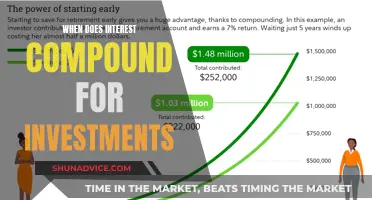
Interest can compound daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, biannually, or annually, depending on the types of investments in your portfolio and where you keep your savings. The more often interest compounds, the faster your money grows. Interest on an account may accrue daily but only be credited monthly. Only when the interest is credited, or added to the existing balance, does the interest begin to earn additional interest.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| How often does interest compound on investments? | Daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, biannually, or annually |
| How does compound interest work? | Interest is earned on the initial principal and on the accumulated interest |
| How does the frequency of compounding impact returns? | The more often interest compounds, the faster your money grows |
| How does interest on loans differ? | Interest on loans may mean you pay more over time due to compound interest |
| What are compounding periods? | Time intervals between when interest is added to an account |
What You'll Learn

How often interest compounds
Interest compounds at different frequencies depending on the type of investment. It can be compounded daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, biannually, or annually. The more often it compounds, the faster your money grows.
For example, interest on an account may accrue daily but only be credited monthly. Only when the interest is credited, or added to the existing balance, does the interest begin to earn additional interest.
The commonly used compounding schedule for savings accounts at banks is daily. However, this may differ depending on the types of investments in your portfolio.
Interest Rates: Impacting Investment Strategies and Returns
You may want to see also

The impact of compounding frequency
The frequency of compounding interest on investments varies. It can be daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, biannually, or annually. The more often it compounds, the greater compounding's impact. This means that the more often interest is added to an account, the faster the money in the account grows. For example, interest on an account may accrue daily but only be credited monthly. Only when the interest is credited, or added to the existing balance, does the interest begin to earn additional interest.
The type of investment also determines how often interest compounds. For example, the commonly used compounding schedule for savings accounts at banks is daily. However, the compounding schedule for investments in the stock market may be different.
It is important to note that the impact of compounding frequency is not always positive. While more frequent compounding can lead to faster money growth, it can also result in paying more over time. For example, some private lenders may use compound interest on debt, such as credit card debt. Most issuers compound interest charges daily, which is why it is important to stay on top of credit card payments and avoid charges beyond what one can afford.
Interest Rates: Investing and Growing the Economy
You may want to see also

How to make the most of compound returns
Interest can compound daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the types of investments in your portfolio and where you keep your savings. The more often interest compounds, the faster your money grows. For example, interest on an account may accrue daily but only be credited monthly. It is only when the interest is credited, or added to the existing balance, that the interest begins to earn additional interest.
To make the most of compound returns, you should keep in mind that the frequency of the interest or returns you earn on your savings and investments matters. Anytime you invest money in the stock market, you're giving it a chance to benefit from compounding.
You can use a compound interest formula or a compound interest calculator to calculate compound interest on your savings. This will allow you to compare how interest compounded daily compares with interest compounded annually or monthly.
It is also important to review your lending agreement or reach out to your lender to better understand how interest will affect what you owe. Some private lenders may use compound interest on your debt.
Vanguard's Fixed Interest Investments: What Are Your Options?
You may want to see also

How compound interest works for your savings
Interest compounds at different frequencies, depending on the type of investment. It can be compounded daily, monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. The more often interest compounds, the faster your money grows.
For example, if you invest £100 at an annual interest rate of 5%, at the end of the year you will have £105. If you leave that money in the account, the following year you will earn 5% on £105, giving you £110.25 at the end of the second year. This is because, in the second year, you are earning interest on the interest from the first year.
The frequency of compounding can have a significant impact on the growth of your savings. For example, if you invest £100 at an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded daily, you will have £105.12 at the end of the year. This is because the interest is calculated and added to your account balance every day, so you are earning interest on the interest more frequently.
The type of investment you choose will also affect the frequency of compounding. For example, if you invest in the stock market, your money will have the opportunity to benefit from compounding. On the other hand, if you have a loan or credit card debt, you may be paying compound interest, which can increase the amount you owe over time.
Savings Accounts: Lower Interest Rates than Investments?
You may want to see also

How compound interest works for your investments
Interest can compound daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the types of investments in your portfolio and where you keep your savings. The more often interest compounds, the faster your money grows.
For example, interest on an account may accrue daily but only be credited monthly. Only when the interest is credited, or added to the existing balance, does the interest begin to earn additional interest. The commonly used compounding schedule for savings accounts at banks is daily.
Compound interest is interest you earn on your initial principal and on your accumulated interest. For instance, any money you've put in a 401(k) account is benefiting from compound interest.
It's important to note that the frequency of the interest or returns you earn on your savings and investments matters. The more often it compounds, the greater compounding's impact. Anytime you invest money in the stock market, you're giving it a chance to benefit from compounding.
Interest Rates and Investment: Exploring the Inverse Relationship
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Interest can compound daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, biannually, or annually. The more often it compounds, the faster your money grows.
Compound interest is interest you earn on your initial principal and on your accumulated interest.
Interest on an account may accrue daily but only be credited monthly. Only when the interest is credited, or added to the existing balance, does the interest begin to earn additional interest.
Anytime you invest money in the stock market, you're giving it a chance to benefit from compounding. Keep on top of your credit card payments and avoid making charges beyond what you can afford.