Financial risk management is the process of identifying and analysing risks, then making investment decisions based on either accepting or mitigating them. Financial risks are events or occurrences that have undesirable or unpredictable financial outcomes or impacts. These risks are faced by both individuals and corporations. Financial risk management is a continuous process, as risks can change over time.
Financial risks can be quantitative or qualitative, and it is the job of a finance manager to use the available financial instruments to hedge a business against them. Financial risk management strategies include risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk retention.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Financial risk management involves identifying the potential downsides in any investment decision and deciding whether to accept the risks or take measures to mitigate them. |
| Importance | Financial risk management is important because it helps investors achieve their goals while offsetting any associated losses. |
| Risk Types | Financial risks include credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, market risk, legal risk, country risk, foreign-exchange risk, reputational risk, and more. |
| Risk Management Strategies | Strategies include avoidance, retention, sharing, transferring, and loss prevention and reduction. |
| Risk Measurement | Risk is often measured using standard deviation, a statistical measure of dispersion around a central tendency. |
What You'll Learn

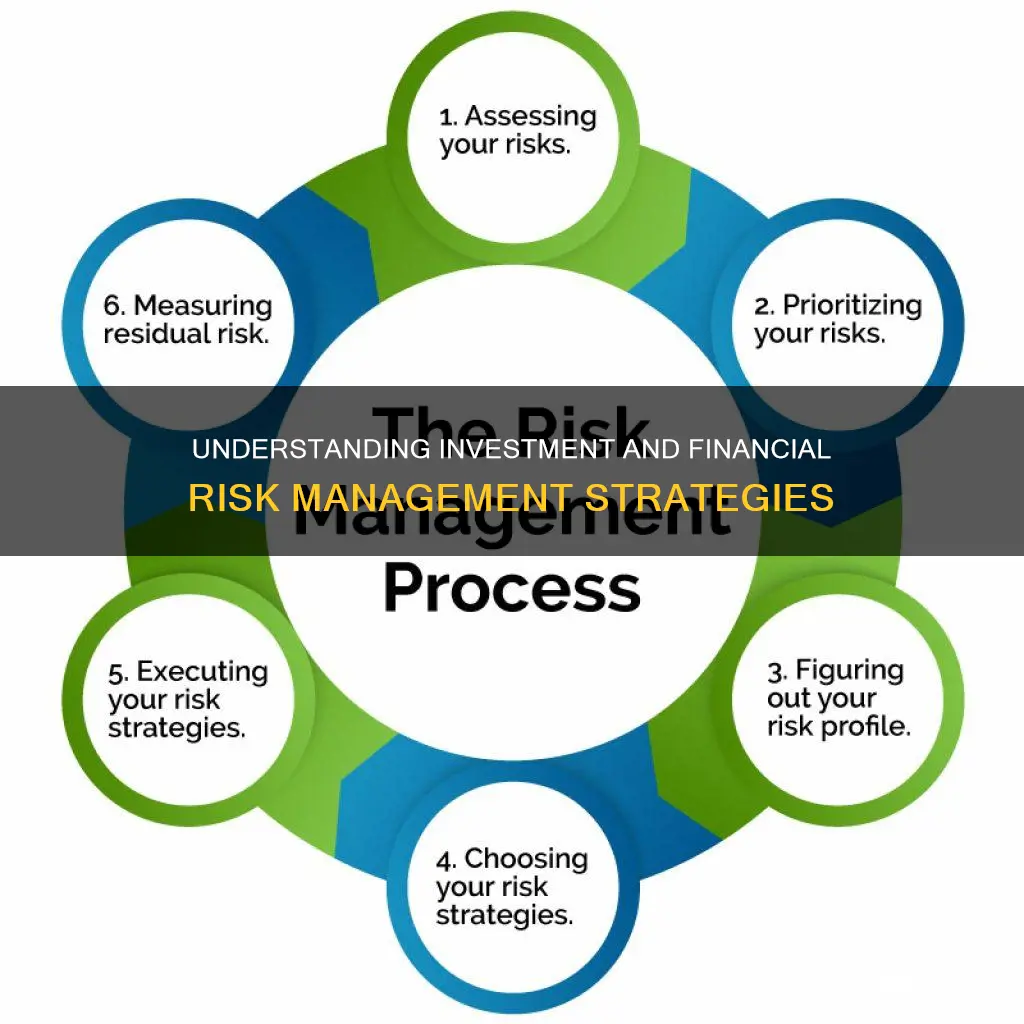
Identifying and analysing risks
Identifying Risks
The first step is to identify the potential risks that may arise. These can be internal or external to a company. It is important to involve stakeholders from different departments as they may offer diverse perspectives. A SWOT analysis can be a useful tool to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, providing a comprehensive view of the business environment.
Understanding Risk Factors
Once the risks are identified, it is crucial to understand the factors contributing to them. This includes reviewing financial statements, such as balance sheets and statements of financial positions, to grasp the company's financial health and potential vulnerabilities. Analysing revenue sources, customer credit terms, and the impact of market conditions are also essential aspects of this step.
Analysing Probability and Impact
For each identified risk, assess the likelihood of it occurring and the potential consequences. This analysis involves assigning numerical values or using subjective judgment to build a theoretical model. It helps to prioritise risks and determine their potential financial impact on the business.
Developing a Risk Management Plan
Based on the analysis, develop a plan to address the risks. This may involve risk avoidance, retention, sharing, transferring, or implementing loss prevention and reduction strategies. The chosen approach should align with the company's risk tolerance and overall business strategy.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Risk management is an ongoing process. It is important to monitor the implemented strategies and make adjustments as necessary. Regularly reviewing and updating the risk management plan ensures that the business can adapt to changing market conditions and emerging risks.
Utilising Risk Analysis Techniques
There are various techniques available for risk analysis, including fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and quantitative analysis. Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's intrinsic value by assessing its assets, earnings, and financial performance. Technical analysis involves studying historical data such as returns, trade volume, and share prices to identify patterns and inform decision-making. Quantitative analysis employs financial ratio calculations to assess a company's historical performance and financial health.
Prioritising and Mitigating Risks
Prioritise risks based on their severity and likelihood of occurrence. Develop strategies to mitigate the highest-priority risks first. This may involve diversifying investments, purchasing insurance, or implementing hedging techniques to reduce exposure to specific risks.
Incorporating Risk Accountability
Incorporate risk accountability across the organisation. Provide appropriate training to employees to ensure they understand the importance of risk management and their role in mitigating risks. This fosters a culture of risk awareness and encourages proactive risk management at all levels of the organisation.
Understanding Active Management Fees: Strategies and Costs
You may want to see also

Deciding whether to accept or mitigate risks
When deciding whether to accept or mitigate risks, it is essential to first identify and analyse the potential risks associated with a particular investment decision or financial activity. This involves evaluating both quantitative and qualitative risks and considering various factors such as historical behaviours, market dynamics, and internal processes. By doing so, individuals or organisations can determine the likelihood and potential impact of different risks.
The next step is to decide on a strategy to manage the identified risks. This decision depends on the nature of the risks and the risk appetite of the individual or organisation. There are several strategies that can be employed, including risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk retention.
Risk avoidance involves eliminating activities that expose an individual or organisation to risk. For example, an individual may choose to avoid using credit to make purchases, thereby avoiding the risk of debt financing. Similarly, a corporation may decide against expanding operations into an area with high political and regulatory uncertainty.
Risk reduction focuses on minimising potential losses or reducing their severity. This can be achieved through diversification, hedging, or implementing internal controls. For instance, an individual may diversify their investment portfolio to reduce the impact of negative market movements. A corporation may use hedging strategies to minimise exposure to currency fluctuations.
Risk transfer involves shifting the risk to a third party. Individuals may purchase insurance policies to protect against risks such as premature death or property damage. Corporations may also buy insurance to cover potential losses due to damage, theft, or other risks.
Risk retention is the acceptance of responsibility for a particular risk. This strategy is often chosen when the cost of mitigating the risk outweighs the potential benefits. For example, a lumber producer may choose to retain the risk of fluctuating commodity prices instead of using futures contracts, as hedging may put them at a disadvantage if prices move favourably.
The decision to accept or mitigate risks should be based on a comprehensive understanding of the risks involved and the potential impact on the individual or organisation's financial goals. It is important to note that risks cannot always be eliminated, but effective risk management strategies can help minimise potential losses and improve the likelihood of achieving desired financial outcomes.
Be Your Own Boss: Manage Your Investments Independently
You may want to see also

Risk avoidance
A risk avoidance strategy is designed to deflect as many threats as possible to avoid the costly and disruptive consequences of a damaging event. Leaders must identify and assess the risks their organization faces and determine how to eliminate the chances of those risks causing damage to the organization.
For example, a building company that decides to halt all construction work during an electrical storm to avoid the risk of someone getting hurt is a clear case of risk avoidance. Similarly, a utility company that decides to have certain critical systems run on an air-gapped network to eliminate the risk of a cyber attack is following a risk avoidance strategy.
Investors could avoid all risk of losing their capital value by placing all their assets in a federally guaranteed savings account instead of buying stocks, whose values would likely fluctuate.
While risk avoidance can completely or nearly eliminate a potentially damaging risk and instill confidence in an organization's continued operation, it can also slow down operations and limit opportunities for increasing sales, cultivating new customers, and developing new revenue streams.
In the context of investment and financial risk management, risk avoidance can be an important strategy to protect an individual's or organization's assets and avoid financial losses. It involves not taking on certain actions or investments that are deemed too risky. This could include avoiding volatile investments, choosing safer assets with little to no risks, or diversifying investments to mitigate overall risk.
Diversifying Investments: Managing Financial Risk Strategically
You may want to see also

Risk reduction
At the individual level, risk reduction can be achieved through diversification. For instance, an individual can reduce the risk of severe losses in their investment portfolio by diversifying across different types of securities, industries, sectors, and markets. This ensures that if one part of the portfolio declines, the rest may still be growing. Diversification can also be achieved by varying investment styles, such as growth, income, and value.
Another risk reduction strategy for individuals is to hold sufficient emergency funds and maintain multiple income streams. This provides a safety net in case of unexpected expenses or loss of income.
Corporations can employ hedging strategies to reduce their exposure to certain risks, such as foreign currency transactions to mitigate currency fluctuations. They can also use financial instruments, such as insurance, to transfer the risk of damage, theft, or employee mistakes to a third party, such as an insurance company.
Additionally, corporations can manage operational risk through effective internal controls, processes, and systems. This includes implementing compliance programs, monitoring regulatory changes, and seeking legal advice to mitigate legal and regulatory risks.
Overall, risk reduction strategies are essential for both individuals and corporations to minimise potential losses and protect their financial well-being.
JPMorgan's Emerging Manager Program: Investment Opportunities?
You may want to see also

Risk transfer
The most common example of risk transfer is insurance. When an individual purchases insurance, they are protecting themselves against financial risks. For instance, car insurance provides financial protection against physical damage or bodily harm resulting from traffic incidents. The individual is shifting the risk of financial loss from a traffic incident to an insurance company and, in exchange, the insurance company will typically require periodic payments from the individual.
Another method of risk transfer is through indemnification clauses in contracts. An indemnification clause ensures that potential losses will be compensated by the opposing party. In this case, the parties involved commit to compensating each other for any harm, liability, or loss arising from the contract. For example, a contract writer may include an indemnification clause stating that they will indemnify the client against any copyright claims. Therefore, if the client receives a copyright claim, the contract writer would cover the costs of defending against the claim and any resulting damages.
Wealth Management: Exploring Investment Vehicle Options
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Financial risk is the possibility of losing money on an investment or business venture. It generally relates to the odds of losing money and can result in the loss of capital for interested parties.
There are several types of financial risk, including:
- Market risk
- Credit risk
- Liquidity risk
- Operational risk
- Legal risk
- Foreign exchange risk
- Reputational risk
Financial risk management is the process of identifying, analysing and making decisions about financial risks. It involves deciding whether to accept the risks or take measures to mitigate them. This is an ongoing process as risks can change over time.







