Mutual funds are a popular investment choice, especially for retirement accounts like 401(k)s. They are a relatively hands-off way to invest in many different assets at once. When you buy into a mutual fund, you gain exposure to a wide mix of assets that are selected for the fund by a professional money manager. These assets can include stocks, bonds, real estate, derivatives, and other securities. Mutual funds are known for the diversification they offer, allowing investors to spread risk across multiple investments.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A mutual fund is a company that pools money from many investors and invests the money in securities. |
| Investment types | Stocks, bonds, short-term debt, real estate, derivatives, and other securities. |
| Benefits | Professional management, diversification, affordability, liquidity. |
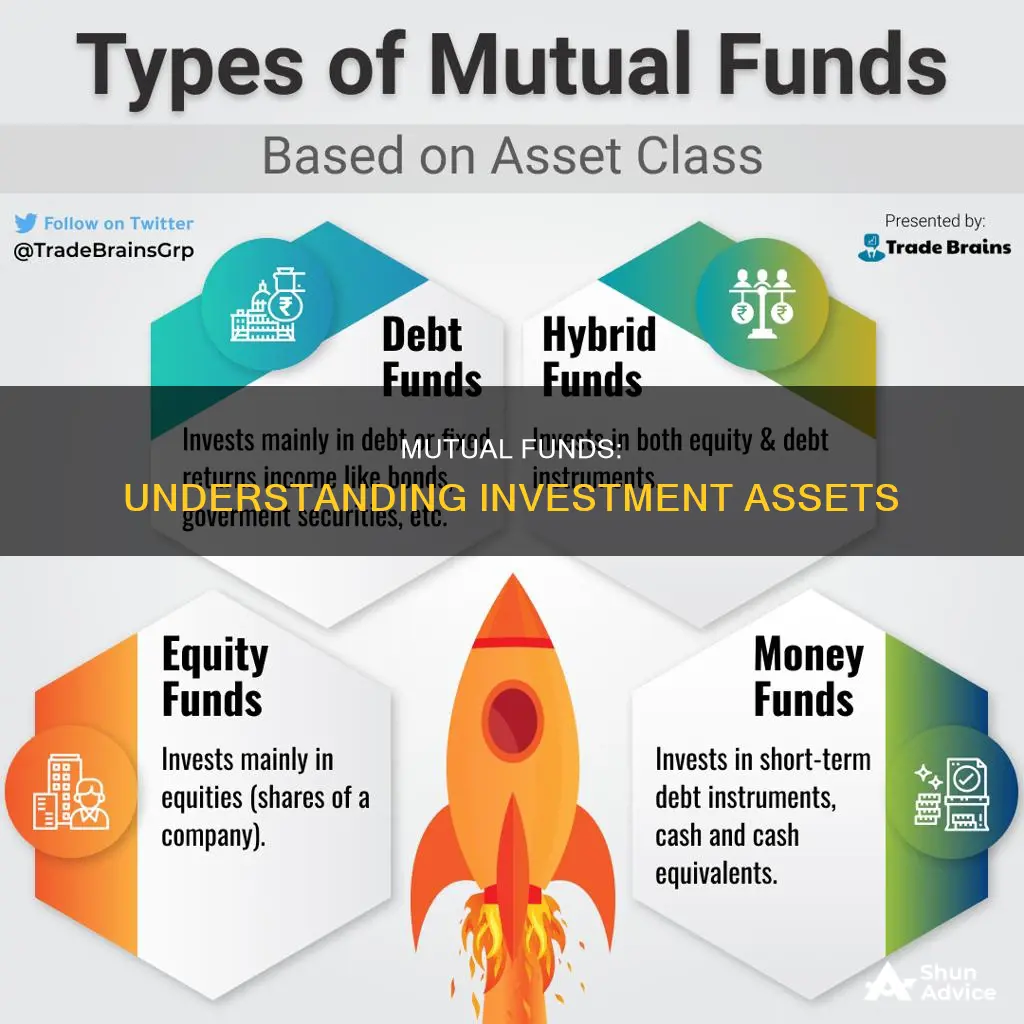
| Types of mutual funds | Money market funds, bond funds, stock funds, target date funds, stock mutual funds, bond mutual funds, balanced funds, index funds. |
| How to invest | Decide between active and passive funds, calculate your budget, decide where to buy, understand fees, manage your portfolio. |
| Fees | Annual fees, expense ratios, commissions, redemption fees, account fees, sales charges or loads, exchange fees, purchase fees. |
| Share classes | Class A, B, C, and transaction shares, each with different fees, charges, and investment horizons. |
| Risks | Market risk, interest rate risk, management risk, inflation, interest rate fluctuations, changing market conditions. |
What You'll Learn

Stocks
- Growth stocks: These are companies that are growing their revenues, cash flow, and earnings at rates that are much greater than their peers.
- Value stocks: Sometimes the share prices of perfectly solid and healthy public companies drop well below their true value due to larger market developments outside of the company's control. When a stock's price is low but its business fundamentals are good, it's considered a value stock.
- Dividend stocks: Companies that pay dependable dividends are viewed as providing shareholders with a steady stream of income.
- Blue-chip stocks: These are the stocks of large, established public companies that have become household names, like Apple, Disney, and Microsoft. Blue-chip stocks have a proven track record of dependable performance and a history of regular dividend payments.
Mutual funds that invest in stocks are known as stock mutual funds or equity mutual funds. These funds carry the highest potential rewards but also higher inherent risks. The performance of large-cap, high-growth funds, for example, is typically more volatile than stock index funds that seek only to match the returns of a benchmark index like the S&P 500.
When investing in stocks, you'll need an account. You can opt for a tax-advantaged account such as an individual retirement account (IRA) or a taxable brokerage account.
Equity Funds: When to Invest for Maximum Returns
You may want to see also

Bonds
Mutual funds are a type of investment where multiple investors pool their money together to purchase a large variety of securities, including bonds. A bond fund is a mutual fund or an exchange-traded fund (ETF) that buys and sells debt instruments like government and corporate bonds.
The percentage of interest is fixed in advance. Bonds are rated by credit rating agencies such as Moody's and Standard and Poor's to help investors. There are broadly two types of bonds: government bonds and corporate bonds. When governments are in need of money, they can only issue bonds. On the other hand, businesses issue bonds instead of seeking loans or overdrafts from banks as interest rates are cheaper on bonds, and the bond market offers better terms.
The three major types of bonds are corporate, municipal, and treasury bonds. Corporate bonds are debt instruments issued by a company to raise capital for initiatives like expansion and research and development. The interest earned from corporate bonds is taxable but usually offers higher yields than government or municipal bonds. Municipal bonds are issued by cities, towns, or states to raise money for public projects such as schools, roads, and hospitals. The interest earned from municipal bonds is tax-free. Treasury bonds, also known as T-bonds, are issued by the US government and are considered risk-free.
Bond funds are mutual funds that typically invest in a variety of bonds, such as corporate, municipal, treasury, or junk bonds. Bond funds usually pay higher interest rates than bank accounts, money market accounts, or certificates of deposit. They allow investors to invest in a range of bonds, managed by professional money managers, for a low investment minimum.
There are also bond funds that have a mix of different types of bonds to create multi-asset class options. The types of bond funds available include US government bond funds, municipal bond funds, corporate bond funds, mortgage-backed securities (MBS) funds, high-yield bond funds, emerging market bond funds, and global bond funds.
Money Market Index Funds: A Smart Investment Strategy
You may want to see also

Money market funds
There are several types of money market funds, including government, prime or short-term credit, and municipal funds. Government money funds invest primarily in cash, government securities, and repurchase agreements. Prime money funds invest in floating-rate debt, commercial paper, and other non-Treasury assets. Municipal money funds invest in municipal bonds and debt securities, offering tax-exempt income for investors.
Liquid Fund Investment: A Beginner's Guide to Getting Started
You may want to see also

Real estate
There are several types of REITs, including apartment, factory outlet, healthcare, hotel, industrial, mortgage, office, and shopping centre REITs. Real estate mutual funds can be open- or closed-end and are either actively or passively managed. They can be purchased through a financial advisor or, in some cases, via online brokerages.
Compared to real estate, mutual funds have higher average returns, are more liquid, have a lower initial investment threshold, and are less risky. However, real estate offers tangible assets, potential rental income, and tax benefits. It is important to carefully consider financial goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, capital requirements, market conditions, and tax considerations when deciding between investing in real estate or mutual funds.
Inverse Funds: Strategies for Savvy Investing
You may want to see also

Derivatives
There are four main types of derivatives: forwards, futures, options, and swaps. Forwards are customised contracts in which two parties agree to transact at a future date and a predetermined price. Futures are standardised contracts in which the buyer is obligated to purchase or the seller is obligated to sell the underlying security at a pre-agreed future date and price. Options are contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell the underlying security at a pre-agreed price by a specific date. Swaps are contracts in which two parties exchange financial instruments, typically involving cash flows based on a notional principal amount.
When evaluating mutual funds that use derivatives, it is important to consider the extent of their derivatives usage and the amount of borrowing involved. Checking the fund's holdings, sizing the exposure, identifying the reference assets, and stress-testing the strategy can help investors understand the risks and potential returns.
Mutual Fund Investment: Where to Begin?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are four main types of mutual funds: money market funds, bond funds, stock funds, and target date funds. Each type has different features, risks, and rewards.
Mutual funds offer professional investment management and potential diversification. They also offer three ways to earn money: dividend payments, capital gains distributions, and increased net asset value (NAV).
All funds carry some level of risk. With mutual funds, you may lose some or all of the money you invest because the securities held by a fund can go down in value. Dividends or interest payments may also change as market conditions change.