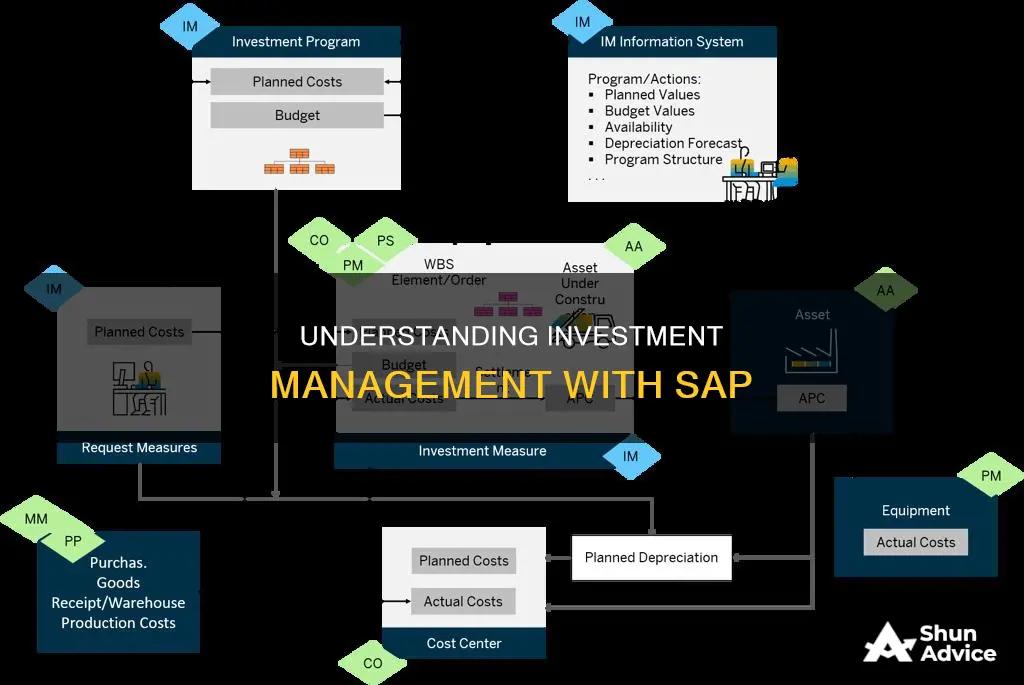
Investment Management (IM) is an important SAP product used to automate financial planning, investments, and other related processes. It is particularly useful for investments in research and development, capital structuring, and projects and maintenance. SAP IM enables the development and monitoring of an organisation's strategic plans, such as a capital investment plan, which helps to plan limited capital resources by integrating clear and detailed links between assets and expected delivery or capacity outcomes. The SAP IM module is used to control capital expenditures and manage various investment securities of an organisation, such as shares and bonds. It also helps in assigning and controlling budgets for capital expenditures and advertising.
What You'll Learn

Investment Programs and Positions
All budget items (positions) are assigned to an investment program. The investment program is for a specified fiscal year and reporting currency. In a large group, spanning multiple jurisdictions, currencies, and even fiscal periods, it is often necessary and more convenient to maintain multiple investment programs. Reporting is done by Investment Program.
Investment Program Positions are budget items within an Investment Program. Hierarchical budget structures can be defined by linking positions to each other. Individual investment measures (e.g. projects or internal orders) can only be linked to the lowest-level positions in the structures. SAP provides functionality for adding positions into the program structure, and ‘rolling-up’ budget from the lowest level budget positions to the higher-level hierarchy nodes. Key attributes of an Investment Program Position include organisation assignment (company and plant), investment reason, and asset class.
Within SAP, two sets of control values can be maintained: Plans and Budgets. Plans are more like ‘soft’ targets or forecasts and can be exceeded, whereas Budgets are ‘hard’ limits, and procurement in excess of the allocated budget is generally prevented. Plans can be structured into multiple versions (based on periodic reforecasts, for example), whereas there is only a single version of the budget for an approval year.
The Investment Program supports both top-down and bottom-up planning and budgeting. The roll-up of budget adjustments from the lowest level to the top is automated, however, the top-down cascade of budget is normally manually processed.
Is a 529 College Savings Plan a Smart Investment?
You may want to see also

Appropriation Requests
The Appropriation Requests feature in SAP Investment Management serves as a link between Investment Programs (the source of the budget) and Investment Measures (which receive a budget allocation for procurement). Appropriation Requests are typically used to capture budget item requests for the following year and to call off the budget in the current year. They are segmented into types that distinguish the required approval roles and processes for the request, the relevant data fields to present, and the target investment measure type. For example, request types can be used to distinguish between complex capital investment projects that have a project as a control measure, and non-routine maintenance projects, which leverage maintenance orders and are not capitalised.
The reasons for an investment, such as sustenance, growth, risk, and compliance, are captured in Appropriation Requests. Where multiple investment reasons motivate a particular investment, these reasons can be proportionately assigned by percentage for reporting purposes. However, as subsequent transactions in SAP Investment Management can only accommodate a single investment reason assignment, it is considered best practice to simply assign the primary motivating rationale.
Scale and priority are two further assignments that help to classify requests. Scale is usually based on the overall investment value and is used to drive business case preparation requirements and approval stages. Priority indicates the relative urgency of the request, with risk and compliance initiatives often attracting a higher default priority.
Based on the request type, specific user roles can be assigned, including the applicant (requestor) and the responsible person (delivery manager). Additional roles can be manually assigned or derived. The SAP workflow can be configured to transition the approval routing and notifications to these roles.
A key feature of Appropriation Requests is the automatic creation of measures. One or multiple measures can be created from a single request, and planned costs are transferred automatically. Most initiatives may have alternative implementation alternatives, which are reflected in SAP as 'variants'. Each variant comprises an investment and overhead cost profile, as well as projected revenues or cost savings. A preliminary investment analysis can be performed on these planned costs and benefits to provide standardised metrics, including internal rate of return, net present value, and payback period.
Documents can be linked to an Appropriation Request variant using the document management system. As part of the annual budgeting and planning process, depreciation simulations can be executed for Appropriation Requests, based on the specified asset class of the approved variant and the planned capitalisation date.
The status of a request is important, especially from the perspective of the requester. When a request is submitted, the status changes to 'for approval'. Once reviewed and prioritised, it will be 'approved' overall. If multiple alternatives are proposed, one will achieve a status of 'approved'. Once included in the investment program, the request may receive a user status of 'budgeted'. The critical status is 'released' and 'replaced by measure', indicating that the request has performed its role and a project (or order) has been created for procurement activities to commence.
While Appropriation Requests are useful, there are some gaps in their functionality. The primary reason for organisations not deploying them is the end-user experience. The structure of Appropriation Requests is too complex, and while some flexibility is provided by user fields and data model extensions, the classification and qualitative justification requirements of real-world business cases and expenditure requests are not effectively supported.
Additionally, executive approval is challenging as very few organisations use all the data fields available, and many require the inclusion of additional classifications. This results in a cumbersome process that is impractical for executives to consume directly in SAP.
Building a Robust Investment Portfolio: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Budget Distributions and Returns
The essence of SAP Investment Management is the allocation of budget to Investment Measures. The budget in the Investment Program is typically approved annually and defines the total capital budget available per Investment Program Position and by future fiscal year. On the approval of Capital Expenditure Requests, the budget is distributed to recipient Investment Measures.
Any project budget not utilized by a project can be returned to the Investment Program and re-allocated to alternative projects or positions. This is done using transaction IM52 in SAP.
The budget in the Investment Program is created using the approved plan as a guide. The budget is an agreement with the organization about proposed spending levels. Changing circumstances can render this ceiling inappropriate, and at this stage, a return can be created to give back some of the original budget, or a supplement can be added to document the assignment of an additional budget.
The budget for a project can be entered using Transaction CJ30 or by selecting Project System > Financials > Budgeting > Original Budget > Change.
To ensure that the budget for the assigned items is not exceeded, use Transaction IM52 or follow the menu path Accounting > Investment Management > Programs > Budgeting > Budget Distribution > Edit.
The process of creating a new fiscal year and carrying forward the budget from the old year is complex, but SAP Note 444444 provides instructions on how to proceed and avoid any pitfalls.
Due Diligence: GRC and Investment Management Explained
You may want to see also

Budget Availability Check
Budget availability control is a feature of the budget process for internal orders. This feature allows the system to check if there is a budget available for the internal order before allowing the posting of costs.
The customisation of availability control involves the following steps:
- Maintain the budget profile: Define parameters such as currency translation, investment management, availability control, and budgeting currency. Determine the time frame for the budget, whether it will be in total or annual values, and the exchange rate type.
- Maintain number ranges for budgeting
- Define tolerance limits for availability control: Indicate if overspending should trigger a warning or error message, and define the usage percentage that will trigger the action.
- Specify exempt cost elements from availability control: Define cost elements to be ignored in the internal order availability control.
- Maintain the budget manager: Assign an SAP user to receive emails when specified tolerance levels are reached.
The SAP IM module helps in assigning and controlling budgets for capital expenditures. It enables the creation of an investment tree, which depicts how the budget will be distributed. It also ensures effective planning and controlling of costs, including budget authorisation.
The budgeting process for investment programs involves creating a budget in SAP CO after the investment program has been planned and approved. The budget is more than just a plan; it's an agreement with the organisation about proposed spending levels, and any budget changes will be documented. The budget can be created using Transaction IM32 or by following the menu path Accounting > Investment Management > Programs > Budgeting > Edit Original.
If you've already prepared plan data for the investment program, you can copy this data by selecting Edit > Copy View. Adjust the values to meet your requirements by selecting Edit > Revaluate. Once you're satisfied with the budget, you can ensure it can't be exceeded on associated elements using Transaction IM52 or by following the menu path Accounting > Investment Management > Programs > Budgeting > Budget Distribution > Edit.
Assessing Investment Managers: Strategies for Performance Evaluation
You may want to see also

Project Monitoring
Data Collection and Reporting
Maintaining accurate and timely data is essential for effective project monitoring. This includes collecting and analyzing information such as plan, budget, forecast, actual expenditure, and commitment data at a granular level. SAP provides robust data collection tools, including the ability to attach and classify supporting documents using the Document Management System. Additionally, SAP Analytics Cloud offers advanced charting, analysis, and predictive analytics capabilities, enabling more informed decision-making.
Investment Programs and Budgetary Control
SAP Investment Management allows users to create investment programs that serve as a basis for budget and investment planning. These programs consist of company-specific criteria, such as geographical factors, organizational setup, or the overall size of the plan. The project planner allocates budget values at different position levels within the investment program and distributes them to assigned investment measures. Investment measures can be projects, plant maintenance orders, or internal orders, providing detailed investment planning and operational execution measurement.
Appropriation Requests and Cost Planning
Appropriation requests are an integral part of project monitoring in SAP Investment Management. They allow users to plan and schedule future investments, conduct intelligent pre-investment analysis, and connect each request to a specific investment program. Cost planning in SAP Investment Management prevents duplication of efforts by allowing planners to plan costs directly at the investment program level or make changes as needed.
Work Breakdown Structures (WBS)
Effective use of WBS elements within the project definition is crucial for controlling project execution. WBS elements provide cost summarization and help monitor cost and schedule performance. It is important to strike a balance between having too few or too many WBS elements to ensure efficient control and avoid administrative burdens. SAP provides coding-mask functionality to help users interpret the level and purpose of various WBS elements.
Project Templates and Standardization
Project templates play a vital role in maintaining consistency in project setup, enhancing project execution, control, and analysis. While project managers may have the flexibility to modify templates, central administrators can ensure standardization by creating projects on their behalf. This centralized approach streamlines the process and reduces potential errors.
SAP Fiori Apps
Adopting SAP Fiori as the user interface technology offers significant benefits for project monitoring. Fiori apps provide user-friendly access to all participants, enabling project managers to easily initiate and update project structures, statuses, and plans. Senior executives can also directly approve budgets and outcomes within the system using any device. This enhances collaboration and streamlines the project monitoring process.
Reviving Nature: Planting vs. Preservation, Where Should We Invest?
You may want to see also







