Mutual funds are a popular investment option for individuals, offering an attractive combination of diversification, affordability, professional management, and liquidity. When determining the best mutual fund for very small investments, it is essential to consider your risk profile, investment goals, and time horizon.
For those with a high-risk appetite and long-term investment goals, small-cap mutual funds can be a good option. Small-cap funds invest in small companies with high growth potential but carry significant volatility due to their lack of financial strength. These funds are ideal for aggressive investors with a long-term investment horizon of at least seven years.
When choosing a small-cap mutual fund, it is crucial to examine the fund's history, expense ratio, fund manager's performance, and consistency of returns over different market cycles. Additionally, investors should ensure that the fund aligns with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
- Brandes Small Cap Value Fund
- Applied Finance Explorer Fund
- Hennessy Cornerstone Mid Cap 30 Fund
- Bridgeway Small Cap Value Fund
- FPA Queens Road Small Cap Value Fund
- DFA US Targeted Value Portfolio
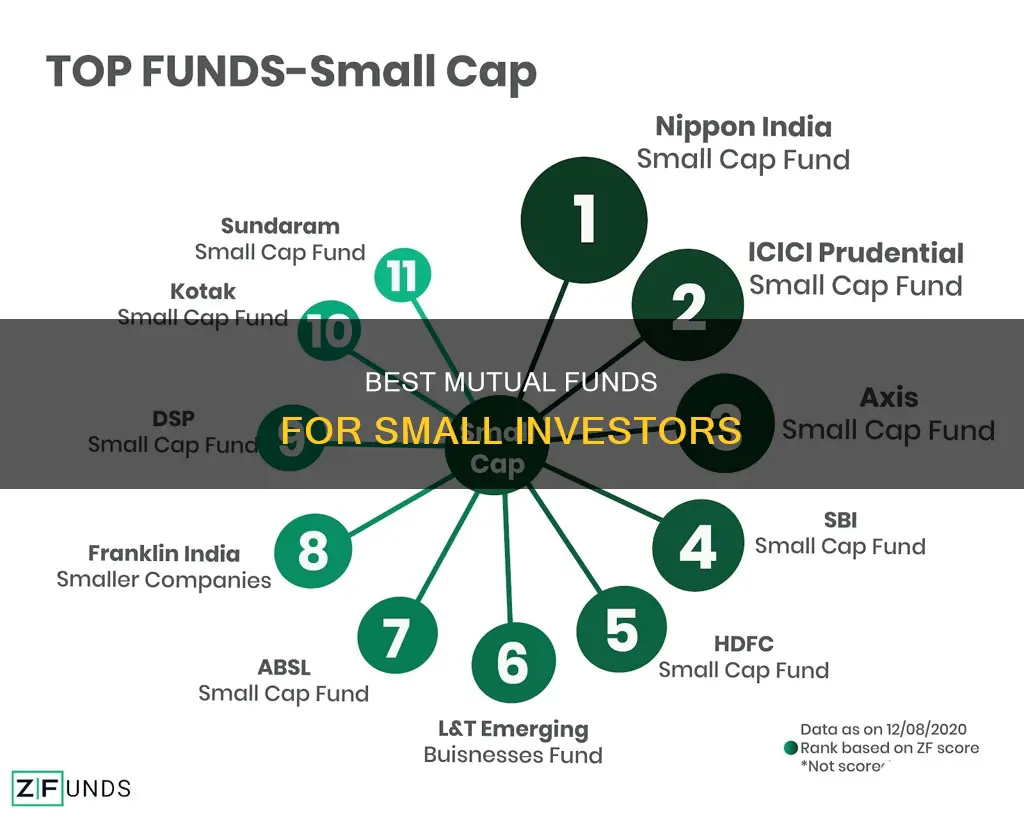
- Nippon India Small Cap Fund
- Invesco India Smallcap Fund
- Franklin India Smaller Companies Fund
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Best-performing U.S. equity mutual funds | FSELX, SCIOX, Fidelity Select Semiconductors, Fidelity Series Growth Company, Fidelity Select Technology, Fidelity Growth Company Fund, Columbia Seligman Tech & Info Adv, Fidelity Series Blue Chip Growth, Fidelity Blue Chip Growth |
| Best Small Value funds | Brandes Small Cap Value Fund, Applied Finance Explorer Fund, Hennessy Cornerstone Mid Cap 30 Fund, Bridgeway Small Cap Value Fund, FPA Queens Road Small Cap Value Fund, DFA US Targeted Value Portfolio, AMG River Road Small Cap Value Fund, Columbia Small Cap Value Fund I, Sterling Capital Behav Sm Cp Val Eq Fd |
| Best Mutual Funds of October 2024 | Fidelity International Index Fund (FSPSX), Fidelity U.S. Sustainability Index Fund (FITLX), Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX), Shelton Nasdaq-100 Index Fund Investor (NASDX), Schwab Fundamental US Large Company Index Fund (SFLNX), Fidelity Intermediate Municipal Income Fund (FLTMX), Dodge & Cox Income Fund (DODIX), Vanguard Long-Term Investment-Grade Fund Investor Shares (VWESX), Schwab Fundamental US Small Company Index (SFSNX), T. Rowe Price Mid-Cap Growth Fund (RPMGX) |
| Best Small Cap Mutual Funds in 2024 | Quant Small Cap Fund, Nippon India Small Cap Fund, Bank of India Small Cap Fund, Invesco India Smallcap Fund, Edelweiss Small Cap Fund, Franklin India Smaller Companies Fund, Canara Robeco Small Cap Fund, Kotak Small Cap Fund, Sundaram Small Cap Fund, ICICI Prudential Smallcap Fund, Union Small Cap Fund, Aditya Birla Sun Life Small Cap Fund, Bandhan Small Cap Fund, Baroda BNP Paribas Small Cap Fund, Mahindra Manulife Small Cap Fund, Motilal Oswal Small Cap Fund, PGIM India Small Cap Fund, Quantum Small Cap Fund |
What You'll Learn
- Small-cap funds: Invest in small companies with lower valuations and slower growth rates than peers
- Active vs passive funds: Actively managed funds are more expensive but aim to beat the market, while passive funds are cheaper and aim to mimic it
- Fees: Management fees, sales commissions, marketing fees, and other expenses can eat into returns
- Risk and return: Different types of mutual funds carry different levels of risk and potential returns
- Tax implications: Capital gains and dividends from mutual funds are taxed differently depending on the fund type and investment period

Small-cap funds: Invest in small companies with lower valuations and slower growth rates than peers
Small-cap funds are a type of mutual fund that focuses on investing in small-cap stocks, which are stocks of companies with a market capitalization between $250 million and $2 billion. These funds offer investors the opportunity to get in on the ground floor of up-and-coming young companies with significant growth potential.
Small-cap funds have historically outperformed large-cap funds, but they also come with higher volatility and more risk. The stocks in small-cap funds tend to be more sensitive to market changes and more vulnerable to economic downturns, which can lead to sudden and wide price fluctuations.
When considering small-cap funds, it's important to evaluate the following:
- Earnings and revenue growth: Look for companies that are growing and increasing their revenue, even if they are not yet profitable.
- Price-to-earnings ratio: This metric compares the current share price to the earnings per share, providing a measure of the value of the company's shares.
- Price-to-sales ratio: If the company doesn't have earnings per share, use the price-to-sales ratio to evaluate its performance relative to other small-cap stocks.
Small-cap funds can be a good choice for investors who are willing to take on more risk to enhance their portfolio returns. They offer the potential for significant growth and have traditionally traded at higher valuations than their large-cap counterparts. However, it's important to carefully evaluate the growth potential and financial health of small-cap companies before making investment decisions.
RRSP Investment Strategies: Where to Begin?
You may want to see also

Active vs passive funds: Actively managed funds are more expensive but aim to beat the market, while passive funds are cheaper and aim to mimic it
When it comes to investing, there are two main approaches: active and passive investing. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it's important to understand the differences before deciding which approach is right for you.
Active investing involves a more hands-on approach, where a portfolio manager actively selects investments based on their perceived worth, with the goal of "beating the market" and achieving better returns than certain standard benchmarks. This approach typically involves more frequent trading and can be more expensive due to research and portfolio management costs. Active investing offers the potential for higher returns but also comes with higher risks. It may be suitable for those who want to take advantage of short-term price fluctuations and are willing to pay higher fees for the expertise of a portfolio manager.
On the other hand, passive investing involves buying and holding investments over the long term, often in the form of mutual or exchange-traded funds. Passive investors aim to match the performance of market indexes rather than trying to outperform them. This approach is generally more cost-effective, as it involves less frequent buying and selling, and passive funds typically have lower fees than active funds. While passive investing may result in smaller returns, it can be a more stable and cost-efficient strategy. It is often recommended for those who want to invest for the long term and are comfortable with a buy-and-hold strategy.
When deciding between active and passive funds, it's important to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and fees. Active funds may be more suitable if you're comfortable with higher risks and fees and are seeking higher returns. On the other hand, passive funds may be a better option if you prefer a more hands-off approach, lower fees, and are willing to accept market-level returns. Ultimately, many investors choose to blend active and passive strategies to diversify their portfolio and manage risk.
Active Investing Advantages:
- Flexibility: Active managers can buy stocks that they believe have high potential, even if they deviate from a specific index.
- Hedging: Active managers can use strategies like short sales and put options to manage risks.
- Tax management: Active advisors can tailor tax strategies to individual investors, such as offsetting taxes on winning investments with losses from others.
Active Investing Disadvantages:
- Expensive: Actively managed funds have higher expense ratios due to research and trading costs, which can impact overall returns.
- Active risk: Active managers have the freedom to buy any investment that meets their criteria, which may lead to costly mistakes.
- Management risk: Fund managers are human and can make incorrect decisions, affecting the fund's performance.
Passive Investing Advantages:
- Ultra-low fees: Passive funds have lower fees since they don't require stock picking and simply follow a specific index.
- Transparency: It's clear which assets are held in a passive fund, providing investors with more information.
- Tax efficiency: The buy-and-hold strategy of passive funds typically results in lower capital gains taxes.
Passive Investing Disadvantages:
- Limited: Passive funds are tied to specific indexes or investments and may not allow investors to react to market changes.
- Small returns: Passive funds aim to match the market, so they may not provide significant returns during boom periods.
- Reliance on others: Passive investors rely on fund managers to make investment decisions, which may limit their control.
When choosing between active and passive funds, it's essential to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Additionally, keep in mind that the performance of funds can vary over time, and past performance does not guarantee future results. It's always a good idea to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best approach for your specific situation.
SBI Multicap Fund: A Comprehensive Guide to Investing
You may want to see also

Fees: Management fees, sales commissions, marketing fees, and other expenses can eat into returns
When investing in mutual funds, it is important to be aware of the various fees that may be charged by the fund manager. These fees can eat into your returns, so it is important to understand them before investing. Here are some common fees associated with mutual funds:
Management fees
Also known as "expense ratios," these fees cover the cost of paying fund managers and investment advisors. They are usually expressed as a percentage of the total assets of the fund and can vary depending on the fund. Actively managed funds tend to have higher expense ratios than passively managed funds.
Sales commissions
These are fees paid to brokers or salespeople who sell the fund to investors. They can be charged when you buy or sell shares of the fund and are usually referred to as "front-end" or "back-end" sales loads. It is best to look for “no-load” mutual funds to avoid paying these fees.
Marketing fees
Also known as 12b-1 fees, these fees cover the cost of marketing and selling the fund. They are capped at 1% of the fund's assets and are paid out of the fund's assets, reducing the returns for investors.
Other expenses
These can include a variety of costs such as custodial, legal, accounting, and administrative expenses. These fees are usually included in the fund's expense ratio but can also be charged separately.
It is important to carefully review the prospectus of a mutual fund before investing to understand all the fees and expenses associated with the fund. High fees can significantly reduce your returns over time, so it is crucial to consider them when choosing a mutual fund. Additionally, some brokers offer no-transaction-fee mutual funds, which can help reduce costs for investors.
Equity Index Funds: A Beginner's Guide to Investing
You may want to see also

Risk and return: Different types of mutual funds carry different levels of risk and potential returns
When considering the best mutual fund for very small investments, it's important to understand the different types of mutual funds and the varying levels of risk and potential returns they carry. Here are some key points to consider:
Stock Mutual Funds (Equity Mutual Funds)
Stock mutual funds offer the highest potential rewards but also come with higher risks. They invest directly in stocks, providing investors with the opportunity for significant gains. However, the performance of these funds can be volatile, and losses are possible. Different categories of stock mutual funds carry different levels of risk. For example, large-cap, high-growth funds tend to be more volatile than stock index funds that aim to match the returns of a benchmark index like the S&P 500. Stock mutual funds are suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance and a longer investment horizon.
Bond Mutual Funds (Fixed-Income Funds)
Bond mutual funds invest in a range of bonds, providing a more stable rate of return compared to stock funds. They are considered a safer investment option as governments and companies typically pay back their debt. While the potential average returns are lower than stock funds, bond funds can offer a more consistent income stream. Bond mutual funds are ideal for investors seeking a more conservative approach with lower risk and stable returns.
Money Market Mutual Funds
Money market mutual funds are considered one of the safest investment options, investing in high-quality, short-term debt instruments. They are designed for investors who want to protect their capital while still earning a modest interest rate, typically between 1% and 5% annually. Money market funds are a good choice for those seeking capital preservation with very low risk and stable returns.
Small-Cap Mutual Funds
Small-cap mutual funds focus on investing in small companies, typically those beyond the top 250 in market capitalisation. While these funds can deliver impressive returns, they also carry a high level of risk due to the volatile nature of small companies' stock performance. Small-cap funds are suitable for aggressive investors with a long-term investment horizon, usually seven years or more, who can tolerate the potential ups and downs.
Sector-Specific Funds
Some mutual funds focus on specific sectors or industries, such as infrastructure, technology, or healthcare. These funds can provide specialised exposure to a particular area of the market. However, they carry the risk of being heavily impacted by industry-specific events or market conditions. Sector-specific funds may be suitable for investors with a strong understanding of the particular sector and a higher risk tolerance.
Balanced Funds (Hybrid Funds)
Balanced funds, also known as hybrid funds, invest in a mix of stocks and bonds, providing a blend of growth potential and income generation. These funds offer a diversified approach, aiming to balance risk and return. They are often designed for investors with moderate risk tolerance, as they provide exposure to the stock market while also offering the stability of bond investments.
Fund Performance and Track Record
When evaluating mutual funds, it's important to consider their performance history and track record. Look for funds that have consistently outperformed their peers and benchmark indices over the long term, typically three to five years or more. This demonstrates the fund's ability to generate strong returns across different market cycles. Additionally, consider the fund manager's track record and their success in navigating different market conditions.
Expense Ratios and Fees
Expense ratios and fees play a crucial role in determining the net returns of your investment. Higher expense ratios mean a larger portion of your investment goes towards covering fund management fees rather than generating returns. Look for funds with lower expense ratios and fees to maximise your potential profits.
In summary, different types of mutual funds carry varying levels of risk and potential returns. When choosing a mutual fund, it's essential to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Diversification across different types of funds can help balance risk and return, and it's important to evaluate each fund's performance history, expense ratios, and the fund manager's track record.
Fidelity Funds: Exploring AMD Investment Opportunities
You may want to see also

Tax implications: Capital gains and dividends from mutual funds are taxed differently depending on the fund type and investment period
When it comes to mutual funds, there are a few things to keep in mind regarding tax implications, specifically in relation to capital gains and dividends. Firstly, it's important to understand the difference between ordinary income and capital gains. Ordinary income includes short-term capital gains, which are gains from assets held for less than a year, and is taxed at standard income tax rates. On the other hand, long-term capital gains, which are gains from assets held for more than a year, are generally taxed at lower rates.
Now, let's break down the tax implications of mutual funds:
Mutual Fund Distributions:
Mutual funds must distribute any dividends and capital gains earned on their holdings over the previous year. These distributions are considered taxable income, even if the money is reinvested in additional fund shares. The tax rate depends on factors such as the holding period and the type of distribution (ordinary income or capital gains).
Fund Types:
The taxation rules differ based on the type of mutual fund. For example, equity mutual funds, debt mutual funds, and hybrid mutual funds have different taxation rules. Equity funds, where more than 65% of the total fund is invested in equity shares, have different tax treatments for short-term and long-term capital gains. Short-term capital gains are taxed at a flat rate, while long-term capital gains up to a certain threshold are tax-exempt, and gains exceeding this limit are taxed at a lower rate. Debt funds, on the other hand, will be treated as short-term capital gains regardless of the holding period if purchased after a certain date.
Dividends:
Dividends are a portion of the profit distributed among investors by mutual fund companies. As per recent amendments, dividends received by investors are added to their taxable income and taxed at their respective income tax rates. Previously, dividends were tax-free as companies paid dividend distribution tax before distributing profits.
Capital Gains:
Capital gains refer to the profit realised when investors sell their capital assets at a higher price than their total investment amount. The tax treatment of capital gains depends on the holding period. Short-term capital gains, from assets held for less than a year, are typically taxed at ordinary income tax rates. Long-term capital gains, from assets held for more than a year, are usually taxed at lower capital gains tax rates.
Holding Period:
The time between the purchase and sale of mutual fund units impacts the tax rate payable on capital gains. In most cases, holding your investment for a longer period results in a lower tax liability.
Tax-Efficient Funds:
Investors concerned about tax exposure may consider investing in tax-efficient equity funds. These funds are managed with the goal of limiting capital gain distributions by keeping holdings turnover low and harvesting losses to offset realised gains.
Securities Transaction Tax (STT):
When buying or selling units of an equity fund or a hybrid equity-oriented fund, the government levies an STT of 0.001%. There is no STT on the sale of debt fund units.
In summary, the tax implications of mutual funds depend on various factors, including the fund type, the holding period, dividends, and capital gains. It's important to understand these factors and consult a tax professional to ensure proper reporting of investment income.
Unlocking Private Equity Fund Investment: A Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The best small-cap mutual funds to invest in as of October 2024 include:
- Quant Small Cap Fund
- Nippon India Small Cap Fund
- Bank of India Small Cap Fund
- Invesco India Smallcap Fund
- Edelweiss Small Cap Fund
- Franklin India Smaller Companies Fund
- Canara Robeco Small Cap Fund
- Kotak Small Cap Fund
- Sundaram Small Cap Fund
- ICICI Prudential Smallcap Fund
- Union Small Cap Fund
- Aditya Birla Sun Life Small Cap Fund
- Bandhan Small Cap Fund
The best mutual funds to invest in for 2024 include:
- ICICI Prudential Infrastructure Fund
- Nippon India Small Cap Fund
- Bandhan Infrastructure Fund
- DSP India T.I.G.E.R. Fund
- Nippon India Power & Infra Fund
- Franklin Build India Fund
- Invesco India PSU Equity Fund
- Canara Robeco Infrastructure Fund
- Invesco India Infrastructure Fund
- JM Aggressive Hybrid Fund
- Bank of India Mid & Small Cap Equity & Debt Fund
- ICICI Prudential Equity & Debt Fund
- HDFC Balanced Advantage Fund
- ICICI Prudential Multi Asset Fund
- Bank of India Credit Risk Fund
- ICICI Prudential Retirement Fund - Hybrid Aggressive Plan
- Edelweiss Aggressive Hybrid Fund
- Kotak Multi Asset Allocator FoF - Dynamic
- UTI Aggressive Hybrid Fund
- Kotak Equity Hybrid Fund
- Aditya Birla Sun Life Medium Term Fund
- Bank of India Short Term Income Fund
- Aditya Birla Sun Life Credit Risk Fund
- UTI Dynamic Bond Fund
- Baroda BNP Paribas Credit Risk Fund
- UTI Medium to Long Duration Fund
- ICICI Prudential Credit Risk Fund
- Invesco India Credit Risk Fund
As of September 2024, the best-performing mutual funds in terms of five-year returns include:
- FSELX
- SCIOX
- Fidelity Select Semiconductors
- Fidelity Series Growth Company
- Fidelity Select Technology
- Fidelity Growth Company Fund
- Columbia Seligman Tech & Info Adv
- Fidelity Series Blue Chip Growth
- Fidelity Blue Chip Growth
The best small-value mutual funds to invest in as of October 2024 include:
- Brandes Small Cap Value Fund
- Applied Finance Explorer Fund
- Hennessy Cornerstone Mid Cap 30 Fund
- Bridgeway Small Cap Value Fund
- FPA Queens Road Small Cap Value Fund
- DFA US Targeted Value Portfolio
- AMG River Road Small Cap Value Fund
- Columbia Small Cap Value Fund I
- Sterling Capital Behav Sm Cp Val Eq Fd