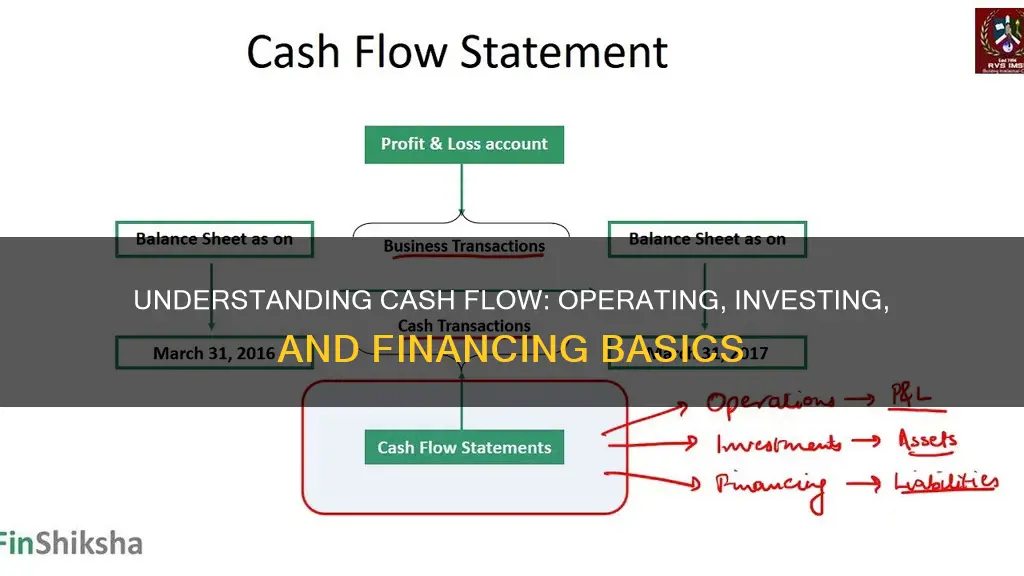
Cash flow is a critical financial metric that provides valuable insights into a company's financial health and operational efficiency. It can be categorised into three types: Operating cash flow, Investing cash flow, and Financing cash flow. These categories represent different sources and uses of cash within a business, and understanding them is essential for effective financial management and decision-making. Operating activities refer to the day-to-day business operations of a company, including sales, marketing, production costs, salaries, and taxes paid. Investing activities involve the purchase and sale of long-term assets, such as property, equipment, and investments in other companies. Financing activities, on the other hand, are the ways in which a company raises capital to fund its operations, including issuing stocks, bonds or taking on loans. Together, these three types of cash flow activities give a comprehensive view of a company's financial health, efficiency, and growth prospects.
What You'll Learn
- Operating activities include sales, inventory, operating expenses, salaries, and taxes
- Investing activities involve long-term assets, such as property, equipment, and securities
- Financing activities include raising capital through debt, stock, or loans, and repaying debt
- Cash flow statements help analyse a company's financial health, efficiency, and profitability
- Negative cash flow from investing activities can indicate long-term investments in the company's health

Operating activities include sales, inventory, operating expenses, salaries, and taxes
Operating activities are the functions of a business directly related to providing its goods and/or services to the market. These are the company's core business activities, such as manufacturing, distributing, marketing, and selling a product or service. Operating activities are a crucial element of the income statement and will generally provide the majority of a company's cash flow.
Inventory costs are a key operating expense. They include the direct costs of production, such as the purchase of raw materials. These costs are also referred to as the cost of goods sold (COGS).
Operating expenses are expenditures needed for running a firm's day-to-day operations. They include employee payroll, rent, marketing fees, accounting fees, supplies, utilities, and so on. They are the costs of running a business's day-to-day activities and are recorded on the company's income statement at the end of the fiscal year.
Some taxes are also considered operating expenses, such as property taxes, employee payroll taxes, and any other taxes related to operational activities.
Smart Ways to Invest $10K for Profits
You may want to see also

Investing activities involve long-term assets, such as property, equipment, and securities
Investing activities involve transactions related to long-term assets, such as property, equipment, and securities. These are important components of a company's cash flow statement as they provide insights into its investment strategies and utilisation of resources.
Long-term investments are assets that a company intends to hold for more than one accounting period, typically over a year. They are not used in daily operations but are meant to generate returns such as capital gains, dividends, or interest income. Examples include stocks, bonds, real estate, and mutual funds. On the other hand, property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) are tangible assets used in the production and distribution of goods and services. They include machinery, buildings, and vehicles. Both types of assets are subject to depreciation over time, except for land.
Investing activities include the purchase or acquisition of such long-term assets, as well as the sale or disposal of existing ones. These transactions are recorded in the investing section of the cash flow statement, providing information on the sources and uses of cash related to these activities. Positive cash flow in this section indicates cash inflow from the sale of assets, while negative cash flow indicates cash outflow for the purchase of assets.
Analysing the investing activities section of the cash flow statement helps stakeholders understand the company's investment strategies and capital allocation decisions. For example, an increase in capital expenditures may indicate that the company is investing in future operations or expanding its physical assets. Conversely, a decrease in the value of non-current assets from one period to another may signal the sale or disposal of assets to raise cash.
It is important to note that negative cash flow from investing activities is not always a negative indicator of a company's financial health. It often signifies that the company is investing in the long-term, such as in research and development, or acquiring physical assets to support its operations and future growth. As long as these investments are managed well, they can lead to significant gains and positive financial outcomes in the long run.
Target's Direct Investment Plans in India
You may want to see also

Financing activities include raising capital through debt, stock, or loans, and repaying debt
Financing activities are an essential component of a company's financial strategy, encompassing transactions related to raising capital and managing debt. These activities are crucial for a company's growth and stability, and they have a direct impact on its financial health and long-term sustainability.
Financing activities include a range of transactions that involve the movement of funds between a company and its investors, owners, or creditors. One key aspect is raising capital through various means, such as debt instruments, loans, or stock issuance. When a company requires additional funds for growth, expansion, or investment, it can turn to external sources for capital.
Debt financing is a common method where companies sell debt instruments, such as bonds, bills, or notes, to investors. In return, the company receives the needed capital, and the investors become creditors, expecting the principal amount and interest to be repaid in the future. This type of financing is often favoured by small and new companies as it facilitates their growth plans. Additionally, the interest paid on debt financing is usually tax-deductible, making it a more cost-effective option compared to equity financing.
On the other hand, equity financing involves issuing stock to investors in exchange for capital. Unlike debt financing, equity financing entails giving up a portion of ownership and decision-making power to the investors. While this option may be more expensive in the long run due to ongoing dividends and profit-sharing, it does not carry the same repayment obligations as debt.
Another aspect of financing activities is the repayment of debt. Companies that have borrowed funds through loans, credit facilities, or other debt instruments need to make regular interest payments and principal repayments. These outflows are reflected in the company's cash flow statement and are crucial for maintaining the confidence of investors and creditors.
The financing section of the cash flow statement provides valuable insights into a company's financial management and long-term planning. It shows how a company raises capital, repays its debts, and manages its relationships with investors and creditors. A positive cash flow in this section indicates that the company is attracting more capital, while a negative cash flow may suggest a focus on debt reduction or rewarding investors.
Overall, financing activities are a critical aspect of a company's financial strategy, impacting its ability to raise capital, manage debt, and achieve its economic goals. By understanding these activities, stakeholders can assess a company's financial health, stability, and potential for growth.
Smart Investment Strategies: Making the Right Choices
You may want to see also

Cash flow statements help analyse a company's financial health, efficiency, and profitability
Cash flow statements are essential for analysing a company's financial health, efficiency, and profitability. They provide a detailed picture of the company's cash flow over a specific period, typically quarterly or annually. This statement is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
The operating activities section details the cash flow generated from the company's regular goods or services, including revenue and expenses. It shows how much cash the company's core operations are bringing in and is crucial for determining if the company can fund its activities without external money. A positive cash flow indicates the business is doing well, while a negative cash flow may signal that the company is spending more than it is making.
The investing activities section reflects the company's investments in long-term assets, such as property, equipment, or other businesses. This section indicates whether the company is investing in future growth or selling off assets to raise cash. A negative cash flow in this section is not necessarily negative, as it could mean the company is investing in its future growth.
The financing activities section details the cash flow from debt and equity financing. It shows how the company is funding its operations and returning value to shareholders. This section also reveals how the company is raising capital and includes any dividend payments, stock repurchases, or debt repayments.
Together, these three sections provide valuable insights into the company's financial health and efficiency. They show where the money is coming from, how it is being spent, and the final cash balance. This information is crucial for investors, creditors, and business owners, helping them make informed decisions about the company's financial health, sustainability, and growth prospects.
Financial Planner Investment Manager: Key Questions to Ask
You may want to see also

Negative cash flow from investing activities can indicate long-term investments in the company's health
Negative cash flow from investing activities can be a good indicator of a company's long-term strategy and future prospects. While negative cash flow is often seen as a sign of poor performance, this is not always the case when it comes to investing activities. This is because negative cash flow in this area can indicate that a company is making significant investments in its future growth and health.
Investing activities are a critical component of a company's cash flow statement, reflecting capital movements and long-term strategies. When a company has a negative cash flow from investing activities, it means that it has invested more cash than it has generated from its investments during a specific period. This could include purchases of physical assets, investments in securities, or research and development. For example, a company may invest in fixed assets such as property, plant, and equipment, or make long-term investments in new technologies or acquisitions. These investments can be essential for the company's future operations and competitiveness in the market.
A negative cash flow from investing activities can signal to investors and analysts that the company is making strategic decisions for its long-term growth. It indicates that the company is allocating resources towards initiatives that may lead to significant gains and expansion in the future. This is particularly true for growing companies that are investing in long-term fixed assets or well-established companies making occasional investments in property and equipment.
However, it is important to analyse the entire cash flow statement to understand the context of the negative cash flow. Investors should assess the company's specific situation and review its financial health by comparing the cash flow statement with the balance sheet and income statement. This comprehensive analysis will help determine if the negative cash flow is a strategic investment or a warning sign of poor financial management.
In summary, negative cash flow from investing activities can be a positive indicator of a company's long-term health and growth prospects. It showcases a company's commitment to investing in its future, which may lead to greater strength and profitability in the future. Therefore, stakeholders, investors, and financial professionals should regularly analyse these cash flow patterns to gain insights into the company's investment strategies and overall financial standing.
Easy Equities: A Simple Guide to Getting Started
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Operating cash flow is the money a company makes from its daily operations, such as sales and operating expenses. It shows if a company can fund its activities without needing outside money and is key to knowing if a company is financially stable.
Investing cash flow refers to the cash transactions related to the purchase or sale of long-term assets, such as property, equipment, or investments in securities.
Financing cash flow refers to transactions related to raising and repaying capital, such as the issuance of equity, dividend payments, receiving loans, and repayment of loans.







