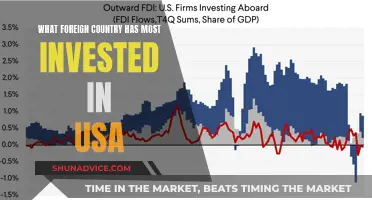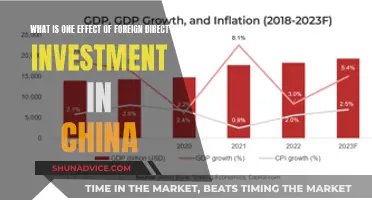
Foreign trade and foreign investment are deeply intertwined, forming the backbone of the global economy. Foreign trade, which encompasses the exchange of goods, services, and capital across international borders, is a vital mechanism for facilitating economic growth and development. Simultaneously, foreign investment, the influx of capital from one country to another, plays a pivotal role in driving economic expansion, creating jobs, and fostering technological advancements. This interrelationship is crucial as foreign investment often fuels the expansion of foreign trade, enabling businesses to access new markets, enhance production capabilities, and diversify their supply chains. Understanding this dynamic interplay is essential for policymakers, businesses, and investors alike, as it shapes strategies for international trade agreements, investment promotion, and economic development.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Foreign trade refers to the exchange of goods, services, and capital across international borders, while foreign investment involves the investment of capital in foreign countries by entities from another country. |
| Interrelationship | Foreign trade and foreign investment are closely linked and often reinforce each other. Foreign investment can stimulate trade by creating new markets, improving infrastructure, and enhancing productivity, which in turn attracts more foreign investment. |
| Impact on the Economy | Foreign investment can lead to increased exports, improved technology transfer, and the creation of new industries, thus boosting a country's economic growth and development. Foreign trade, on the other hand, provides access to a wider market, reduces costs, and increases competition, which can drive innovation and efficiency. |
| Market Access | Foreign investment often facilitates market access for a country's exports, especially in cases where the investor has a strong domestic market or can provide a competitive advantage in international trade. |
| Capital Flows | Foreign investment is a significant source of capital inflows for many countries, which can help finance trade deficits, infrastructure projects, and other economic activities. |
| Political and Social Factors | The relationship between foreign trade and investment is influenced by political stability, regulatory frameworks, and social factors in the host country. Favorable policies and conditions can attract more foreign investment and trade. |
| Recent Trends | Recent global trends show a shift towards more diversified and complex trade networks, with a focus on regional trade agreements and supply chain resilience. Foreign investment is also becoming more targeted towards sustainable and green initiatives. |
| Challenges | Challenges include potential negative impacts on local industries, environmental concerns, and the need for effective governance to manage the flow of capital and ensure equitable distribution of benefits. |
What You'll Learn

Foreign Trade Facilitates Investment Opportunities
Foreign trade and foreign investment are deeply intertwined, with each driving and enabling the other in a complex and mutually beneficial relationship. This interconnection is particularly evident when examining how foreign trade facilitates investment opportunities, creating a virtuous cycle of economic growth and development.
Foreign trade serves as a gateway to new markets, allowing businesses to expand their reach beyond their domestic borders. By engaging in international trade, companies gain access to a wider customer base, diverse supply chains, and a variety of resources that may not be available locally. This expansion of market opportunities is a powerful magnet for investment. Investors are drawn to markets with strong trade potential, as it presents a clear pathway to profitability and growth. For instance, a country with a thriving export sector, such as electronics or agricultural products, becomes an attractive investment destination for foreign entities seeking to tap into these markets.
The process of foreign trade also involves the establishment of complex supply chains and networks. As businesses engage in international trade, they often require additional infrastructure, logistics, and support services. This demand for specialized services and infrastructure attracts foreign investors who see opportunities to provide these much-needed resources. For example, a foreign investor might set up a logistics company to facilitate the efficient transportation of goods across borders, or an investor might establish a financial institution to cater to the unique needs of international trade, such as trade financing and currency exchange. These investments in supporting industries further enhance the trade environment, creating a positive feedback loop.
Moreover, foreign trade encourages the development of specialized industries and clusters. As trade flows increase, certain regions may become known for specific products or services, attracting further investment. Foreign investors are often drawn to these specialized hubs, as they offer a concentrated ecosystem of expertise, talent, and resources. This phenomenon is particularly evident in sectors like technology, where Silicon Valley in the United States has become a global investment magnet due to its reputation as a hub for innovation and startup activity. Similarly, regions known for their textile manufacturing or automotive assembly may attract foreign investors seeking to capitalize on these established industries.
In addition, foreign trade fosters economic stability and growth, which are essential prerequisites for attracting foreign investment. When a country engages in successful international trade, it generates revenue, creates jobs, and stimulates economic activity. This stability and growth potential make the country an appealing investment destination. Foreign investors are more likely to commit capital to markets that demonstrate a track record of successful trade, as it indicates a lower risk environment and a higher potential for long-term returns.
In summary, foreign trade and foreign investment are inextricably linked, with foreign trade acting as a catalyst for investment opportunities. It opens doors to new markets, attracts specialized services and industries, and fosters economic stability. By facilitating trade, countries create an environment that not only attracts foreign investors but also encourages the development of robust and diverse economies. This interrelationship highlights the importance of promoting and supporting foreign trade as a strategic means to drive economic growth and development.
Invested Wealth: When to Use It and Why
You may want to see also

Investment Flows Influence Trade Patterns
The relationship between foreign trade and foreign investment is a dynamic and intricate one, where each influences and shapes the other in significant ways. When a country attracts foreign investment, it often leads to an increase in its exports, as the investment brings new technology, expertise, and access to global markets. This is particularly evident in the case of developing nations, where foreign direct investment (FDI) can catalyze the growth of local industries, making them more competitive and attractive to international buyers. For instance, a country with a strong automotive industry might attract foreign investors who bring advanced manufacturing techniques and a global network of suppliers and buyers, thus boosting the country's auto exports.
Foreign investment also plays a crucial role in the development of infrastructure and the creation of new industries, which in turn can stimulate domestic production and exports. This is often seen in the case of resource-rich countries, where foreign investors might establish new mining or oil extraction operations, leading to increased production and exports of these commodities. The influx of foreign capital and expertise can also lead to the transfer of technology and skills, enhancing the productivity and quality of local goods, which can further boost a country's exports.
The impact of investment flows on trade patterns is not limited to the immediate boost in exports. It can also lead to the diversification of a country's export base, reducing its reliance on a few key products. For example, a country that attracts FDI in the technology sector might see a rise in the export of software and IT services, alongside traditional goods. This diversification can make the country's economy more resilient and less vulnerable to fluctuations in the prices of a single commodity.
Moreover, foreign investment can facilitate the integration of a country into global supply chains. Investors often seek to establish production hubs in regions with favorable investment conditions, which can lead to the development of regional trade networks. This is evident in the rise of 'factory Asia', where countries like China, Vietnam, and Indonesia have become major manufacturing hubs, attracting FDI and becoming key players in global supply chains. As a result, these countries have seen a significant increase in both imports and exports, contributing to their economic growth and development.
In summary, foreign investment and foreign trade are deeply intertwined, with investment flows having a profound impact on trade patterns. The benefits of foreign investment can lead to increased exports, diversification of the economy, and the integration of a country into global supply chains. Understanding this relationship is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike, as it highlights the importance of creating an environment that attracts foreign investment while also fostering a robust and competitive trade sector.
Understanding Foreign Direct Investment: A Comprehensive Definition
You may want to see also

Trade Liberalization Encourages Foreign Investment
Trade liberalization, the process of reducing or eliminating trade barriers, has a significant impact on fostering foreign investment. When a country opens up its markets and reduces restrictions on trade, it creates an environment that is more attractive to foreign investors. This is because liberalization often leads to increased market access, which is a crucial factor for investors, especially multinational corporations. With fewer barriers, companies can more easily enter new markets, expand their operations, and tap into a wider consumer base. This accessibility and the potential for growth are powerful incentives for foreign direct investment (FDI).
One of the key benefits of trade liberalization is the establishment of more favorable conditions for foreign investors. Lower tariffs, fewer quotas, and simplified regulatory processes can significantly reduce the costs and complexities associated with doing business in a foreign market. This is particularly important for investors who are looking to enter new territories or expand their existing operations. For instance, a company might be more inclined to invest in a country that offers reduced import duties and streamlined customs procedures, as these factors directly impact their profitability and operational efficiency.
Moreover, trade liberalization often goes hand in hand with economic reforms that improve the overall business environment. These reforms may include legal and regulatory changes that enhance property rights, strengthen contract enforcement, and improve the transparency of government processes. Such reforms can boost investor confidence, as they provide a more stable and predictable legal framework. For example, a country that liberalizes trade and simultaneously implements reforms to protect intellectual property rights is likely to attract more foreign investors, especially those in knowledge-intensive industries.
The relationship between trade liberalization and foreign investment is also evident in the increased competition and market dynamics that arise. When trade barriers are lowered, domestic and foreign firms compete more intensely, which can drive innovation and improve efficiency. This competitive environment encourages foreign investors to bring in new technologies, management practices, and capital, further stimulating economic growth. Additionally, the expansion of local markets due to increased trade can create a more attractive investment proposition, as it provides a larger customer base and potential for market share gains.
In summary, trade liberalization plays a pivotal role in encouraging foreign investment by creating a more open and conducive business environment. It reduces the barriers to entry, improves market access, and enhances the overall investment climate. As a result, foreign investors are more likely to channel their capital into the liberalized market, contributing to economic development and the growth of international trade. Understanding this interrelationship is essential for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the strategic benefits of implementing trade liberalization measures.
Wax Patterns: Perfect for Investment Casting Jewelry
You may want to see also

Investment Returns Impact Trade Deficits
The relationship between foreign trade and foreign investment is a complex and dynamic one, with each influencing the other in significant ways. When a country engages in foreign trade, it opens up opportunities for foreign investment, and vice versa. Foreign investment can take various forms, such as direct investment, portfolio investment, and other types of capital flows. These investments often play a crucial role in facilitating international trade by providing the necessary capital, technology, and expertise to support the production and export of goods and services.
In the context of trade deficits, investment returns can have a substantial impact. A trade deficit occurs when a country's imports exceed its exports, resulting in a negative balance of trade. This situation can be influenced by various factors, including the flow of foreign investment. When a country attracts significant foreign investment, it often leads to increased production and the development of new industries, which can, in turn, boost exports. However, if the investment is primarily focused on import-intensive sectors, it may contribute to a trade deficit. For instance, if a country attracts foreign investment in manufacturing industries that rely heavily on imported raw materials and components, the demand for imports could outpace the country's export capacity, leading to a trade gap.
The impact of investment returns on trade deficits is twofold. Firstly, the returns generated from foreign investments can directly affect a country's trade balance. When foreign investors earn profits from their investments, they may repatriate these returns to their home countries, potentially reducing the country's foreign exchange reserves. This outflow of capital can put pressure on the country's currency and, in some cases, contribute to a trade deficit if the investment is not balanced by an equivalent level of exports. Secondly, the nature of the investments can shape the composition of a country's exports. Foreign investment in sectors that are not competitive in the global market or that have a low export potential might not significantly improve the trade balance.
Managing the relationship between foreign investment and trade is crucial for a country's economic stability and growth. Governments and policymakers should carefully consider the types of investments they attract, ensuring that they promote sustainable and balanced trade. Diversifying investment portfolios and encouraging foreign investment in sectors with high export potential can help mitigate the risks associated with trade deficits. Additionally, implementing policies that support local industries and promote technology transfer can ensure that foreign investment contributes positively to the country's trade performance and overall economic development.
In summary, the interrelation between foreign trade and foreign investment is a critical aspect of a country's economic strategy. Investment returns can significantly influence trade deficits, and understanding this relationship is essential for policymakers to make informed decisions. By carefully managing investment flows and promoting strategic investments, countries can strive for a more balanced and sustainable trade environment.
Unlocking Home Equity: A Smart Investment Strategy?
You may want to see also

Trade Policies Shape Investment Strategies
The relationship between foreign trade and foreign investment is a dynamic and intricate one, where trade policies play a pivotal role in shaping investment strategies. When a country implements trade policies, it sends a clear signal to investors about the economic environment and the potential for growth. These policies can either attract or deter foreign investors, depending on their design and implementation.
One of the most common trade policies is the imposition of tariffs, which are taxes on imported goods. While tariffs can protect domestic industries from foreign competition, they can also create a less favorable environment for foreign investors. Higher tariffs may increase the cost of imported raw materials and intermediate goods, making it more expensive for foreign investors to operate in the market. As a result, investors might seek alternative destinations where trade policies are more investor-friendly.
On the other hand, trade liberalization, which involves reducing or eliminating tariffs and other trade barriers, can have a positive impact on foreign investment. Lower tariffs make it more cost-effective for investors to import goods and services, reducing operational costs. This, in turn, can attract foreign investors who are looking for efficient supply chains and access to global markets. For instance, a country that implements a comprehensive free trade agreement (FTA) with multiple trading partners is likely to see an increase in foreign direct investment (FDI) as investors take advantage of the reduced tariffs and improved market access.
Investment promotion policies are another critical aspect of trade that influences investment strategies. These policies include measures such as tax incentives, special economic zones, and streamlined regulatory processes. By offering tax breaks or subsidies to foreign investors, governments can encourage capital inflows and create a more attractive investment climate. Special economic zones, which offer tax and regulatory advantages, can also attract foreign investors by providing a conducive environment for business operations.
In summary, trade policies have a direct and significant impact on foreign investment decisions. Investors closely monitor trade policies as they can affect the profitability and feasibility of their ventures. A country's trade policies can either facilitate or hinder the flow of foreign investment, making it essential for policymakers to carefully consider the potential consequences of their trade decisions. Understanding this interrelationship is crucial for governments and investors alike to foster a thriving and mutually beneficial trade and investment environment.
Robinhood App: A Beginner's Guide to Investing
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Foreign trade and foreign investment are closely intertwined concepts that significantly impact the global economy. Foreign trade refers to the exchange of goods, services, and capital across international borders, while foreign investment involves the investment of capital in foreign countries by individuals, corporations, or governments. These two factors are interrelated as they often go hand in hand, creating a symbiotic relationship.
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in fostering international trade. When a company or individual invests in a foreign country, they often establish a presence there, which can lead to increased exports from the home country. For example, a foreign investor might set up a manufacturing plant in a new market, producing goods that are then exported back to their home country or sold locally. This, in turn, stimulates trade between the two nations. Additionally, foreign investment can create a demand for imported raw materials, intermediate goods, and services, further boosting trade flows.
Absolutely. Foreign trade can create opportunities and attract foreign investment. A country with a robust and diverse export sector may become an attractive destination for investors looking to tap into new markets. For instance, a country with a strong manufacturing base and a wide range of export products can attract foreign investors who want to access these markets. Moreover, foreign trade agreements and policies can facilitate foreign investment by reducing barriers to entry, providing incentives, and establishing favorable conditions for investors.
The interconnection between foreign trade and investment offers numerous advantages. It promotes economic growth and development by creating jobs, increasing productivity, and generating revenue. Foreign investment can bring capital, technology, and expertise to host countries, enhancing their infrastructure and business environment. As a result, local industries can become more competitive, and the overall standard of living may improve. Additionally, this relationship fosters cultural exchange, encourages innovation, and strengthens international relations, leading to a more interconnected and prosperous global economy.