The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program offers foreign nationals and their families a direct pathway to permanent US residency (green cards) and the opportunity to apply for citizenship. The program was established in 1990 to stimulate foreign investment in US businesses, with a preference for investment in rural areas and areas of high unemployment. To qualify, individuals must invest in a new commercial enterprise (NCE), creating at least 10 full-time jobs and complying with all United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) regulations. The minimum investment amount is $800,000 for projects in targeted employment areas (TEAs) and $1,050,000 for projects in non-TEAs. EB-5 investments can be structured as either regional center or direct investments. Direct EB-5 investments must be equity investments to qualify for the EB-5 program.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Investment Type | Direct equity investment |
| Investment Amount | $800,000 for projects in Targeted Employment Areas (TEAs) or $1,050,000 for projects in non-TEAs |
| Job Creation | 10 new full-time jobs for U.S. workers |
| Job Duration | At least two years |
| Job Type | Direct, permanent, and operational roles |
| Investor Involvement | Active and hands-on; direct investors take a managerial role |
| Investment Structure | Direct investment into a New Commercial Enterprise (NCE) |
| Business Type | New or existing business that has been restructured or expanded |
| Business Plan | Required, including financial projections, job descriptions, and hiring schedule |
| Investor Nationality | Indian, Russian, Chinese, South American, and Western European investors are common |
What You'll Learn

Direct EB-5 investments must be equity investments
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program was established in 1990 to stimulate foreign direct investment in new business development, with a preference for investments in rural and high-unemployment areas. The program allows foreign nationals to obtain permanent residency in the United States in exchange for qualifying investments. To qualify for the EB-5 visa, foreign nationals must invest in a new commercial enterprise (NCE), create at least 10 full-time jobs, and comply with all United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) regulations.
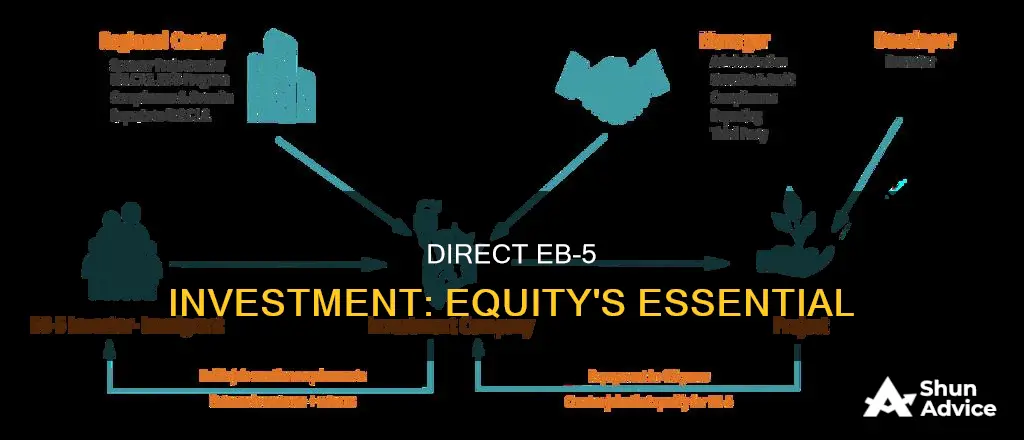
There are two types of EB-5 investments: direct investments and indirect investments through a regional center. Direct EB-5 investments must be equity investments, where the investor invests directly into an NCE. The NCE is typically a new enterprise or a troubled business, and it must create at least 10 full-time jobs for U.S. workers. These jobs must be permanent, lasting for at least two years, and they must meet the specific needs of the business with corresponding salaries. The investor must also be involved in the management of the NCE, with the level of involvement depending on the nature of the investment and the management structure.
One key difference between direct and indirect EB-5 investments is how job creation is calculated. For direct investments, only the jobs created directly by the NCE can be counted towards the employment requirement. These jobs are typically operational positions associated with the day-to-day operations of the NCE. On the other hand, indirect investments through regional centers can count direct, indirect, and induced jobs. Indirect jobs result from the EB-5 project's spending on goods and services, while induced jobs are created by employees spending their wages in the local community.
Another difference between the two investment types is the structure. Direct EB-5 investments are made directly into the NCE, which is responsible for creating the required jobs. Loan models are not typically viable for direct investments because they involve multiple entities. However, an investor can make a direct investment in a subsidiary owned by a parent company, in which case the parent company is considered the NCE. In contrast, indirect investments through regional centers involve multiple entities, including the NCE and a job-creating entity (JCE). The NCE typically loans money to the JCE to hire staff and develop the project.
When choosing between direct and indirect EB-5 investments, it is important to consider the pros and cons of each option. Direct investments offer more control to the investor, who takes a managerial role. However, they are less common and may be more costly. Indirect investments through regional centers offer more flexibility in job creation and allow for pooling of funds from multiple investors. They also provide a more passive approach for investors who prefer to entrust the management of the investment to a designated regional center.
Understanding Investment Management Fees: Cost Analysis
You may want to see also

Investors must create 10 full-time jobs for US workers
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program was established by Congress in 1990 to stimulate the U.S. economy through foreign investment in new business development. The program offers permanent green cards to foreign nationals in exchange for qualifying investments.
For an investment to qualify for the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program, it must create at least 10 new full-time jobs for U.S. workers. These jobs must be permanent, full-time positions requiring a minimum of 35 working hours per week. The jobs can be either directly or indirectly created, depending on whether the investment is made through a regional center or not.
Direct investments must create direct jobs, meaning the entity that received the investment employs the U.S. workers directly. Indirect investments, on the other hand, can create indirect jobs, which are held outside of the entity that received the investment but are created as a result of it.
The jobs created must be filled by qualifying employees, who can be U.S. citizens, lawful permanent residents, or other immigrants authorized to work in the U.S., including conditional residents, temporary residents, asylees, refugees, or persons residing in the U.S. under suspension of deportation. This definition does not include the immigrant investor, their spouse, or their children.
To ensure compliance with the job creation requirements, investors must keep detailed records of job creation. They must also submit a comprehensive business plan that demonstrates how the required number of jobs will be created within two to three years of approval. This plan must include job descriptions, a staffing plan, a hiring schedule, and a detailed description of how the investment meets the EB-5 program requirements.
Planning Savings and Investments: Strategies for Financial Freedom
You may want to see also

The investment must remain at risk for a minimum of two years
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program was established in 1990 to stimulate foreign direct investment in new business development, with a preference for investments in rural and high-unemployment areas. Through this program, foreign nationals can qualify for permanent green cards in exchange for qualifying investments.
The EB-5 investment must remain at risk for a minimum of two years. This means that the investment funds must remain invested and at risk until the EB-5 investor has held their temporary green card for at least two years. If the investment is repaid before the end of this two-year period, the EB-5 investor will be ineligible for permanent residency under the EB-5 program.
The two-year minimum at-risk period is a crucial aspect of the EB-5 program, as it ensures that the investment remains in place long enough to have a meaningful impact on the local economy. During this time, the business must create 10 new full-time jobs for US workers, which contributes to job creation and stimulates the local economy.
The two-year period also allows for a more stable investment environment, providing a degree of certainty for both the investor and the business owner. It gives the business owner time to put the investment funds to use effectively and plan for the future, knowing that the capital will remain in place for a minimum of two years. For the investor, it provides an opportunity to assess the performance of the investment and make more informed decisions about their permanent residency application.
Overall, the requirement for the EB-5 investment to remain at risk for a minimum of two years helps to ensure that the program achieves its goals of stimulating economic development and creating jobs, while also providing a degree of stability and certainty for all parties involved.
Building an Investment Portfolio: Teaching Kids About Money
You may want to see also

The business must be a new commercial enterprise
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program was established in 1990 to stimulate foreign direct investment in new business development, with a preference for investment in rural and high-unemployment areas. Through this program, foreign nationals can qualify for permanent green cards in exchange for qualifying investments.
A qualifying EB-5 investment is an investment in a new commercial enterprise that directly creates at least 10 new full-time jobs for U.S. workers. The EB-5 investment must remain at risk for at least two years.
- An original business
- An existing business that has been purchased and restructured, or reorganised in such a way that a new commercial enterprise results
- An expansion of an existing business through the investment, where there is at least a 40% increase in the net worth or the number of employees.
The business must be a for-profit activity formed for the ongoing conduct of lawful business. This includes any sole proprietorship, partnership (either limited or general), holding company, joint venture, corporation, business trust, or other entity that is publicly or privately owned.
The business must be established after November 29, 1990. If the business was established before this date, a new commercial enterprise may be established by:
- The purchase of an existing business and subsequently restructuring or reorganising the business such that a new commercial enterprise results
- Expansion of an existing business
Foreign Investment in India: Why File?
You may want to see also

The business must be located in a targeted employment area (TEA)
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program was established in 1990 to stimulate foreign direct investment in new business development, with a preference for investments in rural and high-unemployment areas. The program offers permanent green cards to foreign nationals in exchange for qualifying investments.
The minimum qualifying investment in the United States depends on the geographic location of the commercial enterprise. Lower minimum qualifying investments are available within high-unemployment areas or rural areas, designated as Targeted Employment Areas (TEAs).
A business must be located in a rural or high-unemployment area to qualify as a TEA. A TEA based on high unemployment is a geographic area with an unemployment rate of at least 150% of the national average rate at the time of application and investment. A TEA qualified as a rural area must be outside a metropolitan statistical area or outside the boundary of any city or town with a population of 20,000 or more, according to the most recent decennial census.
The EB-5 investment amount is halved for projects in TEAs, with a minimum investment of $500,000 as of August 2021. This makes investing in a TEA a more affordable option for EB-5 investors.
The United States Department of Homeland Security is the sole authority for designating Targeted Employment Areas. The EB-5 visa applicant must provide sufficient evidence that their project is located within a rural or high-unemployment area to receive TEA designation. This evidence should be reliable and verifiable and could include a map demonstrating the census tract(s) included in the proposed TEA and details of the calculations of the weighted average unemployment rate for the proposed TEA.
The TEA requirements are the same for both Regional Center projects and Direct EB-5 projects.
Personal Investment Management: Your Wealth, Your Control
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The minimum investment amount for an EB-5 visa is $800,000 for projects in Targeted Employment Areas (TEAs) and $1,050,000 for projects in non-TEA areas.
The main difference lies in the form of investment and the job creation criteria. Direct EB-5 investments are made as equity investments, whereas indirect EB-5 investments are made as loans. Direct EB-5 projects can only count jobs directly created by the new commercial enterprise (NCE), whereas indirect EB-5 projects can also count indirect and induced jobs created through the positive economic impact of the project on its area.
Direct EB-5 investors have more control over their investment and take an active role in managing the business. They can also choose their own projects and take on a managerial role. Additionally, direct EB-5 investments do not depend on the reauthorization of the regional center program, reducing the risk for investors.







