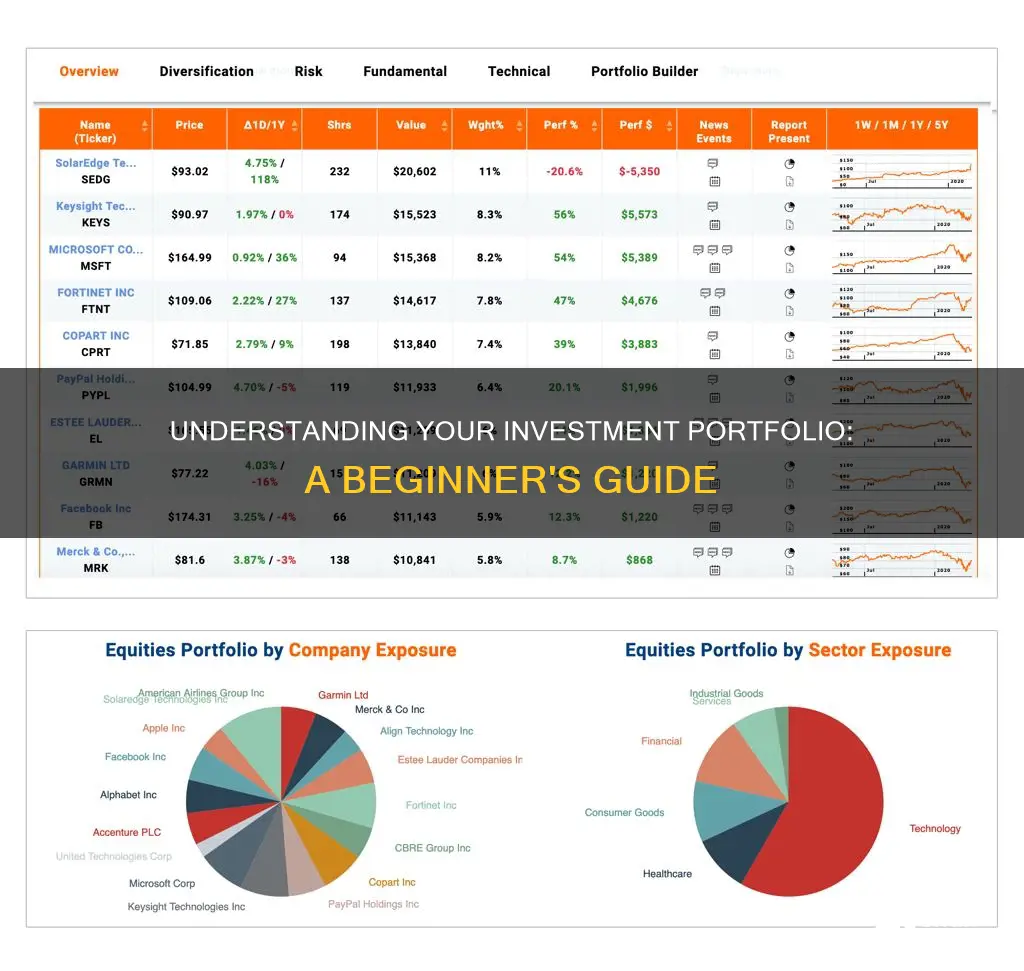
An investment portfolio is a collection of financial assets owned by an investor. It is a set of investments held by an individual or institution that aims to generate returns over time while managing risk. Portfolios can include a variety of different assets, such as stocks, bonds, cash, cash equivalents, commodities, currencies, and real estate. The key to a successful portfolio is diversification, which means not putting all your eggs in one basket. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions, investors can reduce the impact of any single asset's poor performance on the portfolio and mitigate risk.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To generate returns over time while managing risk |
| Contents | Stocks, bonds, cash, cash equivalents, real estate, commodities, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), currencies, art, private investments, gold, oil, and more |
| Management | Can be managed by the investor, a money manager, financial advisor, or another finance professional |
| Diversification | A key concept in portfolio management; aims to reduce risk and maximise returns |
| Risk | Depends on the investor's risk tolerance, financial goals, and timeline |
| Time horizon | The amount of time an investor has to invest; affects the level of risk that can be taken |
| Rebalancing | Regular rebalancing is important to maintain the desired asset allocation |
What You'll Learn

Stocks, bonds, and other securities
An investment portfolio is a collection of financial investments, which may include stocks, bonds, and other securities. Stocks, bonds, and cash are generally considered the core of a portfolio, but portfolios can also include a wide range of other assets, such as real estate, gold, paintings, and other art collectibles.
Stocks
Stocks represent shares in the ownership of a company, including a claim on the company's earnings and assets. As such, stockholders are partial owners of the company. When the value of the business rises or falls, so does the value of the stock. Stocks are generally bought and sold electronically through stock exchanges, with the two primary exchanges in the United States being the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASDAQ).
Bonds
Bonds are fixed-income instruments and investment products where individuals lend money to a government or company at a certain interest rate for a specified amount of time. The entity repays individuals with interest in addition to the original face value of the bond. Bonds are used to finance projects and operations. Owners of bonds are debtholders, or creditors, of the issuer. The initial price of most bonds is typically set at par or $1,000 face value per individual bond. The actual market price of a bond depends on the credit quality of the issuer, the length of time until expiration, and the coupon rate compared to the general interest rate environment.
Other Securities
The term "security" refers to a multitude of different investments, such as stocks, bonds, investment contracts, notes, and derivatives. Securities can be broadly categorized into two distinct types: equity and debt. However, some hybrid securities combine elements of both equities and debts. Equity securities represent ownership interest held by shareholders in an entity, while debt securities represent borrowed money that must be repaid, with terms that stipulate the size of the loan, interest rate, and maturity or renewal date.
Investing: A Smarter Option Than Saving for Your Future
You may want to see also

Risk and return
Risk
Risk refers to the potential for financial loss in an investment portfolio. Different types of investments carry varying levels of risk. For example, stocks are often considered riskier than bonds, as they fluctuate more in value, while bonds are generally safer but offer lower potential returns. Understanding and managing risk is crucial for investors. Diversification is a key risk management strategy, where investments are spread across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions to reduce the impact of any single asset's poor performance.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance is an individual investor's ability and willingness to take on risk. It is influenced by factors such as age, financial circumstances, and investment goals. Younger investors with a longer time horizon are generally more comfortable taking on higher-risk investments, as they have more time to recover from potential losses. In contrast, older investors nearing retirement may have a lower risk tolerance and prefer more conservative investments.
Return
Return refers to the profit or gain generated by an investment portfolio over time. The expectation of earning returns is a key motivator for investors. Returns can come in the form of capital appreciation, which is an increase in the value of an investment, or income received through dividends, interest, or rent. Different types of investments offer varying potential returns, and investors need to consider their risk tolerance and investment goals when deciding on their portfolio's asset allocation.
Risk-Return Trade-off
There is a trade-off between risk and return in investment portfolios. Generally, higher-risk investments offer the potential for higher returns, while lower-risk investments tend to provide lower returns. For example, stocks are considered riskier but have historically delivered higher returns over the long term compared to other asset classes. Investors need to carefully assess their risk tolerance and financial goals to determine the appropriate balance between risk and return in their portfolios.
Diversification and Risk-Return
Diversification plays a crucial role in managing risk and optimizing returns. By spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors, investors can reduce the impact of any single investment's performance on their portfolio. Additionally, diversification can help investors access different risk and return profiles. For instance, including both stocks and bonds in a portfolio can provide a balance between higher-risk, higher-return stocks and lower-risk, lower-return bonds.
In summary, risk and return are critical factors in investment portfolio management. Effective management of risk through diversification and careful consideration of risk tolerance can help investors optimize their portfolios for potential returns while staying within their comfort zone. Understanding the risk-return trade-off is essential for making informed investment decisions and constructing a well-balanced portfolio.
Portfolio Investments: Global Politics' Impact
You may want to see also

Diversification
For example, if you invest all your money in one company and it goes bankrupt, you lose everything. However, if you split your investment across four companies, you reduce the odds of losing money by 75%. Diversification allows investors to balance risk and return to achieve desired results for their financial goals.
There are many ways to diversify. One can invest in different types of investment instruments, such as stocks, debentures, mutual funds, fixed deposits, and gold. At a high level, these can be classified into three categories: fixed income, equity, and gold. Fixed income or debt is the lowest-risk asset class, while equity has the highest risk and highest returns. Gold sits in the middle in terms of risk and can act as a hedge against inflation.
Different asset classes also perform differently in various economic cycles. For instance, fixed income outperforms equity in bear markets, while equity does better in bull markets. By diversifying across asset classes, investors can smoothen portfolio volatility and achieve good long-term returns.
Mutual funds are a great way to diversify. They pool money from different investors and invest in a wide range of securities, providing exposure to various asset classes and industries. This allows investors to benefit from diversification with a smaller investment.
The key to successful investing is finding the right balance between your comfort level with risk and your time horizon. A well-diversified portfolio will include a mix of assets suited to your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Savings and Investments: Your Guide to Financial Freedom
You may want to see also

Asset allocation
An investment portfolio is a collection of financial investments like stocks, bonds, commodities, cash, and cash equivalents, including exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds. A portfolio may also consist of alternative investments like art, real estate, or collectibles. Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of investment portfolio management and refers to the process of selecting and dividing up your investments across various asset classes. It is a strategic approach to investing, where the aim is to balance risk and reward to meet specific financial goals and objectives.
Risk and Return:
Different asset classes offer varying levels of risk and potential return. Stocks, for example, generally provide higher potential returns over the long term but come with higher risks and volatility. On the other hand, bonds are considered less risky but typically offer lower returns. By diversifying across asset classes, an investor can aim for a balance between risk and return that aligns with their goals.
Age and Investment Horizon:
Age and investment horizon play a crucial role in asset allocation. Younger investors with a longer investment horizon can typically afford to take on more risk by allocating a larger portion of their portfolio to stocks or other growth-oriented investments. As an investor gets closer to retirement or needs access to their funds, the allocation shifts towards more conservative investments like bonds and cash to preserve capital and provide stable income.
Risk Tolerance:
Risk tolerance is an individual's ability and willingness to take on investment risk. It is a key consideration in asset allocation. Those with a higher risk tolerance may be comfortable with a larger allocation to volatile assets like stocks, while those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach with a focus on capital preservation.
Diversification:
Diversification is a core principle of effective asset allocation. By spreading investments across various asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of specific risks associated with individual investments. Diversification helps smooth out portfolio returns and can provide a more consistent performance over time.
Rebalancing:
Over time, the performance of different asset classes varies, and this can cause an investment portfolio to drift from its original allocation. Rebalancing is the process of periodically buying or selling assets to return the portfolio to its intended allocation. This discipline ensures the investor maintains their desired level of risk and stays on track with their financial goals.
In summary, asset allocation is a strategic and personalized approach to investing. It involves allocating capital across various asset classes to balance risk and return, considering factors like age, investment horizon, risk tolerance, and financial goals. Effective asset allocation, along with diversification and rebalancing, forms the foundation of a well-constructed investment portfolio.
Savings and Investments: Keys to Economic Growth
You may want to see also

Investment goals
When setting investment goals, it's important to consider your risk tolerance, financial objectives, and time horizon.
For example, a young investor saving for retirement might have a higher allocation of stocks in their portfolio for growth potential. On the other hand, a retiree might favour bonds for income stability and lower risk.
Retirement Planning: As mentioned, retirement is often a key investment goal. For those saving for retirement, a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets like real estate or commodities can provide diversification and potential for long-term growth. As retirement approaches, the portfolio can be adjusted to become more conservative, reducing risk and preserving capital.
Income Generation: Investors seeking regular income may focus on dividend-paying stocks, coupon-yielding bonds, and income-producing real estate. This type of portfolio aims to provide a consistent cash flow while also considering capital preservation.
Wealth Accumulation: Those aiming to accumulate wealth over time may opt for growth-oriented portfolios, which typically include a larger allocation of stocks and higher-risk assets. This strategy suits investors with a long time horizon and a higher risk tolerance.
Capital Preservation: For investors prioritising capital preservation, portfolios with a higher allocation of bonds, cash, and cash equivalents may be suitable. These assets are generally lower risk and more liquid, providing stability and easy access to funds.
Specific Goals: Investment goals can also be tailored to specific objectives, such as saving for a down payment on a house or a child's education. These short-term goals typically involve a more conservative asset allocation, choosing investments with lower volatility, such as bonds and cash.
It's important to note that investment goals can evolve over time, and portfolios should be regularly reviewed and adjusted to align with changing circumstances and objectives.
Investment Options for College Savings: What Are Your Choices?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An investment portfolio is a collection of financial assets owned by an investor. This can include stocks, bonds, cash, real estate, and more. The goal of an investment portfolio is to generate returns over time while managing risk.
An investment portfolio allows you to diversify your investments, reducing the risk of losses. By investing in different asset classes, you can lower the impact of any single asset's poor performance on your overall portfolio.
To create an investment portfolio, you should first determine your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Then, choose a mix of assets that align with your goals and risk tolerance. Finally, regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation.