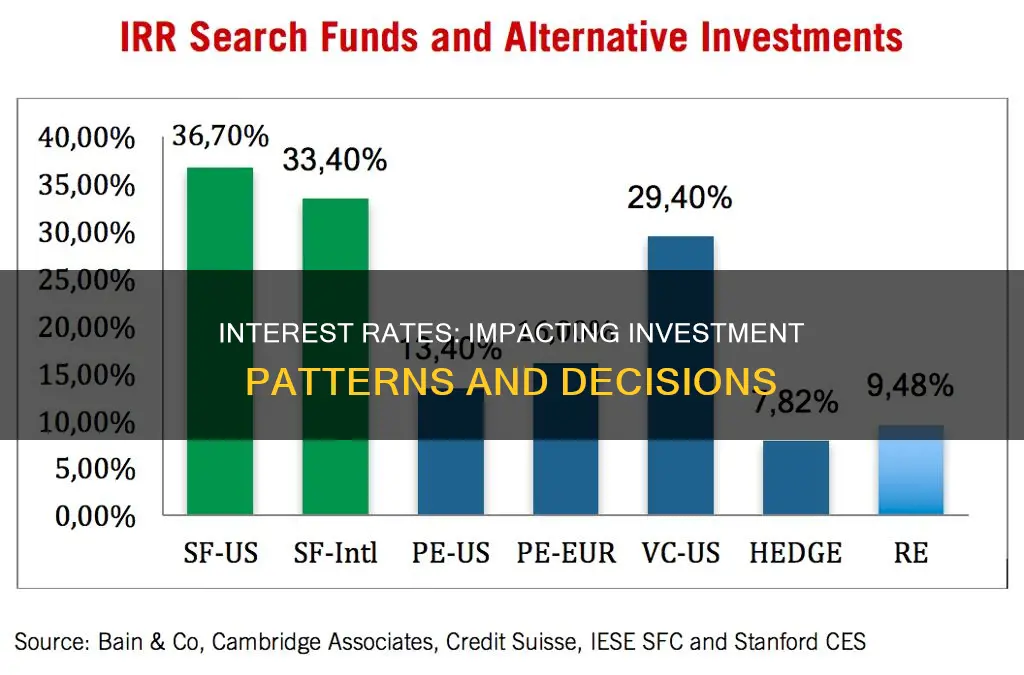
Interest rates have a significant impact on investment patterns. When interest rates are high, investments become more expensive, which can discourage investment. However, some investors may see this as an opportunity for higher returns. Changes in interest rates can have both positive and negative effects on the markets for stocks and bonds, and investors must remain alert to the behaviour of consumers and businesses in the wider world. Understanding the relationship between interest rates and markets can help investors make better financial decisions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Discourages investment | Higher interest rates raise the cost of borrowing and require a higher rate of return to be profitable |
| Affects the economy | High interest rates can have a ripple effect throughout the broader economy, impacting the stock and bond markets |
| Influences consumer and business behaviour | Changes in interest rates can affect the behaviour of consumers and businesses, which stock and bond investors must remain alert to |
| Indicates the position of the issuer | Rising interest rates on investments can indicate whether the issuer is in a good position to pay or is taking a high risk |
What You'll Learn

How interest rates affect the economy
Interest rates can have a significant impact on the economy, affecting both stock and bond markets in different ways. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, which can discourage investment as it raises the bar for profitability. This can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, changing the behaviour of consumers and businesses.
Higher interest rates can also affect the wider economy by influencing the investment patterns of individuals and businesses. For example, investors may become more cautious and less likely to take on risky investments. This could lead to a decrease in overall investment and slower economic growth.
On the other hand, lower interest rates can encourage investment by making borrowing cheaper and increasing the potential for profit. This can have a positive impact on the economy, stimulating growth and creating a more favourable environment for businesses and consumers.
The impact of interest rates on the economy is complex and depends on a variety of factors, including the broader economic context and the behaviour of consumers and businesses. Investors who understand the relationship between interest rates and markets can make better financial decisions and navigate changing economic conditions more effectively.
Interest Rates: Rising Investment Opportunities and Challenges
You may want to see also

How interest rates affect stocks and bonds
Interest rates can have a significant impact on investment patterns, and this can be seen in the markets for stocks and bonds. When interest rates change, it can affect the behaviour of consumers and businesses, which in turn impacts the markets.
Higher interest rates tend to discourage investment as they raise the cost of borrowing and require investments to provide a higher rate of return to be profitable. This can be seen as a negative, but it also tells investors a lot about the issuer of the investment. For example, are they in a good position to pay such an amount, or are they taking a high risk?
On the other hand, lower interest rates can encourage investment as they make borrowing cheaper and may indicate that the issuer is in a strong financial position.
Stock and bond investors need to pay attention to these broader economic factors to make better financial decisions. The Federal Reserve's interest rate changes, for example, can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, impacting both stock and bond markets in different ways.
Understanding the Correlation Between Interest Rates and Investments
You may want to see also

How investors respond to interest rates
Interest rates can have a significant impact on investment patterns, and investors need to be aware of how changes in interest rates can affect their investments. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, which can discourage investment as it raises the bar for profitability. Investors must also consider the wider economy and how changes in interest rates can affect the behaviour of consumers and businesses.
Some investors may choose to ignore rising interest rates, unless they are negatively affected. However, this can be a risky strategy as it may indicate that the issuer is taking on too much risk. It is important for investors to understand the relationship between interest rates and markets, as this can help them make better financial decisions.
On the other hand, low-interest rates can also have an impact on investment patterns. While they may encourage more borrowing and investment, they can also affect the profitability of investments. Investors may need to seek out alternative investments that offer higher returns to compensate for the low interest rates.
Overall, investors need to be alert to changes in interest rates and their potential impact on the markets. By understanding the relationship between interest rates and the economy, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments.
Maximizing Returns: Strategies for High-Interest Investments
You may want to see also

How interest rates affect the cost of borrowing
Interest rates have a significant impact on investment patterns. When interest rates are high, the cost of borrowing increases, which can discourage investment. This is because investments need to provide a higher rate of return to be profitable. However, some investors may view high-interest rates positively, as they can indicate that the issuer is in a strong financial position.
Rising interest rates can also affect the behaviour of consumers and businesses, which stock and bond investors must pay attention to. When the Federal Reserve changes interest rates, it has a ripple effect throughout the broader economy, impacting stock and bond markets differently.
While most investors tend to ignore the impact of rising interest rates, it is essential to consider the financial health of the issuer. High-interest rates may signal that the issuer is taking on too much risk or is unable to pay the required amount.
Overall, interest rates play a crucial role in shaping investment patterns. Investors must carefully consider the potential effects of interest rate changes on their portfolios and the wider economy. By understanding the relationship between interest rates and markets, investors can make more informed financial decisions.
Investment Interest Expense: Reducing Your AGI?
You may want to see also

How interest rates affect the profitability of investments
Interest rates can have a significant impact on the profitability of investments. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, which can discourage investment. This is because investments will need to provide a higher rate of return to be profitable.
Rising interest rates can also affect the behaviour of consumers and businesses, which stock and bond investors must be alert to. For example, when interest rates are high, consumers may be more likely to save than spend, which can impact the profits of companies that rely on consumer spending.
Additionally, high interest rates can tell investors a lot about the issuer. For instance, whether they are in a good financial position to pay such an amount or if they are taking a high risk.
On the other hand, low-interest rates can also have an impact on investments. When interest rates are low, borrowing is cheaper, which can encourage investment and spending. This can have a positive effect on the profits of companies as consumers may be more likely to spend.
Overall, understanding the relationship between interest rates and markets is crucial for investors to make better financial decisions. Changes in interest rates can have a ripple effect throughout the broader economy, affecting stock and bond markets in different ways.
Simple Interest Investments: Yearly Payouts Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Higher interest rates tend to discourage investment since they raise the cost of borrowing and necessitate the need for investments to provide a higher rate of return in order to be profitable.
Interest rates can have a ripple effect throughout the broader economy, affecting both stock and bond markets in different ways.
Investors must remain alert to the behaviour of consumers and businesses in the wider world, as changes in interest rates can affect that behaviour.
A rising interest rate on an investment can indicate whether the issuer is in a good position to pay such an amount or if they are taking a high risk.
Understanding the relationship between interest rates and markets can help investors make better financial decisions.