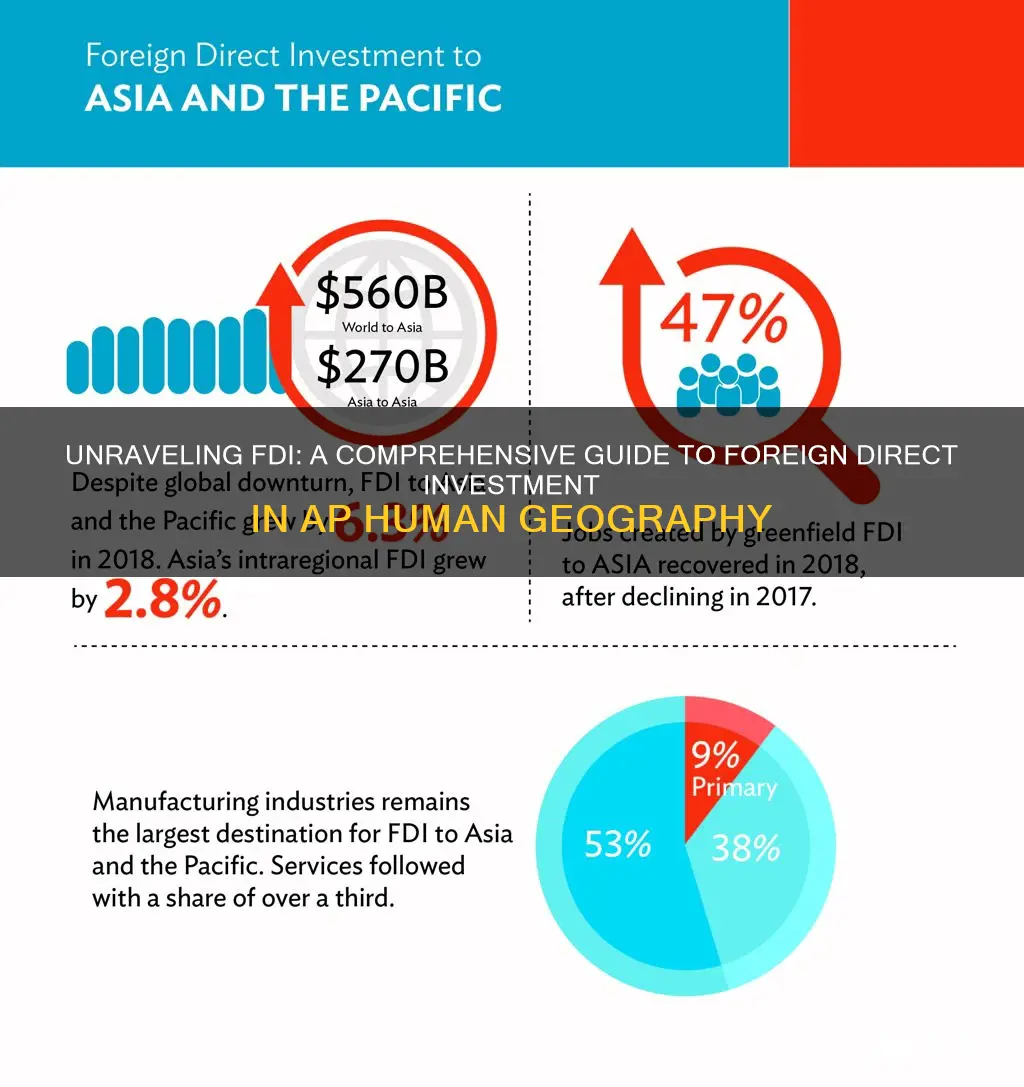
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is a crucial concept in the field of human geography, particularly in the study of international economic relations. It refers to the investment made by a company or individual in a foreign country, where the investor has a significant degree of control over the business operations. FDI plays a vital role in shaping global economic landscapes, influencing trade patterns, and impacting the development of host countries. This paragraph will explore the definition, significance, and various forms of FDI, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential topic in the context of AP Human Geography.
What You'll Learn
- Geographical Distribution: FDI varies by region, influenced by economic policies and market access
- Impact on Local Economies: FDI can boost employment, infrastructure, and technology transfer in host countries
- Multinational Corporations: These entities drive FDI, shaping global economic networks and power dynamics
- Policy and Regulation: Governments play a crucial role in attracting and managing FDI
- Environmental Considerations: FDI's environmental impact is a growing concern, requiring sustainable practices

Geographical Distribution: FDI varies by region, influenced by economic policies and market access
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is a critical aspect of international business and economic development, and its geographical distribution is a fascinating subject in human geography. FDI refers to the investment made by a company or individual in one country into business interests or assets in another country. This type of investment plays a significant role in shaping global economic landscapes and influencing the development of various regions.
The geographical distribution of FDI is not random but rather a result of various factors that attract or discourage investors. Economic policies and market access are two key determinants that vary across regions, leading to diverse FDI patterns. Countries with favorable economic policies often become attractive destinations for FDI. These policies may include tax incentives, subsidies, streamlined regulations, and infrastructure development, all of which aim to reduce the cost of doing business and encourage foreign investors. For instance, a country with a liberalized investment regime, offering tax breaks and simplified procedures, is likely to attract more FDI compared to a country with stringent restrictions and high tax rates.
Market access is another crucial factor influencing FDI distribution. Investors seek regions with large consumer markets or those offering strategic advantages for exporting goods and services. Proximity to major markets or regions with high demand for specific products can significantly impact FDI decisions. For example, a country with a growing middle-class population and a large consumer base might attract FDI in retail, manufacturing, or service industries. Similarly, a region with a well-developed transportation network and trade agreements facilitating the movement of goods can become an attractive FDI hub.
The impact of these factors is evident in the diverse FDI patterns observed globally. Some regions, often referred to as 'investment hubs', consistently attract a significant share of FDI. These hubs are typically characterized by a combination of favorable economic policies and excellent market access. For instance, the United States, the European Union, and certain Asian countries have been major recipients of FDI due to their robust economies, advanced infrastructure, and large consumer markets. In contrast, regions with less favorable conditions may struggle to attract FDI, leading to economic disparities.
Understanding the geographical distribution of FDI is essential for policymakers and investors alike. It helps identify regions with potential for growth and those that may require targeted interventions. By analyzing the factors influencing FDI, governments can design strategies to improve their investment climate and attract foreign capital. Additionally, investors can make informed decisions regarding market entry, expansion, or diversification based on the geographical distribution of FDI and the associated economic opportunities.
Invest with SRS and DBS: A Smart Guide
You may want to see also

Impact on Local Economies: FDI can boost employment, infrastructure, and technology transfer in host countries
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has a profound impact on local economies, particularly in the context of Human Geography, where understanding its effects on host countries is essential. When a foreign company invests in a new country, it brings a range of benefits that can significantly enhance the economic landscape. One of the most notable impacts is the creation of employment opportunities. FDI often leads to the establishment of new businesses or the expansion of existing ones, which, in turn, generates jobs for the local population. This is especially beneficial in regions where unemployment rates are high, as it provides a means to reduce poverty and improve the standard of living. Local communities gain access to new job roles, often requiring specialized skills, which can lead to increased income and a more skilled workforce over time.
The influx of FDI also stimulates infrastructure development. Host countries may receive investments in transportation networks, energy systems, and communication infrastructure. These improvements are crucial for the overall economic growth of the region. Well-developed infrastructure attracts further investment, making the area more appealing for businesses and residents alike. It also enhances connectivity, making it easier for local businesses to access markets and for people to commute, thus fostering a more dynamic and productive economy.
Technology transfer is another significant outcome of FDI. Foreign investors often bring advanced technologies, management practices, and expertise to the host country. This transfer of knowledge can modernize local industries, making them more efficient and competitive. For instance, a foreign manufacturing company might introduce automated production lines, improving productivity and reducing costs. Over time, this can lead to the development of a more sophisticated industrial base, enabling the country to move up the value chain and diversify its economy.
The positive effects of FDI on local economies are not limited to the immediate benefits of job creation and infrastructure development. It can also lead to long-term economic growth and sustainability. As local businesses expand and become more competitive, they may start to export goods and services, increasing the country's revenue from abroad. Moreover, the improved skills and knowledge of the workforce can attract further FDI, creating a cycle of continuous economic development.
In summary, FDI has a transformative effect on host countries' economies. It provides a boost to employment, ensuring that local people have access to better job opportunities. The development of infrastructure and the transfer of technology further strengthen the economy, making it more resilient and capable of supporting long-term growth. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers and economists to harness the full potential of FDI and ensure its benefits are distributed equitably across the host country's population.
Ghana's Foreign Investment: A Path to Economic Growth or a Pitfall?
You may want to see also

Multinational Corporations: These entities drive FDI, shaping global economic networks and power dynamics
Multinational corporations (MNCs) are a pivotal force in the global economy, playing a significant role in the phenomenon of foreign direct investment (FDI). These large, international companies have the financial and operational capabilities to invest in and establish a presence in multiple countries, often driving the flow of capital and resources across borders. FDI, in the context of human geography, refers to the investment made by a company or individual in one country into business interests or assets in another country. MNCs are key players in this process, as they can bring substantial resources, expertise, and market access to host countries.
The impact of MNCs on FDI is multifaceted. Firstly, they often serve as the primary channel for FDI inflows into a country. When an MNC invests in a foreign market, it can create a ripple effect, attracting other investors and fostering a more comprehensive economic relationship. For instance, an MNC's decision to set up a manufacturing plant in a developing country might encourage other businesses to follow suit, leading to a surge in FDI in that region. This is particularly evident in the case of emerging markets, where MNCs can catalyze economic growth and development.
Moreover, MNCs contribute to the global economic network by integrating markets and production processes. They often have complex supply chains that span multiple countries, creating interdependencies in the global economy. For example, a car manufacturing MNC might source raw materials from one country, assemble components in another, and sell the final product in yet another market. This intricate web of connections not only drives FDI but also influences trade patterns and economic policies worldwide. As MNCs expand their operations, they can shape the economic landscape, creating opportunities and challenges for both host and home countries.
The power dynamics associated with MNCs and FDI are also noteworthy. These corporations often possess significant market power, allowing them to influence local businesses and industries. When an MNC enters a new market, it can disrupt existing structures, potentially leading to the rise of new competitors or the consolidation of market share. This dynamic can have both positive and negative consequences, impacting local employment, competition, and innovation. Additionally, MNCs may engage in strategic partnerships or acquisitions, further shaping the global economic landscape and the distribution of power.
In summary, multinational corporations are the driving force behind a significant portion of foreign direct investment, influencing global economic networks and power structures. Their ability to invest, operate, and integrate markets across borders has a profound impact on the flow of capital, resources, and opportunities. Understanding the role of MNCs in FDI is essential for comprehending the complex dynamics of the global economy and the interactions between nations in the modern world.
How Cash Investments Impact Owners' Equity
You may want to see also

Policy and Regulation: Governments play a crucial role in attracting and managing FDI
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is a significant aspect of international business and plays a vital role in the field of Human Geography, particularly in the context of global economic interactions. Governments are indeed key players in this arena, as they possess the power to shape the landscape of FDI through various policy and regulatory measures. These actions can either facilitate or hinder the flow of foreign capital into a country, impacting its economic development and global standing.
One of the primary tools governments employ to attract FDI is through the implementation of investment promotion policies. These policies often include offering incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies, and streamlined regulatory processes to foreign investors. For instance, a government might provide tax exemptions for a certain period to encourage foreign companies to establish a presence in the country, especially in sectors deemed strategic or those that could create significant local employment. Such incentives are designed to reduce the financial burden on investors and enhance the overall attractiveness of the investment destination.
Regulatory frameworks are another critical aspect of government policy in managing FDI. Governments establish rules and regulations that govern the operations of foreign-owned businesses within their borders. These regulations may cover areas such as environmental standards, labor laws, intellectual property rights, and data privacy. By setting clear and consistent rules, governments can ensure that foreign investors operate on a level playing field, promoting fair competition and protecting the interests of local businesses and consumers. Well-designed regulations can also help attract FDI by demonstrating a country's commitment to transparency and accountability.
In addition to attracting FDI, governments are responsible for managing its impact and ensuring sustainable development. This involves implementing policies that encourage the positive spillover effects of FDI, such as technology transfer, skill development, and local supplier development. Governments may also need to address potential challenges, including the environmental and social consequences of foreign investment, particularly in resource-rich sectors. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of FDI requires a nuanced approach, where governments act as facilitators, ensuring that foreign investments contribute to long-term economic growth and social well-being.
Furthermore, international agreements and treaties play a significant role in shaping the FDI landscape. Governments often engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms for FDI, ensuring that their policies align with international standards and best practices. These agreements can provide a framework for resolving disputes, protecting investor rights, and promoting cooperation between countries. By actively participating in global economic forums and negotiations, governments can influence the rules of the game, making their countries more attractive destinations for foreign investors.
FDI's Impact: Unlocking Knowledge Diffusion for Global Growth
You may want to see also

Environmental Considerations: FDI's environmental impact is a growing concern, requiring sustainable practices
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has become a significant global phenomenon, shaping the economic landscape and influencing various sectors, including the environment. As FDI continues to expand, its environmental impact has emerged as a critical concern, prompting the need for sustainable practices to mitigate potential ecological risks. This is especially relevant in the context of AP Human Geography, where understanding the geographical dimensions of FDI is essential.
Environmental considerations in the context of FDI are multifaceted. Firstly, the establishment of foreign-owned enterprises often leads to increased industrial activity, which can result in pollution and habitat destruction. Manufacturing processes, energy consumption, and waste management are key areas of concern. For instance, the construction of factories or power plants may disrupt local ecosystems, leading to air and water pollution, especially if proper environmental regulations are not in place. This is particularly relevant in regions where environmental standards are less stringent, making it crucial to assess the potential ecological footprint of FDI projects.
Secondly, the extraction of natural resources for industrial processes can have severe environmental consequences. Mining, deforestation, and the exploitation of fossil fuels are common practices associated with FDI. These activities can lead to soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and the degradation of natural habitats. For example, the expansion of agricultural land for foreign-owned farms might involve clearing vast areas of native forests, impacting local wildlife and ecosystems. Sustainable practices, such as reforestation efforts, eco-friendly farming techniques, and the adoption of renewable energy sources, are essential to minimize these environmental impacts.
Addressing these environmental challenges requires a comprehensive approach. Governments and international organizations play a vital role in implementing and enforcing environmental regulations. This includes setting standards for emissions, waste disposal, and resource extraction. Additionally, encouraging FDI in sectors that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy, eco-tourism, and green technology, can help balance economic growth with ecological preservation. FDI can also drive the transfer of clean technologies and best practices, fostering environmental awareness and responsibility among local communities.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of FDI is a critical aspect that demands attention and action. By adopting sustainable practices, such as implementing strict environmental regulations, promoting eco-friendly industries, and encouraging responsible resource management, it is possible to mitigate the ecological risks associated with FDI. This ensures that the economic benefits of foreign investment do not come at the expense of the environment, promoting a more sustainable and harmonious global development trajectory. Understanding and addressing these environmental considerations are essential steps towards a more responsible and geographically conscious approach to FDI.
CPF Investment Strategies: Your Guide to Getting Started
You may want to see also







