Venture capital funds (VCFs) are investment vehicles that provide funding to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. In India, VCFs have played a pivotal role in the startup ecosystem, offering not just monetary investment but also strategic guidance and a strong network of connections. While investing in VCFs can be lucrative, it is also risky due to the uncertain nature of startups. This article will explore the process of investing in VCFs in India, the different types of VCFs available, and the key players in the market.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Investment instruments through which individuals can invest in newly-formed start-ups as well as small and medium-sized companies. |
| Type of investor | Individuals with high net worth, companies, or other funds. |
| Management | Managed by a venture capital firm, not an asset management company. |
| Investor risk | Investing in these companies involves considerable risk. |
| Investor reward | Target firms that have the potential to deliver high returns. |
| Investor strategy | Invest in multiple companies at once, so that at least a few will produce high returns. |
| Investor involvement | May seek a chair among the directors of the company and offer expertise and intelligence for better management. |
| Investor funding source | High net worth individuals or institutional investors such as investment banks. |
| Stages of funding | Seed, early, and growth. |
| Stages of VC financing | Pitch, deep dive, negotiation, due diligence, definitive documentation. |
| Stages of VC investing | Seed, early, and late. |
| Functions | Provide finance and skills to develop products, create business plans, evaluate technological innovation, provide networking opportunities, and supply specialist services. |
| Benefits | Business expertise, additional resources and connections, business expansion, better management, risk aversion. |
| Drawbacks | Can be challenging to secure, may result in forfeiture of control and ownership. |
What You'll Learn

Stages of VC financing
Venture capital financing typically follows a series of funding rounds, each representing a different level of company maturity and investor risk tolerance. The various stages can vary depending on the company, but there are typically five to seven stages of VC financing. Here are the common stages of VC financing in India:
Pre-Seed/Seed Round
This is the earliest stage of VC financing, where entrepreneurs are building their business plans and need capital for research and development. At this stage, startups may not have released a product yet and are focused on creating a compelling pitch to attract investors. Angel investors are more common during this round. The amounts raised during the seed round are typically small and used for activities such as market research, product development, and business expansion.
Early Stage Round
The early stage round typically consists of Series A, B, and sometimes C funding. During this stage, companies have completed their research and development and have a business plan and prototype ready. They are now focused on advertising and marketing their product to potential customers. This stage requires a larger infusion of cash to fine-tune the product, expand the team, and conduct any remaining research necessary before the official business launch.
Expansion Stage
Also known as the "emerging stage," this is when the company is seeing exponential growth and needs additional funding to keep up with the demands. Funding at this stage is used for product manufacturing, sales, and increased marketing efforts. As the company is starting to see profitability, VC funding helps grow the business further through market expansion and product diversification.
Late Stage
As the company matures and prepares for an IPO or M&A, it can raise additional capital at this stage to create favourable market conditions for its previous investors. This stage includes Series C and beyond, where the company has achieved success and is looking to build new products, reach new markets, and even acquire other startups. To receive funding at this stage, the company must have a strong customer base, stable revenue, and a desire to expand globally.
Bridge Stage
The final stage of VC financing is the bridge stage, where companies have reached maturity and are transitioning to full-fledged, viable businesses. Funding at this stage is used to support activities such as mergers, acquisitions, or IPOs. Many investors choose to sell their shares at this stage and end their relationship with the company, realising a significant return on their investments.
Small-Cap Funds: When to Invest and Why
You may want to see also

How VCs make money
Venture capitalists (VCs) are financial institutions that invest in early-stage companies with long-term growth potential. They are interested in the company's impact on the world and look for a strong business plan, a clear path to profitability, and a good team and culture within the company. VCs make money in two main ways:
- Management fees: VCs collect fees for managing funds, which are calculated as a percentage of the fund's value every year, typically between 1.25% and 2.5%. These fees cover operational expenses such as paying fund managers and other staff, accounting, audits, taxes, etc.
- Carried interest or "carry": This is the share of the profits earned by the company after the initial investment. Typically, VCs receive a portion of the profits once the fund's assets are dispersed back to the investors. The majority of carries are 20%, but successful businesses may negotiate a larger carry.
In addition, VCs may also make money through their own investments in the companies they fund. They may buy contracts, help improve the company, and then sell their investment for a profit when the time is right.
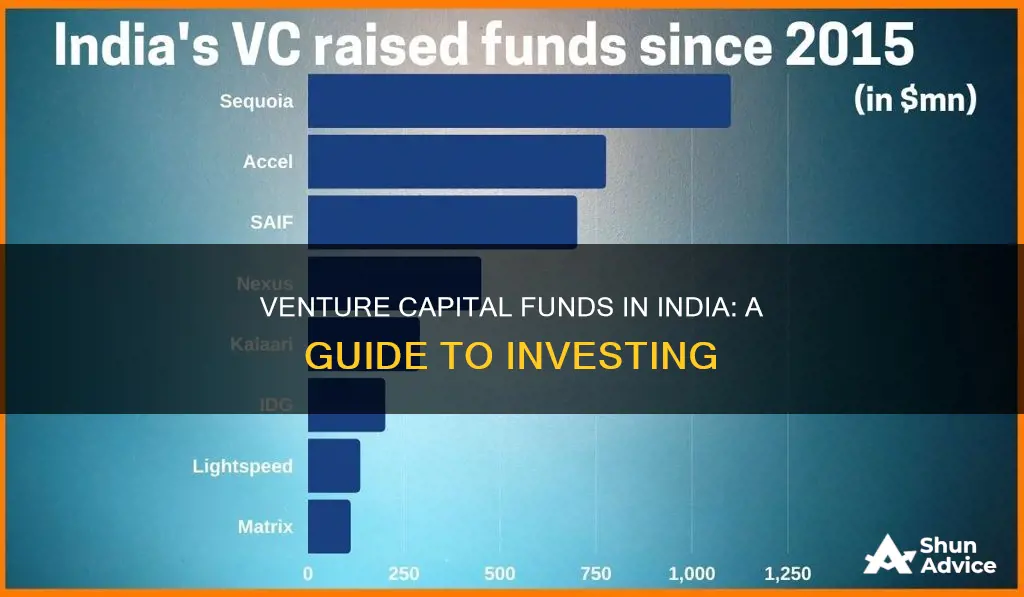
In India, the top VC funds include Accel India, Sequoia Capital India, Nexus Venture Partners, and SAIF Partners, among others. These funds have played a crucial role in fostering innovation and entrepreneurship in the country, providing financial support and strategic guidance to startups.
Sustainable Energy Funds: Where to Invest and How
You may want to see also

Types of VCFs
Venture capital funds (VCFs) can be categorized by their investment stage, which includes seed stage, early stage, and growth stage. Here is a detailed overview of each type:
Seed Stage VCFs:
- These funds provide the initial capital injection to transform ideas into viable businesses.
- Example: India Quotient, founded in 2012, provides seed funding to startups in India across sectors such as Fintech, Consumer Tech, and SaaS.
Early Stage VCFs:
- Early-stage VCFs provide the necessary fuel for fledgling startups to grow and scale their operations.
- Example: Accel India, the Indian arm of the global VC firm Accel, focuses on sectors including Consumer, Enterprise SaaS, Fintech, and Healthcare.
Growth Stage VCFs:
- Growth stage VCFs provide significant capital injections to help startups expand nationally and internationally.
- Example: Sequoia Capital India, the Indian arm of the global VC firm Sequoia, invests across sectors such as Technology, Consumer, and Healthcare.
In addition to these three main types, there are also sector-specific VCFs that focus on particular industries such as consumer tech, fintech, edtech, SaaS, healthcare, and deep tech. Some VCFs may also be categorized based on their geographic focus, such as India-centric or global funds.
Market Downturn: Mutual Fund Investment Strategies and Tips
You may want to see also

Functions of VCFs
Venture Capital Funds (VCFs) are investment vehicles that provide funding to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. They play a critical role in fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, especially in burgeoning startup ecosystems like India's. Here are the key functions of VCFs:
- Providing Finance and Skills: VCFs offer financial support and technical expertise to startups, even at the pre-start stage. This includes seed funding to help entrepreneurs get their business ideas off the ground.
- Business Plan Development: VCFs assist startups in developing comprehensive business plans that focus on market opportunity, product development, financial needs, and overall technological innovation. This support is provided by experienced professionals who help navigate the complex nature of business.
- Evaluation of Technological Innovation: Venture capitalists evaluate the merits and demerits of the technological innovations presented by startups. This allows for the identification of better ways to meet business objectives and efficiently manage technological advancements.
- Networking Opportunities: VCFs have a large network of ventures across different industries. They facilitate professional connections, which are crucial for small businesses to gain exposure and establish themselves in the market.
- Specialist Services: Apart from financial investment, venture capitalists actively offer a broad spectrum of specialist services. These include technical, commercial, managerial, financial, and entrepreneurial expertise to support the growth and development of the startup.
- Expertise and Management: VCFs bring years of expertise and industry connections to the table. They provide valuable advice and guidance to startups, helping them navigate the challenges and risks associated with launching a new venture. VCFs often take a seat on the board of directors, offering intelligence and management skills to ensure better decision-making within the startup.
- Risk Diversification: Venture capitalists invest in multiple young startups across various sectors, understanding that not all investments will succeed. This diversification strategy aims to mitigate risk, with the expectation that at least one firm will achieve massive growth and provide a substantial payout.
Mutual Funds in India: Invest Without a Broker
You may want to see also

Benefits of VCFs
Venture Capital Funds (VCFs) have played a critical role in sparking the startup revolution in India. They have successfully boosted the Indian economy by creating a new paradigm of disruptive economic growth. Many startups have become unicorns, rivalling the best of India Inc, simply because of venture capital funds. Here are some of the benefits of VCFs:
- Business Expertise: Venture capitalists bring valuable expertise, advice, and industry connections. They are expert professionals with deep knowledge of specific market standards and can help businesses avoid many of the downsides usually associated with startups.
- Additional Resources and Connections: Along with monetary aid, VCs can act as HR consultants for startups. They are specialists in hiring the best staff for businesses and can offer other services such as mentoring, alliances, and skill training.
- Business Expansion: Venture capital provides the large funding that a startup requires to expand its business. This form of investment is not typically possible through bank loans or other methods.
- Better Management: Since venture capitalists hold a percentage of equity in the business, they have a say in its management. They can offer great assistance if the founder or promoter is not good at managing the business.
- Risk Aversion: There is no obligation for the promoter or founder of a startup to pay back seed funding from VCs. The VCs take on the investment risk because they believe in the company's future success.
Tata Digital India Fund: A Smart Investment Strategy
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A Venture Capital fund is a financial institution that provides capital to startups or small businesses with high-growth potential. VC funds are crucial for startups in their early stages, as they may lack access to capital markets. They also provide strategic guidance, mentorship, and operational support.
Venture Capital funds work by identifying investment areas that can generate lucrative returns. They act as fund managers and investors, often investing their own money alongside their clients' as a form of commitment. The stages of VC financing include pitching, deep diving, negotiation, due diligence, and definitive documentation.
Venture Capital funds offer several advantages, including business expertise, additional resources and connections, business expansion opportunities, and better management support. They assume the investment risk and do not require repayment if the company fails.