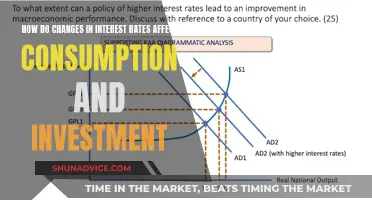
Interest rates are one of the most important factors that determine investment levels. Typically, higher interest rates reduce investment, because higher rates increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable. However, interest rates are not the only factor that influences investment levels. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and the state of technology.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Interest rates influence investment | Typically, higher interest rates reduce investment because they increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable |
| Interest rates are not the only factor | Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and state of technology |
| Interest rates and investment in a liquidity trap | Lower interest rates may have little effect on boosting levels of investment |
| Interest rates and investment projects | If interest rates are 5%, then any investment project would need an expected rate of return of at least greater than 5% |
| Interest rates and investment decisions | Changes in business confidence can have a considerable influence on investment decisions |
What You'll Learn

The impact of higher interest rates on investment
Interest rates are one important determinant of investment. Typically, higher interest rates reduce investment, because higher rates increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable. For example, if interest rates are 7%, then any investment project would need an expected rate of return of at least greater than 7%, and therefore less investment would occur.
Private investment is an increase in the capital stock such as buying a factory or machine. The marginal efficiency of capital (MEC) states the rate of return on an investment project. Specifically, it refers to the annual percentage yield (output) earned by the last additional unit of capital.
In a liquidity trap, lower interest rates may have little effect on boosting levels of investment. Therefore, demand for investment becomes very interest inelastic. This happened during the great recession of 2009 when interest rates were cut to 0.5%, but the economy remained stagnant with little increase in investment.
However, interest rates are not the only factor that determines investment. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and the state of technology.
Mortgage Interest Rates: Higher for Investments?
You may want to see also

The marginal efficiency of capital (MEC)
Interest rates are one important determinant of investment. However, it is not the only factor. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and the state of technology.
Private investment is an increase in the capital stock such as buying a factory or machine. In this context, investment does not relate to saving money in a bank. Investment is inversely related to interest rates for two main reasons. Firstly, if interest rates rise, the opportunity cost of investment rises. Secondly, higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable.
In a liquidity trap, lower interest rates may have little effect on boosting levels of investment. Therefore, demand for investment becomes very interest inelastic. This happened during the great recession of 2009 when interest rates were cut to 0.5%, but the economy remained stagnant with little increase in investment.
Investing in a Low-Interest-Rate Environment: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Liquidity traps
Interest rates are one important determinant of investment. Typically, higher interest rates reduce investment, because higher rates increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable. For example, if interest rates are 7%, then any investment project would need an expected rate of return of at least greater than 7%, and therefore less investment would occur.
However, it is not the only factor. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and the state of technology. For instance, in a liquidity trap, lower interest rates may have little effect on boosting levels of investment. This happened during the great recession of 2009 when interest rates were cut to 0.5%, but the economy remained stagnant with little increase in investment. This was because the credit crunch meant that banks were unable or unwilling to lend.
The accelerator theory states that investment is influenced by rates of change in economic growth. For example, changes in national income create an accelerator effect. Economic theory suggests that, at the macro-economic level, small changes in national income can trigger much larger changes in investment levels.
Investment is inversely related to interest rates, which are the cost of borrowing and the reward to lending. If interest rates rise, the opportunity cost of investment rises. For firms, they will consider the real interest rate – which equals the nominal interest rate minus inflation. If inflation is 10% and nominal interest rates are 9% – we have negative real interest rates. Borrowing money is more desirable as inflation will make it easier to pay it back.
Interest Rates: Investment Incentives or Deterrents?
You may want to see also

The accelerator theory
Interest rates are one important determinant of investment. Typically, higher interest rates reduce investment, because higher rates increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable. For example, if interest rates are 7%, then any investment project would need an expected rate of return of at least greater than 7%, and therefore less investment would occur.
However, interest rates are not the only factor that influences investment. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, and the state of technology.
In a liquidity trap, lower interest rates may have little effect on boosting levels of investment. Therefore, demand for investment becomes very interest inelastic. This happened during the great recession of 2009 when interest rates were cut to 0.5%, but the economy remained stagnant with little increase in investment.
Understanding Investment Interest: How to Make Your Money Work
You may want to see also

Investor confidence
Interest rates are one important determinant of investment. However, it is not the only factor. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and the state of technology.
Economic growth is also a factor in investor confidence. The accelerator theory states that investment is influenced by rates of change in economic growth. If the economy is growing, investors are more likely to be confident and invest.
The marginal efficiency of capital (MEC) states the rate of return on an investment project. Specifically, it refers to the annual percentage yield (output) earned by the last additional unit of capital. If interest rates are high, the MEC needs to be higher for an investment to be profitable. For example, if interest rates are 7%, an investment project would need an expected rate of return of greater than 7% to be worthwhile. Therefore, higher interest rates typically reduce investment.
In conclusion, investor confidence is a key factor in investment. It is influenced by interest rates, economic growth, and other factors. If investors are confident, they are more likely to invest.
Strategies for Investing in Compound Interest Opportunities
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, investment is inversely related to interest rates. Higher interest rates reduce investment because they increase the cost of borrowing and require investment to have a higher rate of return to be profitable.
Interest rates are one important determinant of investment. However, they are not the only factor. Other factors include investor confidence, economic growth, the willingness of banks to lend, accelerator theory, and the state of technology.
Higher interest rates increase the opportunity cost of investment, making it more expensive to borrow money. This can cause firms to postpone their investment decisions until confidence returns and interest rates are lower.
The marginal efficiency of capital (MEC) states the rate of return on an investment project. Specifically, it refers to the annual percentage yield (output) earned by the last additional unit of capital.