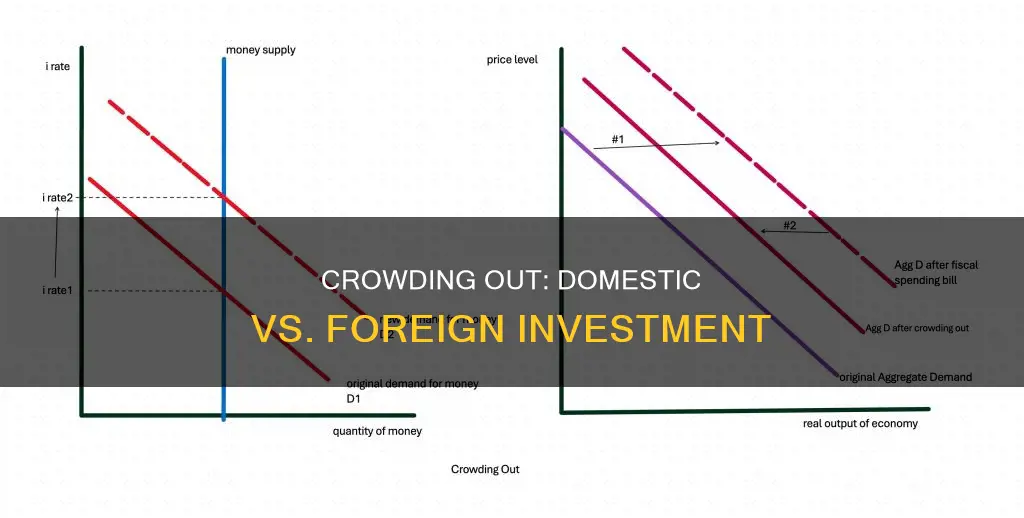
The relationship between crowding out and investment, both domestic and foreign, is a complex and crucial topic in economics. Crowding out occurs when government spending or investment displaces private investment, potentially leading to reduced private sector investment. This phenomenon can have significant implications for both domestic and foreign investors, as it may affect the overall investment climate and economic growth. Understanding the factors that influence crowding out and its impact on investment is essential for policymakers and investors alike, as it can shape economic strategies and decisions. This paragraph aims to explore the question of whether crowding out negatively affects domestic and foreign investment, delving into the potential mechanisms and consequences of this economic concept.
What You'll Learn
- Impact on Domestic Investment: Crowding out can reduce domestic investment by competing for limited resources
- Foreign Investment Flows: Crowding out may deter foreign investors due to economic uncertainty
- Government Spending: Increased government spending can lead to higher taxes, affecting domestic and foreign investment
- Interest Rates: Crowding out can cause interest rates to rise, making borrowing more expensive
- Economic Growth: The effects of crowding out on investment can hinder long-term economic growth

Impact on Domestic Investment: Crowding out can reduce domestic investment by competing for limited resources
The concept of "crowding out" has significant implications for domestic investment, particularly when it comes to the competition for limited resources. When a government increases its borrowing to finance public spending, it often leads to an increase in interest rates, which can have a detrimental effect on private investment. This phenomenon is often referred to as "crowding out."
In an economy, resources are finite, and when the government's demand for these resources increases, it can lead to a reduction in the availability of funds for private investors. For instance, if the government takes out loans to fund infrastructure projects, it may drive up interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses to borrow money for their own expansion or research and development. As a result, domestic investment in private sectors might decrease, as higher interest rates reduce the profitability of investment projects.
This reduction in domestic investment can have a ripple effect on the overall economy. Lower investment can lead to decreased productivity, slower economic growth, and potentially higher unemployment rates. It may also discourage domestic entrepreneurs and businesses from taking risks, further stifling innovation and long-term economic development.
Moreover, the impact of crowding out on domestic investment can be particularly severe during economic downturns or recessions. When the economy is already struggling, the government's increased borrowing can exacerbate the situation, making it even more challenging for private investors to secure financing. This can create a vicious cycle, where reduced investment further weakens the economy, leading to even more borrowing by the government to stimulate economic activity.
In summary, the process of crowding out can significantly impact domestic investment by competing for limited resources, especially in times of economic stress. Understanding this relationship is crucial for policymakers to design effective fiscal and monetary policies that balance public spending with the need to encourage private investment for long-term economic growth.
Understanding Net Cash Flow from Investing Activities
You may want to see also

Foreign Investment Flows: Crowding out may deter foreign investors due to economic uncertainty
The concept of "crowding out" in the context of foreign investment flows can significantly impact the attractiveness of a country as an investment destination. When a government's fiscal policies, such as increased government spending or higher budget deficits, lead to higher interest rates, it can result in "crowding out" domestic and foreign private investment. This phenomenon occurs because higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing the incentive for businesses and individuals to invest. As a result, the overall investment in the economy decreases, which can have detrimental effects on economic growth and development.
In the case of foreign investment, crowding out can be particularly concerning. Foreign investors often seek stable and predictable economic environments with favorable investment conditions. When a country's fiscal policies lead to economic uncertainty, it may deter these investors. For instance, if a country's government increases spending significantly, it might result in higher inflation, currency fluctuations, and an uncertain business environment. These factors can make foreign investors hesitant to commit their capital, as they may fear reduced returns or even potential losses.
The impact of crowding out on foreign investment flows can be far-reaching. Foreign investment is crucial for many developing and emerging economies as it brings capital, technology, and expertise, fostering economic growth and development. A decrease in foreign investment due to economic uncertainty can hinder these countries' progress, limiting their ability to attract much-needed capital for infrastructure, research, and development projects. Moreover, it can lead to a vicious cycle where reduced investment further stifles economic activity and job creation.
To mitigate the potential negative effects of crowding out, governments can adopt various strategies. One approach is to ensure that fiscal policies are well-communicated and transparent, providing investors with a clear understanding of the economic environment. Additionally, governments can focus on creating a stable and predictable regulatory framework, offering incentives for foreign investors, and promoting economic reforms to enhance the overall investment climate. By implementing such measures, countries can attract foreign investment despite potential crowding-out effects and maintain a healthy balance between government spending and private investment.
In summary, the concept of crowding out in the context of foreign investment flows highlights the delicate balance between government fiscal policies and the investment climate. Economic uncertainty caused by crowding out can deter foreign investors, impacting a country's economic growth and development. Recognizing the importance of foreign investment, governments should strive to create an environment that encourages investment while managing fiscal policies to avoid adverse effects on the overall investment landscape.
Understanding Foreign Portfolio Investment: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Government Spending: Increased government spending can lead to higher taxes, affecting domestic and foreign investment
Increased government spending is a double-edged sword that can have significant implications for both domestic and foreign investment. When a government decides to boost its spending, it often does so through various means, including increased taxation, borrowing, or a combination of both. While these actions are intended to stimulate economic growth and address specific societal needs, they can inadvertently create a challenging environment for investors.
One of the most direct consequences of increased government spending is the potential rise in taxes. Governments may impose higher tax rates on individuals and businesses to fund their expanded operations. This can lead to a decrease in disposable income for households and potentially discourage investment from domestic sources. Higher taxes might also prompt businesses to reconsider their investment strategies, as they may need to allocate more funds towards tax payments, leaving less for expansion, research, and development.
For foreign investors, the impact of increased government spending and taxation can be particularly concerning. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is often attracted by stable political environments, favorable tax policies, and a robust legal framework. When a government introduces higher tax rates, it may create an unfavorable investment climate, especially for international companies that are sensitive to changes in tax policies. This could result in a reduction in FDI, as investors seek more tax-friendly destinations for their capital.
Moreover, the effects of increased government spending can extend beyond immediate tax implications. High government spending might lead to concerns about inflation and economic stability. If the government's increased borrowing leads to a surge in the money supply, it could cause inflationary pressures, eroding the purchasing power of investors and consumers alike. This, in turn, may discourage both domestic and foreign investment, as investors seek assets that can maintain their value in the face of rising inflation.
In summary, while increased government spending can be a necessary tool for economic development and addressing societal needs, it must be carefully managed to avoid negative consequences for investment. Striking a balance between funding public services and maintaining a favorable investment climate is crucial. Governments should consider alternative methods of financing, such as efficient resource allocation, privatization, or attracting foreign investment through targeted incentives, to ensure that their spending initiatives do not inadvertently harm the very investors they aim to support.
Understanding Investment Cash Flows Over Time
You may want to see also

Interest Rates: Crowding out can cause interest rates to rise, making borrowing more expensive
The concept of "crowding out" has significant implications for interest rates, which can have a ripple effect on both domestic and foreign investment. When a government increases its borrowing to finance public spending, it often leads to an increase in the demand for loanable funds, which are typically provided by the private sector. This surge in demand can result in higher interest rates, making borrowing more expensive for businesses and individuals.
In the context of domestic investment, rising interest rates can discourage private sector spending. Businesses might find it more challenging to secure loans for expansion, research, or day-to-day operations at higher interest rates. This could potentially lead to a reduction in investment, as companies may opt to save or invest in less profitable ventures to meet the increased cost of capital. Consequently, the overall economic growth may be hindered, as the private sector's contribution to the economy could be diminished.
For foreign investment, the impact of higher interest rates can be particularly detrimental. Foreign investors often seek attractive investment opportunities with competitive returns. When interest rates rise, the appeal of domestic investments may decrease, as potential returns become less favorable compared to other markets. This could result in a reduction in foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investment, as investors may look elsewhere for more lucrative prospects.
Moreover, the effect of crowding out on interest rates can have a self-reinforcing nature. As the government's borrowing needs increase, it may need to offer higher interest rates to attract lenders. This, in turn, can further raise the cost of borrowing for the private sector, potentially leading to a cycle of increasing interest rates and reduced investment. Such a scenario could have long-term consequences for economic growth and development.
In summary, the phenomenon of crowding out can significantly impact interest rates, making borrowing more expensive. This, in turn, affects domestic and foreign investment decisions. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the potential risks and challenges associated with government borrowing and its influence on the broader economic landscape.
E*Trade Cash Balance Program: Investing Strategies for Beginners
You may want to see also

Economic Growth: The effects of crowding out on investment can hinder long-term economic growth
The concept of "crowding out" is a significant concern in economics, particularly when it comes to the impact on investment, both domestic and foreign. When a government increases its spending, it can lead to a reduction in private investment, a phenomenon often referred to as "crowding out." This effect can have long-lasting consequences on a country's economic growth and development.
In the context of economic growth, the crowding-out effect can be detrimental for several reasons. Firstly, it can lead to a decrease in the overall investment rate. When the government takes on more debt to finance its spending, it may compete with private investors for funds. As a result, private businesses might find it more challenging to secure the capital they need for expansion, research, and development. This reduced access to credit and investment opportunities can stifle private sector growth, which is essential for long-term economic prosperity.
Secondly, crowding out can have a negative impact on the quality of investment. When government spending is prioritized, it may crowd out more efficient and productive private investments. For instance, if a government decides to invest heavily in infrastructure, it might divert resources away from private sector projects that could have a higher rate of return. Over time, this can lead to a misallocation of resources, where the economy fails to benefit from the most productive uses of capital, hindering overall economic growth.
Moreover, the effects of crowding out can extend beyond the domestic investment landscape and impact foreign investment as well. A country's creditworthiness and economic stability are crucial factors in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI). If a government's increased spending leads to higher debt levels and potential economic instability, it may deter foreign investors. This, in turn, can result in a decrease in FDI, which is often a significant contributor to a country's economic growth and development. Foreign investors might seek more stable and attractive investment environments, leading to a brain drain of capital and a loss of potential economic benefits.
In summary, the concept of crowding out has a direct and significant impact on economic growth. By reducing the overall investment rate, potentially lowering the quality of investment, and deterring foreign investors, the effects of crowding out can hinder a country's long-term economic development. Understanding and managing these effects are crucial for policymakers to ensure sustainable economic growth and maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding Proceeds From Equipment Sales: Cash From Investing?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, crowding out can have negative effects on domestic investment. When a government increases its borrowing to finance public spending, it can lead to higher interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow for investment purposes. This may result in reduced private investment, as higher interest rates can discourage borrowing and spending.
Crowding out can potentially deter foreign investment. If a country's government takes on excessive debt, it may signal to investors that the country's fiscal health is at risk. This could lead to a decrease in foreign direct investment (FDI) as investors become more cautious and seek safer investment opportunities elsewhere. Additionally, higher interest rates due to crowding out might make the country less attractive for foreign investors seeking favorable borrowing conditions.
While crowding out is generally associated with negative consequences, there can be some potential benefits. In certain cases, increased government spending can stimulate the economy and create a more favorable business environment. This can attract foreign investment as improved infrastructure, research, and development initiatives may enhance the country's competitiveness. Moreover, if the government's borrowing is used to fund productive projects, it could indirectly support private investment by improving the overall economic conditions and market confidence.