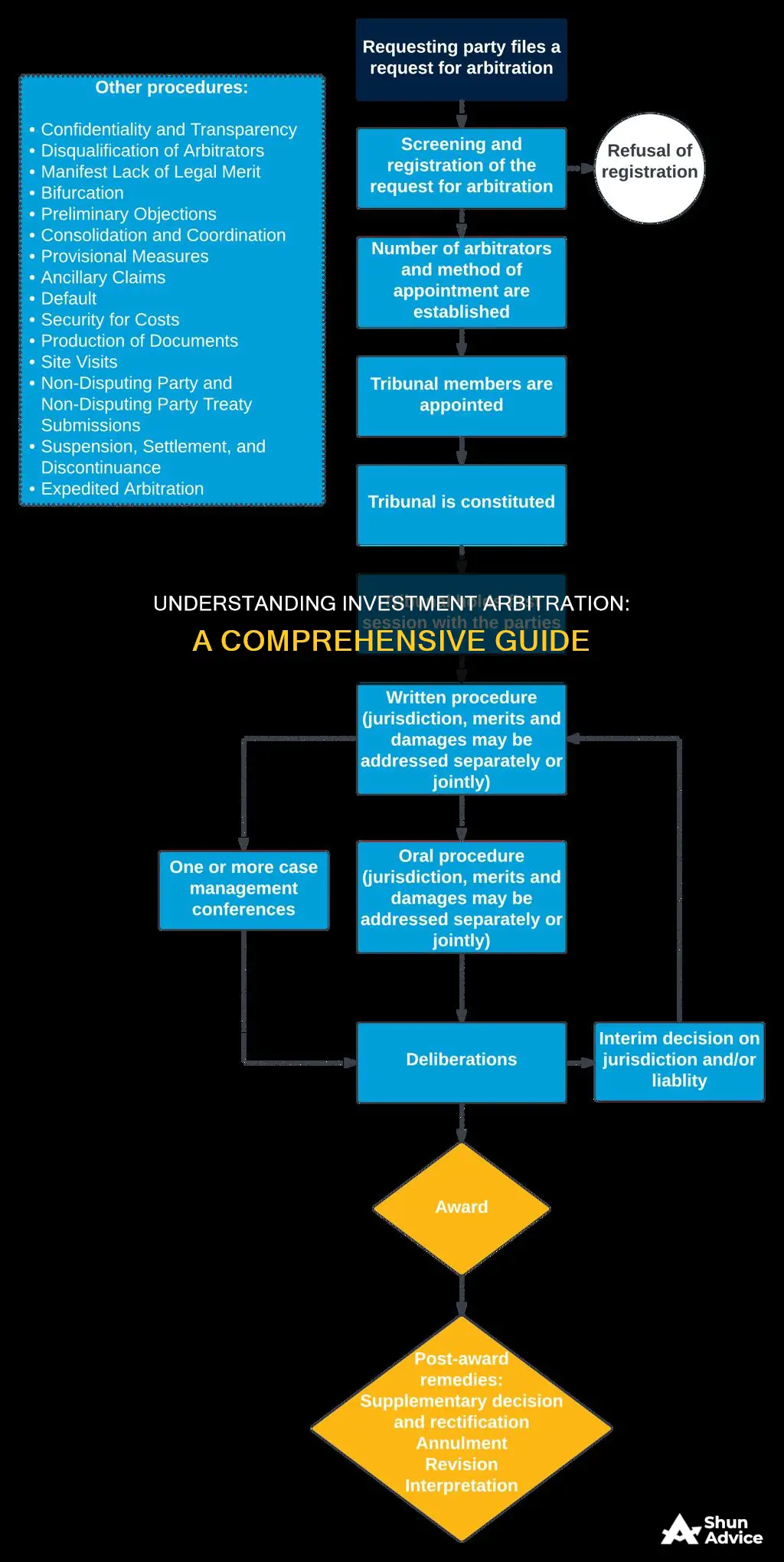
Investment arbitration is a specialized legal process that resolves disputes between foreign investors and host states. It involves an international panel of arbitrators who review the case and make a binding decision. The process is often used to address issues related to international investment agreements, such as the protection of investor rights, fair and equitable treatment, and the enforcement of investment treaties. This method provides a mechanism for investors to seek compensation for alleged breaches of these agreements, offering a more flexible and private alternative to traditional litigation.
What You'll Learn
- Arbitral Institutions: International bodies like the ICC or UNCITRAL oversee and administer investment treaty arbitration
- Treaty Interpretation: Determining the meaning of treaty provisions is crucial for resolving disputes
- Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS): A mechanism allowing investors to sue states for treaty violations
- Procedural Rules: Specific rules govern the conduct of arbitration proceedings, ensuring fairness and efficiency
- Damages and Awards: Calculating and awarding compensation for treaty violations is a key aspect of arbitration

Arbitral Institutions: International bodies like the ICC or UNCITRAL oversee and administer investment treaty arbitration
International arbitration plays a crucial role in resolving disputes related to foreign investments, and it is facilitated by various arbitral institutions and bodies. These institutions are responsible for overseeing and administering the complex process of investment treaty arbitration, ensuring fairness and adherence to established rules. One of the most prominent arbitral institutions is the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). The ICC provides a comprehensive framework for resolving international commercial disputes, including those involving investment treaties. When a dispute arises between an investor and a host state, the ICC can be approached to initiate arbitration. The ICC's role involves selecting a panel of arbitrators who possess the necessary expertise to handle the case, ensuring an impartial and efficient process.
Another significant institution is the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL). UNCITRAL is a global body that promotes the modernization and harmonization of international trade law. It has developed the UNCITRAL Rules of Arbitration, which are widely recognized and utilized in investment treaty arbitration. These rules provide a structured approach to arbitration, outlining the procedures for appointing arbitrators, submitting evidence, and making awards. UNCITRAL also offers a transparent and accessible platform for investors and states to resolve their disputes, ensuring a fair and efficient resolution.
The process of investment treaty arbitration typically begins with the filing of a notice of arbitration by the investor or the affected party. This initiates the formal proceedings, and the chosen arbitral institution will then administer the case. Arbitrators, often selected from a list of qualified individuals, will be appointed to hear the arguments and evidence presented by both sides. These arbitrators are expected to make impartial decisions, considering the specific provisions of the investment treaty in question. The institution's role also includes ensuring that the arbitration process complies with the applicable laws and regulations, providing a structured and fair environment for dispute resolution.
Arbitral institutions like the ICC and UNCITRAL play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of investment treaty arbitration. They provide the necessary infrastructure, rules, and expertise to handle complex disputes. By overseeing the selection of arbitrators, managing the procedural aspects, and ensuring compliance with legal standards, these institutions contribute to the fair and timely resolution of investment-related conflicts. This process is essential for fostering a stable and predictable environment for international investments, encouraging economic growth and cooperation across borders.
The 7-Year Investment Itch: When Do Long-Term Investments Pay Off?
You may want to see also

Treaty Interpretation: Determining the meaning of treaty provisions is crucial for resolving disputes
Treaty interpretation is a critical aspect of investment arbitration, as it forms the basis for understanding the rights and obligations of states and investors under international agreements. When a dispute arises, the interpretation of treaty provisions becomes a central issue, requiring a careful and nuanced approach. The process involves examining the text, structure, and context of the treaty to determine the intended meaning and scope of its provisions.
In investment arbitration, treaties often contain complex and technical language, and the interpretation process requires a thorough understanding of the legal and policy objectives of the treaty. Arbitrators must consider the specific wording of the treaty, including any definitions, exceptions, or limitations, to ensure a precise and fair interpretation. For example, in a dispute involving an investor's right to fair and equitable treatment, the interpretation of the treaty's definition of "expropriation" or "fair and equitable treatment" is crucial. The arbitrator must carefully analyze the treaty's text to determine whether the state's actions meet the threshold of a breach of these obligations.
One key method in treaty interpretation is the use of the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, which provides a framework for understanding the meaning of treaties. This convention emphasizes the importance of the ordinary meaning of the treaty's text, taking into account the context, purpose, and relationship between the treaty's provisions. Arbitrators often rely on this convention to guide their interpretation, ensuring consistency and fairness in the application of treaty obligations.
Additionally, the context and history of the treaty negotiations play a significant role in interpretation. Understanding the political, economic, and social factors that influenced the drafting of the treaty can provide valuable insights. For instance, if a treaty provision is ambiguous, examining the negotiations and discussions between the states involved can help clarify the intended meaning and resolve potential disputes. This contextual approach ensures that the interpretation is not limited to the written text but also considers the broader implications and intentions of the treaty.
In the event of a dispute, the interpretation of treaty provisions is often a complex and challenging task. Arbitrators must carefully analyze the treaty's language, structure, and context, while also considering the legal principles and precedents established in previous cases. The interpretation should be fair and consistent, ensuring that the rights and obligations of both states and investors are respected. By providing a clear and accurate understanding of the treaty, arbitrators can resolve disputes effectively and maintain the integrity of international investment agreements.
The Evolution of Paternal Investment in Primates: Unraveling the Factors that Drive Male Care
You may want to see also

Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS): A mechanism allowing investors to sue states for treaty violations
The concept of Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) is a critical component of international investment agreements, providing a mechanism for investors to seek redress when their rights are allegedly violated by a host state. This system allows investors to initiate legal proceedings against a state for breaches of investment treaties or agreements, ensuring a level of protection and access to justice for foreign investors.
In the context of international trade and investment, ISDS serves as a safeguard for investors, particularly in situations where a state's actions or policies might be perceived as discriminatory or detrimental to the investor's interests. The mechanism is designed to provide a neutral and independent forum for resolving disputes, often through international arbitration, which can result in significant financial compensation for the investor.
When an investor believes that a host state has failed to uphold its obligations under an investment treaty, they can initiate an ISDS process. This typically involves submitting a claim to an international arbitration body, such as the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID), which is an autonomous international organization established by the Convention on the Settlement of Investment Disputes between States and Nationals of Other States. The ICSID is one of the most prominent institutions for ISDS, but other arbitration institutions can also be utilized.
The ISDS process is structured to ensure fairness and transparency. It often involves a panel of arbitrators who are experts in international law and investment matters. The arbitrators' role is to review the case, consider evidence, and make a binding decision. This decision can include financial compensation for the investor, often in the form of damages or restitution, to rectify any losses incurred due to the state's alleged treaty violations.
ISDS has been a subject of debate, with some arguing that it provides necessary protection for investors, while others criticize it for potentially overburdening states with legal challenges. Despite the controversies, ISDS remains a significant feature of international investment law, offering a means for investors to seek justice and compensation when their rights are at stake. This mechanism is particularly important in fostering a stable and predictable environment for international investment, which is crucial for global economic growth and development.
Whiskey Investment: A Guide to the World of Liquid Gold
You may want to see also

Procedural Rules: Specific rules govern the conduct of arbitration proceedings, ensuring fairness and efficiency
The procedural rules in investment arbitration are designed to ensure a fair and efficient process, providing a structured framework for resolving disputes between investors and host states. These rules are crucial as they define the steps, timelines, and procedures that must be followed, ensuring that the arbitration process is transparent, impartial, and in line with international standards. One of the key aspects is the selection of an arbitrator or an arbitral tribunal, which is often done through a mutual agreement between the parties involved. This ensures that the arbitrators are impartial and have the necessary expertise to handle the specific dispute. The rules also outline the submission of written submissions, where each party presents its case through detailed memoranda, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the dispute.
During the arbitration process, the procedural rules dictate the exchange of evidence and the opportunity for cross-examination. This phase is critical as it allows both parties to present their arguments and supporting documentation. The rules often provide a timeline for these submissions, ensuring that the process moves forward efficiently. Additionally, the rules may include provisions for the appointment of an amicus curiae, an independent expert who can provide additional insights and perspectives on the case, further enhancing the fairness of the proceedings.
Another essential aspect is the confidentiality of the proceedings. Investment arbitration often deals with sensitive information, and the rules ensure that all communications and documents remain confidential, protecting the interests of both the investor and the host state. This confidentiality is maintained throughout the process, from the initial submission to the final award. Furthermore, the procedural rules may address the issue of costs and fees, clarifying how the expenses incurred during the arbitration will be borne by the parties, which is a critical consideration for investors.
The rules also cover the final stage of the arbitration, which is the rendering of the award. This document outlines the arbitrator's decision and the remedies or compensation awarded. The rules typically provide a timeframe for the delivery of the award, ensuring that the process concludes promptly. In some cases, the rules may also include provisions for the enforcement of the award, ensuring that the decision is respected and executed as per international law.
In summary, the procedural rules in investment arbitration are meticulously designed to maintain fairness, efficiency, and transparency. These rules provide a structured approach, guiding the entire process from the initial submission to the final award, ensuring that the rights of both investors and host states are protected. By adhering to these rules, investment arbitration aims to provide a reliable and effective mechanism for resolving disputes in the international investment arena.
Unraveling Vanguard Investing: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Mechanics
You may want to see also

Damages and Awards: Calculating and awarding compensation for treaty violations is a key aspect of arbitration
The process of calculating and awarding damages in investment arbitration is a critical component of the legal framework governing international investments. When an investor's rights are violated under an international treaty or investment agreement, the affected party can initiate an arbitration process to seek redress. This process often involves a neutral arbitrator or a panel of arbitrators who are tasked with determining the appropriate level of compensation.
Damages in investment arbitration can be categorized into two main types: compensatory damages and punitive damages. Compensatory damages aim to restore the investor to the position they would have been in had the treaty or agreement not been violated. This typically involves calculating the financial losses incurred by the investor as a direct result of the breach. For example, if a host country's failure to provide adequate protection and security leads to the investor's business being damaged or destroyed, the arbitrator would assess the losses incurred, including any revenue lost, additional costs incurred, and the value of the business at the time of the breach.
The calculation of compensatory damages often requires a detailed analysis of the investor's financial records, business plans, and the specific impact of the treaty violation. Arbitrators may also consider the investor's potential future earnings and the likelihood of recovery. In some cases, the arbitrator may also award interest on the damages to account for the time value of money.
Punitive damages, on the other hand, are awarded to punish the violator and deter similar breaches in the future. These damages are typically reserved for cases where the breach was particularly malicious, fraudulent, or reckless. Punitive damages are not intended to compensate the investor but rather to impose a financial penalty on the wrongdoer. The amount awarded is often significantly higher than the compensatory damages and may be based on a percentage of the compensatory award or a fixed amount determined by the arbitrator.
The process of awarding damages also involves considering the principles of fairness and proportionality. Arbitrators must ensure that the award is reasonable and not excessive, taking into account the severity of the breach, the investor's losses, and the overall context of the investment. Additionally, the arbitrator may need to address issues of jurisdiction, applicable law, and the allocation of responsibility between multiple parties involved in the treaty or investment agreement.
In summary, investment arbitration plays a vital role in resolving disputes and providing compensation for treaty violations. The calculation of damages is a complex process that requires a thorough understanding of the investor's losses, the applicable laws, and the principles of international arbitration. By carefully assessing the facts and applying legal standards, arbitrators can ensure that investors receive fair and adequate compensation, while also sending a strong message about the consequences of treaty violations.
Profiting from the Markets: A Beginner's Guide to Buying and Selling Investments
You may want to see also