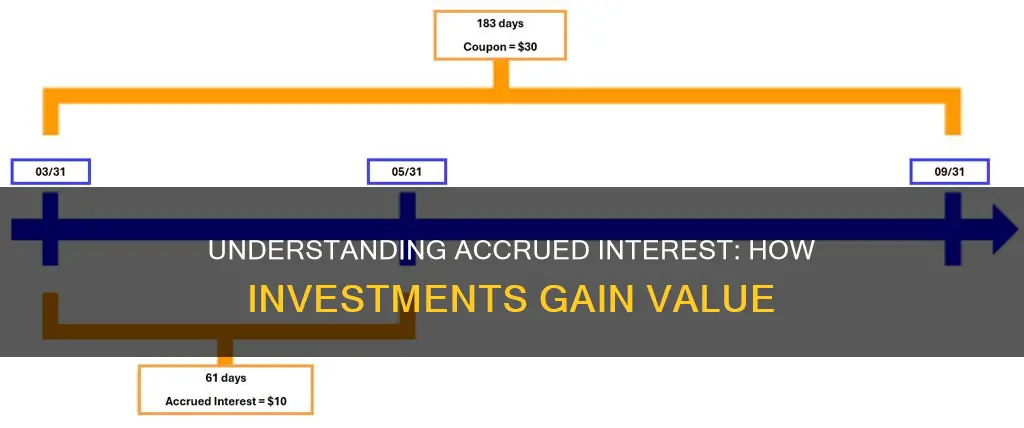
Accrued interest is the interest that has been earned or incurred on an investment but has not yet been paid or received by the end of an accounting period. It is an essential component for understanding an entity's cash flow and financial health. Accrued interest can be owed or earned. For example, accrued interest on a loan adds to how much a borrower owes, while accrued interest on an investment earns income.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Accrued interest is the unpaid interest on an investment that has accumulated over time. |
| Application | Accrued interest is an essential component for understanding an entity's cash flow and financial health. |
| Formula | The formula for calculating accrued interest depends on the principal amount, interest rate, and the time period for which the interest has accrued. |
What You'll Learn

Accrued interest on investments
Accrued interest is the interest that has been earned or incurred on a financial obligation or investment but has not yet been paid or received by the end of an accounting period. It is an essential component for understanding an entity’s cash flow and financial health.
Accrued interest can be owed or earned. Accrued interest on a loan or credit card adds to how much a borrower owes. Accrued interest on a savings account or an investment earns income. It is an increase in investment income or savings.
Accrued interest is an important concept in accounting. It ensures financial statements reflect the entity’s actual financial position by recognising interest as it accumulates, rather than waiting for the cash transaction to occur. This gives a more accurate picture of an entity's financial health.
The formula for calculating accrued interest depends on the principal amount, interest rate, and the time period for which the interest has accrued.
Interest Rate Cuts: Impact on Foreign Investment
You may want to see also

Accrued interest on bonds
Accrued interest can be owed or earned. In the context of personal finance, accrued interest on a loan or credit card adds to the borrower's debt. On the other hand, accrued interest on a savings account or investment earns income.
The formula for calculating accrued interest depends on the principal amount, interest rate, and the time period for which the interest has accrued. This formula can be used to calculate accrued interest on bonds.
Investing: Interest and Cash Flow Interdependence
You may want to see also

Accrued interest on savings accounts
Accrued interest is the unpaid interest that has been earned on a financial obligation or investment but has not yet been paid or received by the end of an accounting period. In the context of savings accounts, accrued interest refers to the interest that has been earned on the account but remains unpaid at the end of the accounting period. This interest is typically calculated based on the principal amount, interest rate, and the time period for which the interest has accrued.
For example, let's say you have a savings account with a principal balance of $10,000 and an annual interest rate of 2%. If you leave the money in the account for one year, you will earn interest on that balance. However, the interest is typically calculated and paid out at specific intervals, such as quarterly or semi-annually.
Let's assume the interest is calculated and paid out quarterly. After the first quarter, you will have accrued interest of $50 (2% of $10,000 divided by four quarters). This $50 is the interest that has accumulated on your savings account but has not yet been paid to you. It represents the income that you have earned on your savings during that quarter.
Accrued interest is an important concept in understanding an entity's cash flow and financial health. By recognising interest as it accumulates, financial statements can reflect the actual financial position of an entity, rather than waiting for the cash transaction to occur. This provides a more accurate representation of the value and performance of savings accounts or investments over time.
Invest Wisely: Utilize UK Compound Interest
You may want to see also

Accrued interest on loans
The formula for calculating accrued interest on loans depends on the principal amount, the interest rate, and the time period for which the interest has accrued. This formula can be used to calculate the accrued interest on a loan or credit card, which adds to the total amount owed by the borrower.
Understanding the Correlation Between Interest Rates and Investments
You may want to see also

Accrued interest on credit cards
The formula for calculating accrued interest on credit cards takes into account the principal amount borrowed, the interest rate applied, and the time period over which the interest has accrued. By using this formula, individuals can understand the impact of accrued interest on their financial obligations.
Understanding accrued interest on credit cards is crucial for effective financial management. It allows individuals to track their debt obligations and make informed decisions about their credit card usage. By staying on top of accrued interest, borrowers can minimise the potential for their debt to spiral out of control.
Dollar Interest Rate Changes: Impact on Your Investments
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Accrued interest is the amount of unpaid interest added after a certain date. In the case of investments, accrued interest is earned.
The formula for calculating accrued interest depends on the principal amount, interest rate, and the time period for which the interest has accrued.
Accrued interest is an essential component for understanding an entity’s cash flow and financial health. It ensures financial statements reflect the entity’s actual financial position by recognising interest as it accumulates, rather than waiting for the cash transaction to occur.