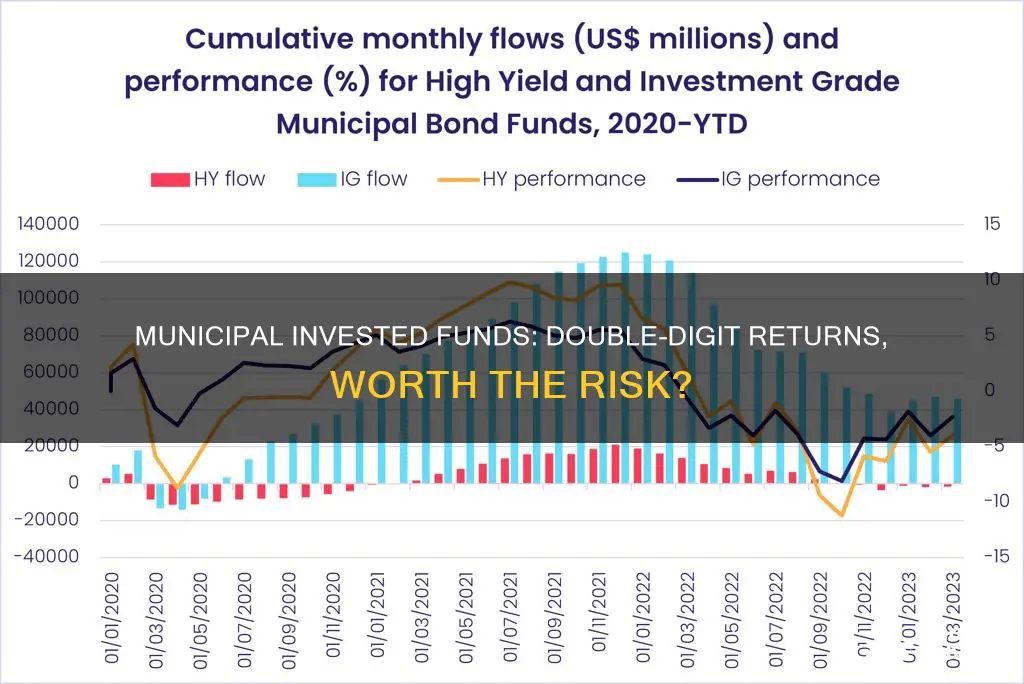
Municipal bonds are debt obligations issued by public entities to fund public projects such as schools, hospitals, and highways. They are commonly offered to pay for capital expenditures, including the construction of highways, bridges, or schools. Municipal bonds are often exempt from most taxes, which makes them attractive to people in higher income tax brackets.
Municipal bonds are issued by state and local governments to raise money for public projects such as schools and roads. They are typically exempt from federal income tax, making them an attractive choice for investors in high tax brackets. Municipal bonds can be divided into two categories: general obligation bonds and revenue bonds. General obligation bonds are used for projects that are unlikely to generate revenue, while revenue bonds are paid back with revenue from specific projects, such as toll roads or entertainment centres.
While municipal bonds may not offer high returns, they are a good option for investors seeking low-risk investments with fixed income. Municipal bond funds offer the benefit of diversification and reduced risk compared to investing in individual municipal bonds. Some top municipal bond funds include the Vanguard Tax-Exempt Bond ETF, the Fidelity Tax-Free Bond Fund, and the T. Rowe Price Tax-Free High Yield Fund.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Municipal bonds are debt obligations issued by public entities to fund public projects such as schools, hospitals, and highways |
| Types | General obligation bonds and revenue bonds |
| Interest | Often exempt from federal, state, and local taxes |
| Risk | Low level of default risk relative to other bond types |
| Issuers | State and local governments |
| Benefits | Stability for your capital with low default rates |
What You'll Learn

Municipal bonds vs. stocks
Municipal bonds, also known as "munis", are fixed-income securities issued by local or state governments to fund public projects. They are considered low-risk investments, with a high expectation of recouping investment plus interest. However, municipal bond rates tend to be lower than potential returns from riskier assets like stocks.
Municipal bonds are often exempt from federal taxes and sometimes state and local taxes, making them attractive to investors seeking to lower their taxable income. This tax advantage means that a lower yield on a municipal bond can be more attractive than a higher-yielding taxable bond once tax savings are factored in. For example, a municipal bond with a 3% yield may be more beneficial than a taxable bond with a 4% yield for an investor with a 37% federal income tax rate and a 7% state tax rate.
Stocks, on the other hand, offer the potential for higher returns but carry more risk. Stocks are a good option for investors with a higher risk tolerance who are seeking capital appreciation. Stocks can be more volatile than municipal bonds, and investors need to carefully research and monitor their stock portfolio to manage risk.
Municipal bonds are suitable for investors looking for a more stable, low-risk investment with tax advantages. Stocks are better for those seeking higher returns and are willing to take on more risk.
- Risk: Municipal bonds are generally considered low-risk investments, backed by the credit of the issuing local or state government. Stocks typically carry more risk, as they are subject to market volatility and the performance of individual companies.
- Returns: Municipal bonds offer lower but more stable returns, while stocks offer the potential for higher returns but with greater variability.
- Taxes: Municipal bond interest is often exempt from federal taxes and sometimes state and local taxes. Stock returns are usually taxed as capital gains or income, depending on the holding period.
- Liquidity: Municipal bonds are relatively liquid, but investors need to consider the bid-ask spread. Stocks are generally more liquid, as they can be bought and sold more easily on stock exchanges.
- Investment goals: Municipal bonds are suitable for income generation and capital preservation, while stocks are often chosen for capital appreciation and wealth accumulation.
- Diversification: Municipal bonds can provide diversification to a portfolio focused on stocks. Including municipal bonds can reduce overall risk and provide a stable source of tax-advantaged income.
A Beginner's Guide to Mutual Funds in the Netherlands
You may want to see also

Tax-free municipal bond funds
Municipal bonds are issued by state and local governments to raise money for public projects such as schools, roads, sewers, airports, and hospitals. They are also known as "muni bonds". Muni bonds are federally tax-free and may be exempt from state and local taxes, depending on the state. This makes them attractive to investors in high tax brackets.
Municipal bonds are typically exempt from federal income tax, but there may be state or local taxes to pay. Municipal bonds are generally very safe investments with a very low historical default rate. However, they may not be the best option for maximising returns, as they tend to have lower yields than corporate bonds.
- Vanguard Tax-Exempt Bond ETF (VTEB)
- Fidelity Tax-Free Bond Fund (FTABX)
- T. Rowe Price Tax-Free High Yield Fund (PRFHX)
- BlackRock Allocation Target Shares: Series E Fund (BATEX)
- Delaware National High-Yield Municipal Bond Fund Institutional Class (DVHIX)
- Vanguard High-Yield Tax-Exempt Fund Admiral Shares (VWALX)
Municipal bonds are not always the best option for investors. They can carry a purchasing-power risk, where the money returned at the end of the bond term may be worth less due to inflation. They also carry an interest rate risk, where, if interest rates rise during the term, investors will be stuck with a poor performer, and the bond will lose value.
It is important to do your research and compare municipal bonds with other investment options before taking the plunge.
Smart Mutual Fund Investing: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Municipal bond funds vs. individual bonds
Municipal bond funds and individual bonds both have their advantages and disadvantages. Here is a comparison of the two:
Municipal Bond Funds
Municipal bond funds are a type of investment fund that focuses on investing in municipal bonds, which are debt securities issued by governments or government-related entities to finance public projects such as roads, bridges, and schools. Municipal bond funds offer investors a diversified portfolio of municipal bonds, reducing the risk of default. They are also more liquid, making them a good option for long-term investments. Additionally, they provide the same tax advantages as individual municipal bonds. However, investors have less control over the specific bonds held in the fund and may face management fees.
Individual Municipal Bonds
Investing in individual municipal bonds gives investors greater control over their portfolio. They can choose which bonds to buy and hold until maturity or sell before maturity. Individual bonds also allow investors to better plan and control their income stream, as they know the maturity and coupon payment dates. However, investing in individual bonds requires more time and financial resources for research and monitoring. It also requires a higher initial investment amount compared to bond funds.
Key Differences
- Control and Transparency: Municipal bond funds offer lower control and transparency since investors don't choose the specific bonds held in the fund. Individual bonds provide greater control and transparency, as investors know exactly what they own.
- Research and Oversight: Municipal bond funds require less research and oversight, as investors don't need to research individual bonds or issuers. Individual bonds require significant research and ongoing monitoring of the financial stability of each issuer.
- Default Risk: Municipal bond funds reduce the default risk by diversifying across different types of bonds. Individual bonds may have a higher default risk, especially if they are not properly diversified.
- Minimum Investment: Municipal bond funds have a lower minimum investment amount, making them more accessible to investors with limited capital. Individual bonds typically require a higher initial investment.
- Liquidity: Municipal bond funds offer higher liquidity, allowing investors to redeem their shares at any time. Individual bonds may be less liquid, and selling before maturity can result in a profit or loss.
- Impact of Interest Rates: Municipal bond funds may be more volatile due to changing interest rates, as the value of the fund is marked to market daily. Individual bonds held to maturity may not be impacted by changing interest rates.
Active vs. Passive Funds: Which Investment Strategy is Right?
You may want to see also

Municipal bond fund management
Municipal bond funds are a great way to invest in municipal bonds, which are debt securities issued by a state, municipality, county, or special purpose district (such as a public school or airport) to finance capital expenditures. Municipal bond funds are typically exempt from federal tax and may also be exempt from state taxes if the investor resides in the state where the bonds are issued.
Municipal bond funds are managed with different objectives, often based on location, credit quality, and duration. They are a good option for risk-averse investors as they offer slow, steady income and provide a balance during turbulent times.
Location
Municipal bond funds can focus on specific states or regions, offering tax advantages to residents of those areas. For example, the Vanguard California Long-Term Tax-Exempt Fund Admiral Shares (VCLAX) is designed for investors in California, a state with high income tax rates.
Credit Quality
Municipal bond funds can vary in terms of credit quality, ranging from investment-grade to non-investment-grade or "junk" bonds. Funds with higher-yielding lower-grade bonds tend to carry more risk but can be diversified to mitigate this risk.
Duration
The duration of a municipal bond fund refers to the sensitivity of its price to changes in interest rates. Longer-duration funds are generally more sensitive to interest rate changes. Funds with different durations can be used to manage interest rate risk, with shorter-term funds performing better when interest rates are rising, and longer-term funds performing better when rates are falling.
Diversification
Municipal bond funds provide diversification by investing in a broad range of municipal bonds, reducing the risk of default associated with individual bonds. Diversification can also be achieved by investing in bonds from different regions, as this reduces concentration risk.
Tax Efficiency
While municipal bond funds are known for their tax advantages, it's important to consider the overall tax efficiency of the fund. For example, funds that include corporate bonds may have lower tax efficiency due to the taxable nature of corporate bond returns.
Fund Expenses
When investing in municipal bond funds, it's essential to consider the fund's expenses, such as expense ratios and minimum investment requirements. Lower expense ratios can result in higher yields for investors.
Risk Management
Municipal bond funds can provide risk management benefits due to their broad diversification. A credit event affecting one region or sector is likely to impact only a small portion of a well-diversified portfolio.
Investor Profile
Municipal bond funds often appeal to conservative investors or those in higher tax brackets due to their tax advantages and steady income. It's important to consider the risk tolerance and investment goals of the target investors when managing a municipal bond fund.
Distribution Policy
Municipal bond funds make regular distributions to investors, which can be monthly, quarterly, semi-annual, or annual. The frequency and amount of distributions depend on the fund's performance and discretion.
Benchmarking and Performance
Municipal bond fund managers can use benchmarks such as the Bloomberg Municipal Bond Index to compare the performance of their funds. This index includes municipal bonds with a minimum credit rating of at least Baa.
Professional Management
A Beginner's Guide to Vanguard 500 Index Fund Investing
You may want to see also

Municipal bond fund diversification
Municipal bond funds are a great way to diversify your investment portfolio, especially if you are in a high tax bracket. Municipal bonds are issued by state and local governments to raise money for public projects such as schools and roads. They are typically exempt from federal taxes and sometimes state and local taxes as well. This makes them an attractive investment option for those looking to reduce their tax burden.
Municipal bond funds are a type of investment fund that invests in municipal bonds. They are managed with varying objectives, often based on location, credit quality, and duration. These funds offer investors the advantages of municipal bond securities, along with diversification against individual issuer risk. This means that even if one municipal bond defaults, it will only affect a small part of the overall fund.
When investing in municipal bond funds, it is important to consider the fund's objective, location, credit quality, and maturity. Fund companies offer municipal bond funds across the entire credit spectrum, from conservative to high-yield options. It is also important to consider the tax implications of investing in municipal bond funds. If you are in a high tax bracket, the tax exemption advantages of municipal bond funds can be very appealing.
- Vanguard Tax-Exempt Bond ETF (VTEB)
- Fidelity Tax-Free Bond Fund (FTABX)
- T. Rowe Price Tax-Free High Yield Fund (PRFHX)
- BlackRock Allocation Target Shares: Series E Fund (BATEX)
- Delaware National High-Yield Municipal Bond Fund Institutional Class (DVHIX)
- Vanguard High-Yield Tax-Exempt Fund Admiral Shares (VWALX)
In conclusion, municipal bond funds can be a great way to diversify your investment portfolio, especially if you are in a high tax bracket. They offer tax advantages, slow and steady income, and a balanced investment option during turbulent times. When investing in municipal bond funds, be sure to consider the fund's objective, location, credit quality, and maturity to ensure it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Mutual Fund Strategies: Diversifying Your Portfolio with Multiple Funds
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Municipal invested funds are funds that invest in municipal bonds, which are debt securities issued by local, county, and state governments to raise capital for public projects such as roads, bridges, and schools.
Municipal bonds offer tax advantages as the interest paid on these bonds is usually exempt from federal income taxes and may also be exempt from state and local taxes. They also have a low risk of default compared to other bonds.
You can invest in municipal bonds by purchasing individual bonds or through a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF), which provides broader diversification and professional management.
Municipal bonds are subject to interest rate risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and call risk. The value of the bonds can fluctuate with changes in interest rates, and there is a risk of the issuer defaulting on the bond.
Municipal invested funds are most suitable for investors in higher tax brackets as the tax advantages of municipal bonds may not outweigh the lower yields for those in lower tax brackets.