Equity cash flow is a type of cash flow measurement that calculates how much money a company has available to pay its stock shareholders. It is the movement of money between a company and its investors. The cash flow statement is one of the three key financial statements, reporting the cash generated and spent during a specific period. It acts as a bridge between the income statement and balance sheet by showing how cash moved in and out of the business. The cash flow statement is typically broken into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. The cash flow statement is important for financial analysis, helping investors to understand whether a company is on solid financial ground.
What You'll Learn
- Equity cash flow calculates the money available to pay shareholders
- It helps analysts and investors evaluate a company's health and market value
- It is shown as a one-line consolidation on the cash flow statement
- It is calculated using net income, depreciation, amortisation, working capital, capital expenditures and net borrowing
- A positive equity cash flow indicates a company's ability to pay shareholders

Equity cash flow calculates the money available to pay shareholders
Equity cash flow is a measurement that calculates the money available to pay a company's stock shareholders. It is also referred to as free cash flow to equity (FCFE). This metric is used by analysts to determine a company's value and health.
FCFE is calculated as the cash from a company's operating activities minus capital expenditures and net debt issued. Operating activities include cash flow from sales, purchases, and other expenses. Capital expenditures refer to the funds used to buy and maintain physical assets such as equipment, buildings, and new technology. Net debt issued refers to the amount of debt a company has borrowed minus the amount it has repaid.
FCFE is composed of net income, capital expenditures, working capital, and debt. Net income is the total revenue earned by a company during a period minus all expenses. Working capital is a liquidity measurement that compares a company's current assets and liabilities.
While FCFE calculates the amount available to shareholders, it does not always equate to the amount paid out to shareholders. A company may decide to use its free cash flow to pay dividends or reinvest in the company.
A positive equity cash flow indicates that a company has funds available to pay shareholders. This is generally viewed as a positive sign by financial analysts. Conversely, a negative cash flow may indicate that a company is experiencing losses or paying back debt, leaving it with less money to pay shareholders.
Positive Cash Flows: A Smart Investment Strategy?
You may want to see also

It helps analysts and investors evaluate a company's health and market value
A statement of cash flow is one of the three key financial statements that details a company's cash flow over a specific period. It is a useful tool for analysts and investors to evaluate a company's health and market value.
The statement of cash flow is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities refer to the cash flow generated from the company's regular goods or services, including revenue and expenses. Investing activities include the cash flow from purchasing or selling assets, such as property or patents. Financing activities detail the cash flow from debt and equity financing, including borrowing and repaying loans, issuing and buying back shares, and dividend payments.
Analysts and investors can use the statement of cash flow to assess a company's financial health and market value in several ways. Firstly, by comparing the cash flow from operating activities to the company's net income, they can evaluate how well the company is managing its operations. A company with a positive cash flow from operating activities that exceeds its net income is considered financially healthy and able to reinvest in its growth.
Secondly, the statement of cash flow provides insights into the company's ability to generate cash and manage its finances. A positive cash flow indicates that the company is bringing in more money than it is spending, allowing it to reinvest in its business, settle debt payments, and explore new growth opportunities. On the other hand, a negative cash flow may indicate financial challenges or a need to address expenditure and income mismatches.
Thirdly, the statement of cash flow can reveal the phase a business is in, whether it is a rapidly growing startup or a mature and profitable company. This information is valuable for investors when deciding whether to invest in a company. It also helps analysts and investors understand the company's financial health and make informed decisions about their investments.
Additionally, the statement of cash flow allows analysts and investors to compare a company's market value of equity to other valuations, such as book value and enterprise value. The market value of equity, also known as market capitalization, is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares. This value represents the total value of the company as decided by investors and can fluctuate significantly throughout a trading day, especially for small companies with fewer investors.
In conclusion, the statement of cash flow is a crucial tool for analysts and investors to assess a company's health and market value. It provides insights into cash flow patterns, financial management, business phase, and market value, enabling informed investment decisions and a comprehensive understanding of the company's financial health.
Pension Plans: Cash, Investments, and Your Retirement Future
You may want to see also

It is shown as a one-line consolidation on the cash flow statement
The cash flow statement is one of the three key financial statements that reports the cash generated and spent during a specific period. It acts as a bridge between the income statement and balance sheet by showing how cash moved in and out of the business.
The cash flow statement is typically broken into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities detail cash flow generated from the company's regular goods or services, including revenue and expenses. Investing activities include cash flow from purchasing or selling assets, using free cash rather than debt. Financing activities detail cash flow from both debt and equity financing.
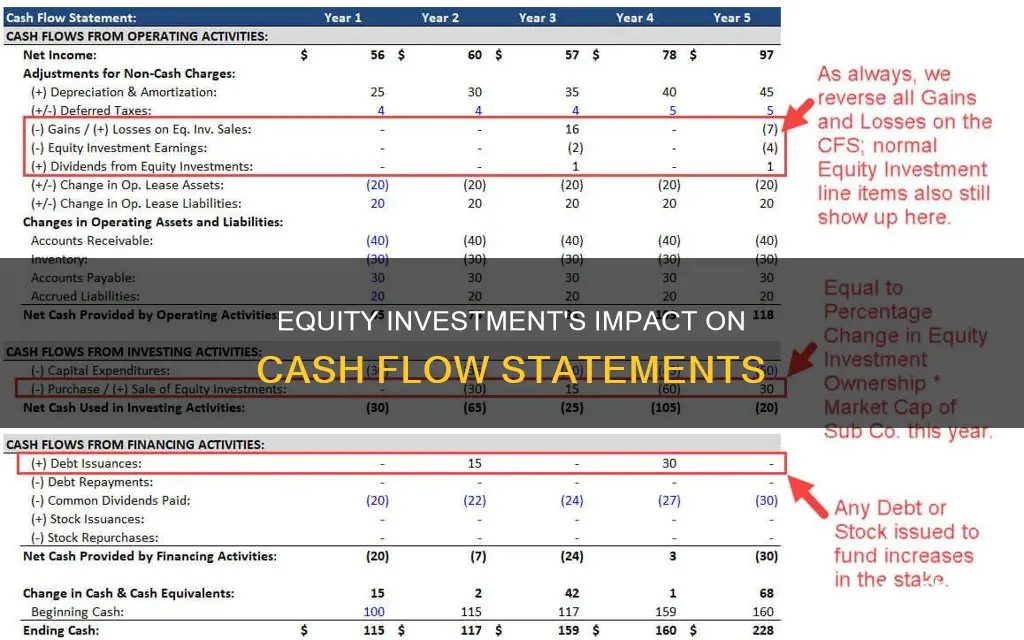
Equity method investments are reported as a one-line consolidation item in the investor's income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. This means that the investor company will report the revenue earned by the investee company in its income statement, along with the percentage of the equity investment in the investee company. The investment will be reflected at the original cost on the balance sheet, with retained earnings added over time.
In the cash flow statement, the equity income is subtracted in the cash flow from operations, and usually, any dividends received are added to the cash flow from operations. This is done to calculate the net cash flow from operating activities.
The cash flow statement provides valuable insights into a company's financial health and operational efficiency. It helps creditors and investors understand the company's liquidity, ability to fund operating expenses, and pay down debts.
Best Places to Invest Your Cash Today
You may want to see also

It is calculated using net income, depreciation, amortisation, working capital, capital expenditures and net borrowing
Equity investment is shown on a statement of cash flow in the financing activities section. This section details the cash flow from financing activities, which result from changes in a company's capital structure.
Financing activities include the issuance and repayment of debt, and the issuance and repurchase of equity. The calculation of equity investment involves using net income, depreciation, amortisation, working capital, capital expenditures, and net borrowing.
Net income is calculated as revenue minus expenses, interest, and taxes. It is an indicator of a company's profitability and is used to calculate earnings per share (EPS).
Depreciation is the process of deducting the total cost of an asset over its useful life. It is calculated using various methods, such as straight-line depreciation, double-declining balance depreciation, and units of production depreciation.
Amortisation is similar to depreciation but is used for intangible assets, such as goodwill, patents, and copyrights. It is calculated by spreading out the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life.
Working capital is the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities. It measures a company's liquidity and short-term financial health.
Capital expenditures (CapEx) refer to the funds used to acquire, upgrade, and maintain physical assets. CapEx is calculated by finding the change in property, plant, and equipment, and adding it to the current depreciation.
Net borrowing refers to the debt borrowed net of the repayment. It is included in the calculation to reflect the proceeds that could be used to distribute dividends or repurchase shares.
By using these components, the calculation of equity investment on a statement of cash flow provides insight into the cash flows attributable to equity investors, allowing them to understand the company's financial health and forecast future costs.
How Cashing Investments Affect Debt Service Coverage
You may want to see also

A positive equity cash flow indicates a company's ability to pay shareholders
A company's cash flow statement is one of its most critical financial documents, offering valuable insight into its financial health. A positive equity cash flow, or free cash flow to equity (FCFE), indicates the company's ability to pay its shareholders. This is calculated by subtracting cash outflows (such as debt and expenses) from cash inflows.
FCFE is a measure of how much cash is available to the equity shareholders of a company after all expenses, reinvestment, and debt are paid. It is composed of net income, capital expenditures, working capital, and debt. Net income is the total amount of revenue earned during a period minus all expenses. Capital expenditures refer to the funds used to buy and maintain physical assets, such as equipment and buildings. Working capital is a liquidity measurement that compares a company's assets and liabilities, and debt refers to the amount borrowed in the current period minus the amount of principal repaid.
A positive equity cash flow indicates that a company has more money flowing into the business than leaving it over a specified period. This is an ideal situation as it allows the company to reinvest in itself and its shareholders, settle debt payments, and find new ways to grow the business. It is important to note that a company can be profitable without being cash flow-positive, and vice versa.
Analysts and investors use FCFE to evaluate a company's health and market value. It is often used as an alternative to the dividend discount model, especially when a company does not pay a dividend. FCFE can help determine if dividend payments and stock repurchases are paid for with free cash flow to equity or some other form of financing. While a positive equity cash flow is generally favourable, analysts also consider other factors such as the company's dividend policy and typical payments.
Investments and Cash Equivalents: What's the Real Difference?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A cash flow statement is a financial statement that tracks the inflow and outflow of cash, providing insights into a company's financial health and operational efficiency. It is one of the three main financial statements, the others being the balance sheet and the income statement.
The main components of a cash flow statement are:
- Cash flow from operating activities
- Cash flow from investing activities
- Cash flow from financing activities
Equity investments are reported as a one-line consolidation item in the cash flow statement. The cash flow statement shows the cash flow, or movement of money, between a company and its investors. This is also referred to as free cash flow to equity (FCFE).