Risk is defined in financial terms as the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return. In other words, risk is any uncertainty with respect to your investments that has the potential to negatively impact your financial welfare. Risk includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment. The level of risk associated with a particular investment or asset class typically correlates with the level of return the investment might achieve.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | The chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return |
| Possibility | Losing some or all of an original investment |
| Assessment | Considering historical behaviours and outcomes |
| Metric | Standard deviation |
| Management | Understanding the basics of risk and how it is measured |
| Correlation | The level of risk associated with a particular investment or asset class typically correlates with the level of return the investment might achieve |
| Types | Market risk, business risk, political risk, currency risk, liquidity risk, inflation risk, exchange rate risk, unsystematic risk |
What You'll Learn

Market risk
Risk is defined in financial terms as the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return. It includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment. The level of risk associated with a particular investment or asset class typically correlates with the level of return the investment might achieve.
Investors can manage market risk by diversifying their investment portfolios. By spreading their investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their overall portfolio. Additionally, investors can employ hedging strategies, such as using derivatives or insurance, to protect themselves from potential losses due to market risk.
It is important to note that while market risk is a significant factor in investing, it is not the only type of risk. Other risks, such as business risk, political risk, and liquidity risk, can also impact investment outcomes. Therefore, investors should carefully consider all types of risks and their potential impact when making investment decisions.
Young Investors: Strategies for Smart Money Moves
You may want to see also

Business risk
Risk is defined in financial terms as the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from the expected outcome or return. Risk includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment.
Another example of business risk is a company's management capabilities. The competence and decision-making skills of a company's management team can significantly impact its financial performance. If a company's management makes poor decisions or fails to adapt to changing market conditions, it could negatively affect the company's financial health and, consequently, the value of its stock.
Financial risk is another type of risk that can impact businesses. This includes the possibility of a company defaulting on its debt obligations or facing liquidity issues. For example, a company with a high debt-to-equity ratio may struggle to make interest payments on its debt, which could lead to a default. Additionally, if a company has a large portion of its assets in illiquid investments, it may face challenges in raising cash quickly in the event of an economic downturn.
Overall, business risk is an important consideration for investors as it can significantly impact the value of their investments. By understanding the various factors that contribute to business risk, investors can make more informed decisions and potentially mitigate some of the risks through diversification and hedging strategies.
Global Share Portfolio: Invest in BizNews for Future Success
You may want to see also

Political risk
Risk is defined in financial terms as the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return. It includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment. The level of risk associated with a particular investment typically correlates with the level of return the investment might achieve.
Overall, political risk is an important factor for investors to consider when evaluating potential investments. By understanding the political landscape and potential risks associated with a particular country or industry, investors can make more informed decisions and better manage their exposure to political risk.
Private Equity Strategies: Recession-Proof Sectors to Invest In
You may want to see also

Liquidity risk
Risk is defined in financial terms as the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from the expected outcome or return. Liquidity risk is the uncertainty of how easy or hard it is to cash out of an investment when you need to. For example, if you need to sell an investment quickly, you may have to accept a lower price than you would have received if you had more time. This type of risk is particularly relevant for investments that are not easily traded, such as property or certain types of bonds. It is also a factor for investments that are highly volatile, as it may be difficult to sell at the desired price within a short time frame.
It is important to note that liquidity risk is not limited to the sale of investments. It also applies to the purchase of investments, as investors may need to quickly access funds to take advantage of attractive investment opportunities. In this context, liquidity risk refers to the potential loss of not being able to act on a time-sensitive investment prospect due to a lack of readily available funds.
Additionally, liquidity risk can impact the broader market and individual companies. During times of financial stress or economic downturns, investors may become more risk-averse and seek to increase their cash holdings, leading to a reduction in market liquidity. This can result in wider bid-ask spreads and increased transaction costs, making it more challenging for companies to raise capital or refinance their debts. As a consequence, companies with weaker financial positions may struggle to access the funding they need to continue their operations, potentially leading to financial distress or even bankruptcy.
A Beginner's Guide to Investing in the Indian Share Market
You may want to see also

Inflation risk
Risk is defined in financial terms as the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return. It includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment. The level of risk associated with a particular investment typically correlates with the level of return the investment might achieve.
There are several types of risk, including market risk, business risk, political risk, currency risk, and liquidity risk. One of the most significant risks that investors face is inflation risk. Inflation risk refers to the purchasing power of an individual or entity. As inflation rises, the cost of goods and services increases, which can eat away at an individual's ability to purchase them. This, in turn, can affect the value of investments. For example, if the inflation rate is higher than the return on an investment, the investor may effectively be losing money in real terms, even if the nominal value of the investment has increased.
Another way to protect against inflation risk is to invest in inflation-protected securities, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) in the United States. These securities are designed to protect against inflation by adjusting the principal amount and interest payments based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI). This ensures that the real value of the investment is maintained, even in a high-inflation environment.
Private Equity Restaurant Investment: Preparation Strategies for Success
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The total risk of an investment is the chance that an investment's actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return. This includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment.
There are several types of risk, including market risk, business risk, political risk, currency risk, and liquidity risk. Purchasing power (or inflation risk) and exchange rate risk are also factors when investing in non-domestic instruments.
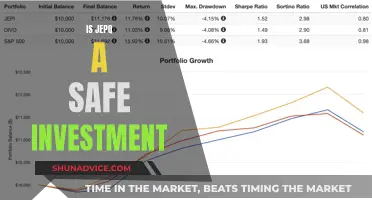
Risk is usually assessed by considering historical behaviours and outcomes. In finance, standard deviation is a common metric associated with risk, as it measures the volatility of asset prices in comparison to their historical averages in a given time frame.
The level of risk associated with an investment typically correlates with the level of return the investment might achieve. Investors who are willing to take on risky investments and potentially lose money should be rewarded for their risk, and so they expect higher returns to compensate for the risks they are taking.