on a company's financial strength and growth prospects rather than market sentiment or short-term trends.
GME: The People's Investment
You may want to see also

Value and Momentum: The formula combines value and momentum strategies for stock picks
The Magic Formula Investing strategy is a popular approach that aims to identify undervalued stocks with strong momentum, offering investors a potential edge in the market. This method combines two fundamental investment strategies: value investing and momentum investing. Value investing focuses on finding stocks that are priced below their intrinsic worth, while momentum investing seeks out stocks that are experiencing upward price trends. By combining these strategies, the Magic Formula provides a comprehensive framework for stock selection.
In this approach, the term 'value' refers to the fundamental analysis of a company's financial health and its valuation relative to its assets, earnings, and cash flow. Stocks with a high value score are considered undervalued, meaning their market price is lower than what the market should be paying based on their intrinsic value. On the other hand, momentum is about the recent performance and trend of a stock's price. Momentum-rated stocks have shown consistent positive price movement over a defined period, indicating strong investor confidence and potential for further growth.
The Magic Formula Investing strategy involves a quantitative process to rank stocks based on these two factors. It uses a set of criteria to calculate a 'Magic Formula' score for each stock, which is a combination of the value and momentum ratings. The formula typically includes financial ratios and metrics such as price-to-book ratio, return on equity, and price-to-earnings ratio, along with momentum indicators like the relative strength index and moving average convergence divergence (MACD). By assigning weights to these factors, investors can identify stocks that exhibit both value and momentum characteristics.
The beauty of this strategy lies in its ability to provide a disciplined and systematic approach to stock selection. Investors can use the Magic Formula to generate a list of potential investment candidates, ensuring that their picks are not solely based on subjective opinions or market trends. The combination of value and momentum allows for a more comprehensive analysis, capturing stocks that are both undervalued and experiencing positive momentum. This dual approach can lead to better risk-adjusted returns over time.
Additionally, the Magic Formula Investing strategy is designed to be adaptable and customizable. Investors can adjust the weights and parameters of the formula to suit their investment style and risk tolerance. This flexibility enables investors to fine-tune the strategy according to their preferences, making it a versatile tool for various investment scenarios. By combining value and momentum, this approach offers a comprehensive and data-driven method to navigate the stock market and potentially outperform traditional investment strategies.
The Power of Compounding: Unlocking the Secret to Tripling Your Investments
You may want to see also

Backtesting: Historical performance validation of the Magic Formula strategy
Backtesting is a crucial step in evaluating the effectiveness of the Magic Formula strategy, as it allows investors to assess the historical performance of the approach and make informed decisions. This process involves simulating the Magic Formula strategy over a specific period using historical market data and comparing the results to a benchmark index or a buy-and-hold strategy. By backtesting, investors can gain valuable insights into the strategy's potential and identify any weaknesses or strengths that may have emerged over time.
The backtesting process typically begins with gathering historical financial data for the stocks or securities that the Magic Formula strategy aims to invest in. This data includes historical prices, volume, and other relevant financial metrics. The next step is to apply the Magic Formula formula to this historical data, calculating the ratings and rankings for each security. The formula, as explained in the initial prompt, considers various financial ratios and metrics to identify undervalued stocks. Once the ratings are calculated, investors can simulate different trading strategies, such as buying the top-rated stocks and holding them for a specified period.
During backtesting, investors can experiment with various parameters and assumptions to optimize the strategy. This includes deciding on the holding period, the frequency of rebalancing, and the initial investment amount. For example, one might choose to hold the stocks for a year, rebalance the portfolio monthly, and start with an initial investment of $10,000. By running multiple scenarios, investors can understand how different assumptions impact the strategy's performance.
The results of the backtest will provide a comprehensive overview of the Magic Formula strategy's historical performance. Investors can analyze key metrics such as the compound annual growth rate (CAGR), maximum drawdown, Sharpe ratio, and the percentage of trades that were profitable. These metrics offer insights into the strategy's risk-adjusted returns, consistency, and overall profitability over the backtesting period. A well-performing backtest can provide confidence in the strategy, while a poor performance may prompt investors to refine the formula or consider alternative approaches.
It is important to note that backtesting has its limitations. Historical data may not always accurately represent future market conditions, and the Magic Formula strategy's performance in a different market environment could vary. Additionally, backtesting assumes that the strategy would have been implemented in real-time, which might not be the case in practice due to various constraints. Despite these limitations, backtesting remains a valuable tool for investors to validate and refine their investment strategies, including the Magic Formula approach.
Unlocking Investment Value: A Guide to Valuation Techniques
You may want to see also

Portfolio Construction: Building a diversified portfolio using the selected stocks
To construct a diversified portfolio using the Magic Formula Investing strategy, you'll need to follow a structured approach to ensure optimal results. Here's a step-by-step guide to building your portfolio:
- Stock Selection: Begin by applying the Magic Formula criteria to a universe of stocks. This typically involves screening for companies with strong financial attributes, such as high return on equity (ROE), low debt, and consistent profitability. You can use financial data providers or software that offers pre-built Magic Formula screens to identify potential stocks. The goal is to select stocks that have the potential for above-average returns while maintaining a low risk profile.
- Ranking and Weighting: Once you have a list of qualified stocks, rank them based on specific factors. The Magic Formula often considers factors like price-to-book value (P/B ratio), return on assets (ROA), and earnings stability. Stocks with higher rankings in these categories are given more weight in your portfolio. This ranking process helps to prioritize stocks with the best fundamental attributes.
- Diversification: Diversification is a key principle in Magic Formula Investing. Aim to build a portfolio with a mix of stocks across different sectors, industries, and market capitalizations. Here's how you can achieve this:
- Sector Allocation: Divide your portfolio into sectors or industries based on their relative weight in the market. For example, you might allocate a larger portion to technology or healthcare, depending on their performance and market trends.
- Market Cap Range: Include stocks from various market capitalizations (small-cap, mid-cap, large-cap) to capture different growth stages and potential.
- Geographical Diversification: Consider international stocks to further diversify your portfolio and reduce country-specific risks.
Portfolio Construction: Now, it's time to construct the actual portfolio:
- Start by selecting the top-ranked stocks based on your criteria. Include a mix of high-ranked stocks to capture the best opportunities.
- Allocate a specific percentage of your portfolio to each selected stock, ensuring that the total allocation equals 100%. The weightings can be based on the ranking or a predetermined strategy.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation. Rebalancing involves buying or selling stocks to adjust the portfolio back to its target weights.
Risk Management: While Magic Formula Investing aims for long-term outperformance, it's essential to manage risk:
- Monitor the financial health and performance of your selected stocks regularly.
- Consider implementing stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on individual stocks.
- Diversification across sectors and market caps helps mitigate overall portfolio risk.
Remember, portfolio construction is an iterative process, and adjustments may be necessary over time. Regularly review and update your portfolio to align with your investment goals and market conditions.
Index Investing: Why the Hate?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Magic Formula Investing is a stock-picking strategy developed by Joel Greenblatt, a renowned value investor. It combines fundamental analysis with a unique formula to identify undervalued companies with high growth potential.
The formula is a quantitative approach that ranks companies based on two key metrics: the return on invested capital (ROIC) and the share price relative to the company's book value per share (BV/EV). Companies with high ROIC and a low BV/EV are considered the best candidates for investment.
Absolutely! The first component, ROIC, measures how efficiently a company utilizes its capital to generate profits. It is calculated by dividing net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT) by the total capital employed. The second component, BV/EV, compares a company's market value to its book value, indicating whether the stock is undervalued or overvalued.
Magic Formula Investing offers several advantages. It provides a systematic way to identify undervalued businesses with strong growth prospects. By focusing on ROIC and BV/EV, investors can potentially uncover hidden gems that might be overlooked using traditional value investing methods. This strategy also encourages a disciplined approach, as it relies on quantitative metrics rather than subjective judgments.
While Magic Formula Investing has gained popularity, it's important to consider its limitations. The strategy may not account for qualitative factors that could impact a company's performance. Additionally, it might not work well in certain market conditions, such as during a recession when growth stocks may struggle. Diversification and further research are essential to mitigate these risks.