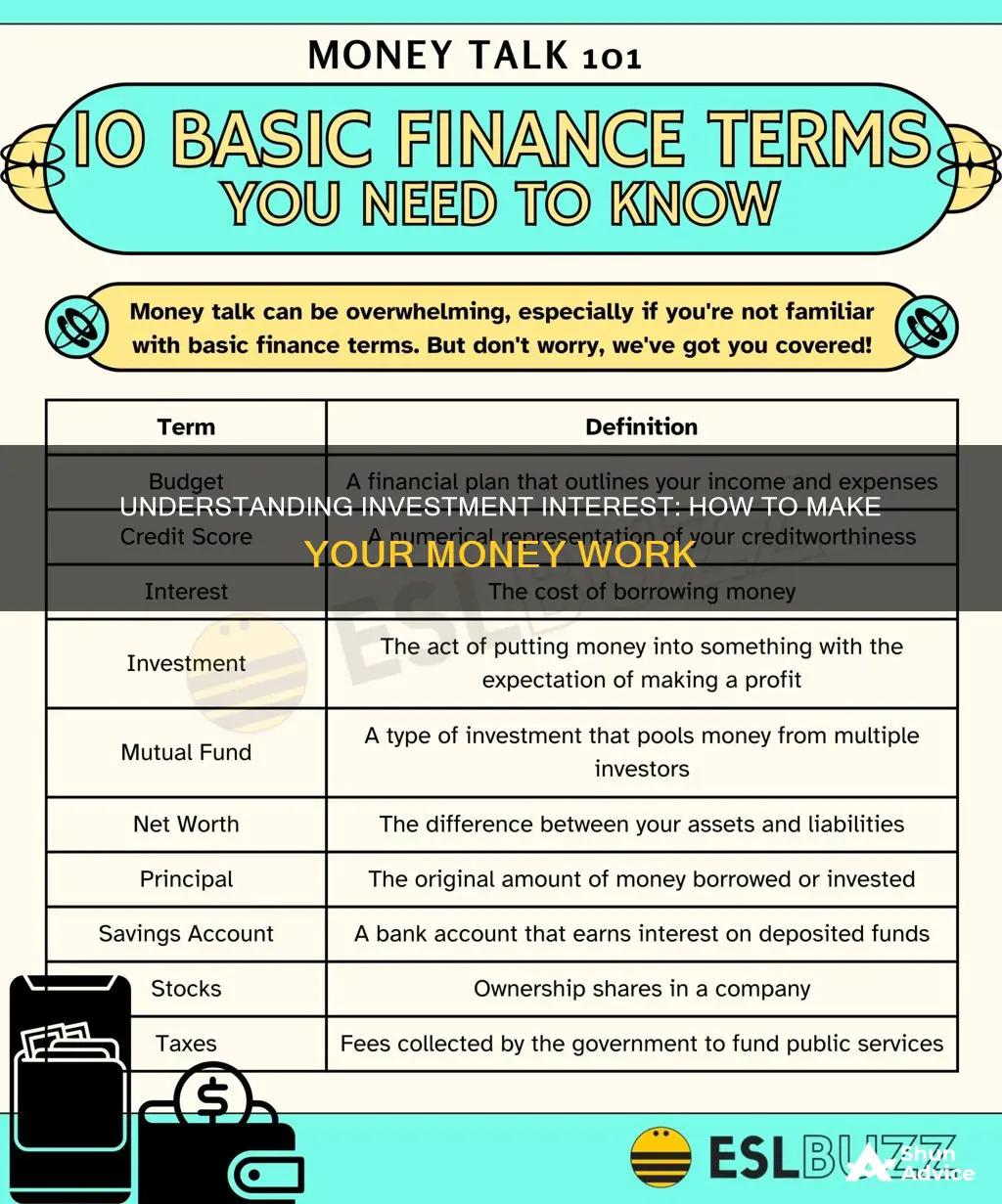
Investment interest is the interest paid on loans used to purchase investments or securities. This can include margin interest used to leverage securities in a brokerage account and interest on a loan used to buy property held for investment. Investment interest is tax-deductible in some circumstances, but not when used for passive ventures, such as investing in a business that the taxpayer owns but does not actively manage.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Interest paid or accrued on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry property held for investment |
| Examples | Margin interest used to leverage securities in a brokerage account; interest on a loan used to buy property held for investment; interest on a margin loan |
| Deductions | Deductible in certain circumstances, but not when used for passive ventures, such as investing in a business that the taxpayer owns but does not actively manage |
| Limitations | Limited to the amount of investment income received, such as dividends and interest |
| Allocation | If an investment is held for both business and personal gain, then any income received must be allocated proportionally between them |
| Reporting | Personal investment interest expense is reported on Schedule A of 1040 |
What You'll Learn

Investment interest expenses
Investment interest does not include qualified residence interest or interest incurred in a passive activity. However, if a passive activity generates portfolio income (interest, dividends, etc.), the portion of the passive activity interest expense allocable to the portfolio income is investment interest rather than passive activity interest.
Property held for investment includes any property producing interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, and gain-generating property other than that used in a trade or business activity or passive activity.
Interest Rates: Impacting Investment Strategies and Returns
You may want to see also

Investment interest deductions
Investment interest is interest paid or accrued on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry property held for investment. Investment interest does not include qualified residence interest or interest incurred in a passive activity. However, if a passive activity generates portfolio income (interest, dividends, etc.), the portion of the passive activity interest expense allocable to the portfolio income is investment interest rather than passive activity interest. Property held for investment includes any property producing interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, and gain-generating property other than that used in a trade or business activity or passive activity.
Investment interest expenses are tax-deductible in some circumstances, but not when used for passive ventures, such as investing in a business that the taxpayer owns but does not actively manage. An investment interest expense deductible is limited to the amount of investment income received, such as dividends and interest. If an investment is held for both business and personal gain, then any income received must be allocated proportionally between them. Personal investment interest expense is reported on Schedule A of 1040. A common example of this type of expense is the application of proceeds from a margin loan, taken out with a brokerage, in order to purchase stock.
Investment interest expenses include margin interest used to leverage securities in a brokerage account and interest on a loan used to buy property held for investment. An investment interest expense is interest charged for a loan related to an investment, such as margin loan interest or interest on an investment property. Investment property also includes an interest involving the conduct of a trade or business that is not considered a passive activity but in which the taxpayer does not materially participate (generally, oil and gas working interests).
The AMT is designed to ensure that certain individuals pay at least a minimum amount of tax by adding back in items that may have been excluded from a traditional tax calculation. Investment interest is one of those deductions disallowed under the AMT.
Invest Wisely, Live Comfortably Off Your Interest
You may want to see also

Investment interest and property
Investment interest is interest paid or accrued on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry property held for investment. This does not include qualified residence interest or interest incurred in a passive activity. However, if a passive activity generates portfolio income (interest, dividends, etc.), the portion of the passive activity interest expense allocable to the portfolio income is investment interest rather than passive activity interest. Property held for investment includes any property producing interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, and gain-generating property other than that used in a trade or business activity or passive activity.
Investment interest expenses include margin interest used to leverage securities in a brokerage account and interest on a loan used to buy property held for investment. Investment interest is tax-deductible in some circumstances, but not when used for passive ventures, such as investing in a business that the taxpayer owns but does not actively manage. An investment interest expense deductible is limited to the amount of investment income received, such as dividends and interest. If an investment is held for both business and personal gain, then any income received must be allocated proportionally between them.
Personal investment interest expense is reported on Schedule A of 1040. A common example of this type of expense is the application of proceeds from a margin loan, taken out with a brokerage, in order to purchase stock. Investment property also includes an interest involving the conduct of a trade or business that is not considered a passive activity but in which the taxpayer does not materially participate (generally, oil and gas working interests). The AMT is designed to ensure that certain individuals pay at least a minimum amount of tax by adding back in items that may have been excluded from a traditional tax calculation. Investment interest is one of those deductions disallowed under the AMT.
Investments: Compounding Interest Options for Your Money
You may want to see also

Investment interest and passive activities
Investment interest is interest paid or accrued on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry property held for investment. Investment interest does not include qualified residence interest or interest incurred in a passive activity. However, if a passive activity generates portfolio income (interest, dividends, etc.), the portion of the passive activity interest expense allocable to the portfolio income is investment interest rather than passive activity interest.
Property held for investment includes any property producing interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, and gain-generating property other than that used in a trade or business activity or passive activity. Investment interest expenses include margin interest used to leverage securities in a brokerage account and interest on a loan used to buy property held for investment.
Investment interest expenses are tax-deductible in some circumstances, but not when used for passive ventures, such as investing in a business that the taxpayer owns but does not actively manage. An investment interest expense deductible is limited to the amount of investment income received, such as dividends and interest. If an investment is held for both business and personal gain, then any income received must be allocated proportionally between them.
Personal investment interest expense is reported on Schedule A of 1040. A common example of this type of expense is the application of proceeds from a margin loan, taken out with a brokerage, in order to purchase stock. Investment property also includes an interest involving the conduct of a trade or business that is not considered a passive activity but in which the taxpayer does not materially participate (generally, oil and gas working interests).
Compound Interest: The Investment Snowball Effect
You may want to see also

Investment interest and tax
Investment interest is interest paid or accrued on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry property held for investment. Investment interest does not include qualified residence interest or interest incurred in a passive activity. However, if a passive activity generates portfolio income (interest, dividends, etc.), the portion of the passive activity interest expense allocable to the portfolio income is investment interest rather than passive activity interest. Property held for investment includes any property producing interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, and gain-generating property other than that used in a trade or business activity or passive activity.
An investment interest expense is any amount of interest that is paid on loan proceeds used to purchase investments or securities. Investment interest expenses include margin interest used to leverage securities in a brokerage account and interest on a loan used to buy property held for investment. An investment interest expense is deductible in certain circumstances. An investment interest expense is interest charged for a loan related to an investment, such as margin loan interest or interest on an investment property. Investment interest expense is tax-deductible in some circumstances, but not when used for passive ventures, such as investing in a business that the taxpayer owns, but does not actively manage.
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) is designed to ensure that certain individuals pay at least a minimum amount of tax by adding back in items that may have been excluded from a traditional tax calculation. Investment interest is one of those deductions disallowed under the AMT.
The Magic of Compound Interest for Long-Term Investments
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Investment interest is interest paid or accrued on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry property held for investment. It does not include qualified residence interest or interest incurred in a passive activity.
An investment interest expense is any amount of interest that is paid on loan proceeds used to purchase investments or securities. Investment interest expenses are tax-deductible in some circumstances.
The AMT is designed to ensure that certain individuals pay at least a minimum amount of tax by adding back in items that may have been excluded from a traditional tax calculation. Investment interest is one of the deductions disallowed under the AMT.