Diversification is a common investing strategy that involves spreading your investments across different assets and asset categories to reduce the risk of loss. By diversifying your portfolio, you can limit your exposure to any one type of asset and reduce the volatility of your portfolio over time. This strategy is particularly important for those saving for retirement or with other financial goals, as it helps to protect against losses and ensures that your capital is preserved. While diversification does not guarantee against loss, it can help to improve your potential returns and stabilise your results.
What You'll Learn

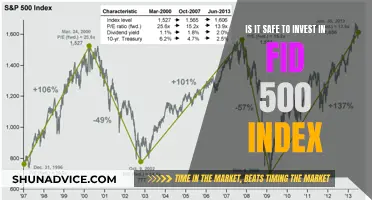
Diversification reduces the pain of losses
Diversification is a common strategy when building an investment portfolio. It involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce the overall risk of an investment portfolio. While diversification does not guarantee against loss, it is an important component of reaching long-range financial goals while minimising risk.
For example, stocks tend to be negatively correlated with bonds. So, in the event of a stock market correction, bonds can provide balance to a portfolio and potentially offset any losses. This concept is known as negative correlation, where pairing assets with negative correlations can lower the overall risk of a portfolio.
Additionally, diversification can help investors avoid the "`chasing returns' mentality, where they overweight their portfolio towards a top-performing asset class. This can be risky because, as Mike Cornacchioli, Senior Strategy Analyst at Citizens Private Wealth Management, notes, "last year's winners are often next year's losers". By diversifying, investors can better withstand dips in performance and stay on course to reach their financial goals.
In summary, diversification is a powerful tool for investors to reduce the pain of losses by lowering portfolio risk and providing more consistent returns. It allows investors to benefit from the performance of multiple assets while reducing the impact of losses, helping them stay on track with their financial goals.
Saving or Investing: Where Should Your Money Go?
You may want to see also

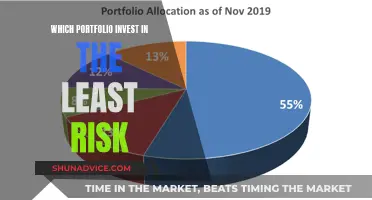
Diversification across asset classes
Diversification is a common investing strategy that can help to reduce the risk of large losses. By spreading investments across different assets, the chances of a portfolio being wiped out by a single negative event are lowered.
A well-diversified portfolio combines different types of investments, known as asset classes, which carry different levels of risk. The three main asset classes are stocks, bonds, and cash alternatives. Stocks generally carry the most risk but also offer the greatest potential for growth. Bonds are less volatile and offer more modest returns, while cash alternatives are considered to carry the least risk but also have the lowest returns.
Some investors also add other investments to their portfolios, such as real estate and commodities like gold and coal. Each asset class tends to perform differently under similar market conditions, so splitting assets among categories helps to balance a portfolio.
For example, stocks are generally considered the most aggressive portion of a portfolio and provide the opportunity for higher growth over the long term. However, this greater potential for growth carries a greater risk, particularly in the short term. Stocks are generally more volatile than other types of assets, so an investment in a stock could be worth less if and when you decide to sell it.
Most bonds provide regular interest income and act as a cushion against the unpredictable ups and downs of the stock market. They often behave differently than stocks and can offer steadier returns with a fixed payout. Investors who are more focused on safety than growth often favour US Treasury or other high-quality bonds while reducing their exposure to stocks.
Cash alternatives may be sensitive to interest rate movements, and a rise in interest rates could result in a decline in the value of these investments. However, they are generally considered to carry the least risk and provide stable returns based on the interest rate or other contractual terms.
By diversifying across asset classes, investors can protect against widespread financial risk. For instance, if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, equity markets may still perform well, but rising rates push down bond prices.
It's important to note that diversification does not guarantee investment returns or eliminate the risk of loss, and it may result in lower portfolio-wide returns. However, it can help to improve potential returns and stabilize results by reducing the overall risk of a portfolio.
Savings Strategies: Maximizing Output from Your Investments
You may want to see also

Diversification across companies
Diversification is a common investing strategy used to reduce the risk of large losses. By spreading investments across different companies, investors are less likely to lose their entire portfolio due to a single negative event impacting a specific holding.
Additionally, diversifying across companies can be done by investing in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These funds typically hold shares in numerous companies, providing exposure to a diverse range of businesses. This option is suitable for investors who may not have the time or inclination to research and select individual stocks.
It's important to note that diversification does not guarantee against losses and may result in lower portfolio-wide returns. However, by diversifying across companies, investors can reduce the impact of company-specific risks and improve the stability of their investment portfolio.
Invest Your Savings: Safe Strategies for Beginners
You may want to see also

Diversification across borders
Diversification is a common investment strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce the overall risk of an investment portfolio. This strategy is particularly important when considering investments across borders.
Political, geopolitical, and international risks can have worldwide impacts, especially regarding the policies of larger nations. For example, legislative changes to corporate tax rates in the US could negatively impact all entities within the country. By diversifying your portfolio to include companies and holdings across different physical locations, you can reduce your exposure to these country-specific risks.
Different countries operating with different monetary policies will also provide different opportunities and risk levels. For instance, a country with a strong economy and stable interest rates may offer more favourable conditions for investors than a country experiencing economic instability and high inflation.
Additionally, diversifying across borders can help you access different sectors and industries that may not be available in your home country. For example, investing in emerging markets or international companies can provide exposure to new opportunities and potentially higher returns.
However, it is important to note that diversifying across borders also comes with its own set of challenges. Varying regulatory environments, currency fluctuations, and political risks can introduce additional complexities and risks to your investment strategy.
Overall, diversifying across borders is a crucial aspect of building a robust and well-rounded investment portfolio. By spreading your investments across different countries and regions, you can reduce country-specific risks, access new opportunities, and potentially improve your overall investment returns.
Understanding the Domestic Saving-Investment Imbalance
You may want to see also

Diversification across time frames
Diversification is a crucial aspect of saving and investing, and this principle also applies when considering different time frames for your investments. Here are four to six paragraphs elaborating on this concept:
When diversifying your investments, it is essential to consider different time horizons. The time frame of an investment refers to the period over which it is expected to generate returns. Some investments are designed for the short term, while others are meant for the long term. For example, a long-term bond typically offers a higher rate of return due to its higher inherent risk, whereas a short-term investment is more liquid and yields lower returns. Diversification across time frames involves allocating your investments across a range of maturities to balance risk and return potential.
By diversifying across time frames, you can smooth out the volatility associated with different investment horizons. For instance, short-term investments may be more susceptible to market fluctuations, while long-term investments can help mitigate the impact of short-term volatility. Diversifying in this manner can provide a more stable overall return and reduce the impact of any single investment's performance on your portfolio's value.
Additionally, diversifying across time frames can help you manage your risk exposure. Investments with longer time frames often carry more risk but may offer higher returns to compensate. By diversifying across various time horizons, you can balance your portfolio's risk and return profile. This approach ensures that you are not overly exposed to the risks associated with any single time frame.
The specific time frames you choose to diversify across will depend on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. If you are investing for retirement, your time horizon may be several decades, allowing you to include longer-term investments in your portfolio. On the other hand, if you are saving for a shorter-term goal, such as a down payment on a house, you may focus on shorter-term investments.
It is important to note that diversification across time frames does not eliminate all risk. Market-wide events or economic downturns can still impact your portfolio, regardless of the time frames of your investments. However, by diversifying, you can reduce the impact of any single event and improve the overall stability of your investment portfolio.
In conclusion, diversification across time frames is a crucial aspect of saving and investing. By allocating your investments across different time horizons, you can balance risk and return potential, smooth out volatility, and work towards achieving your financial goals while managing risk effectively.
Savings vs Investments: Macroeconomics' Distinct Financial Strategies
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Diversification is important because it helps to reduce the risk of losing money and not meeting future financial goals. By spreading investments across different assets, the chances of losing money due to one negative event are reduced.
Diversification is the process of spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. The idea is that by holding a variety of investments, the poor performance of one investment can be offset by the better performance of another.
Diversification can improve potential returns and stabilize results. By owning multiple assets that perform differently, the overall risk of the portfolio is reduced.
Diversification reduces asset-specific risk, which is the risk of owning too much of one stock or one type of asset. However, it does not eliminate market risk, which is the risk of owning any assets at all.
A basic diversified portfolio could include a broadly diversified index fund, bonds, guaranteed returns in the form of CDs, and cash in a savings account.
Diversification may be cumbersome to manage, especially with multiple holdings and investments. It can also be expensive, with transaction fees and brokerage charges adding up. Additionally, diversification may lower overall returns as it optimises for risk-adjusted returns rather than absolute returns.