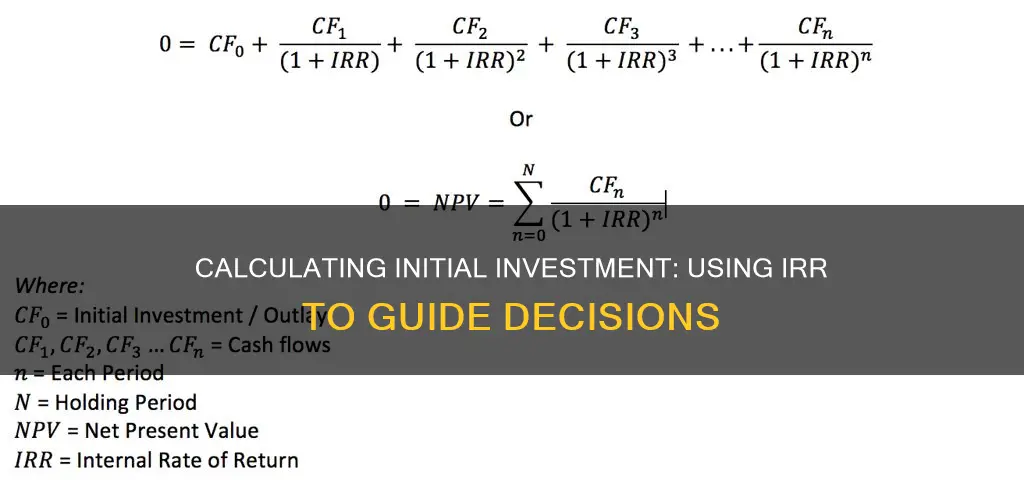
The internal rate of return (IRR) is a metric used to estimate the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by finding the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from the investment equal to zero. In other words, it is the expected compound annual rate of return on an investment.
The IRR formula is as follows:
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) = (Future Value ÷ Present Value)^(1 ÷ Number of Periods) – 1
The IRR can be calculated manually or by using software such as Excel. To calculate the IRR manually, one would set the NPV equal to zero and solve for the discount rate (IRR). This involves a trial-and-error approach until the correct IRR is found.
The IRR is useful for analyzing the potential returns of an investment and can help investors and companies make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is IRR used for? | IRR is used to estimate the profitability of potential investments. |
| IRR formula | IRR = R1 + ((NPV1 * (R2 - R1)) / (NPV1 - NPV2) |
| IRR calculation methods | 1. Using the IRR or XIRR function in Excel or other spreadsheet programs. 2. Using a financial calculator. 3. Using an iterative process where the analyst tries different discount rates until the NPV equals zero. |
| IRR and NPV | IRR calculations rely on the same formula as NPV. IRR is not the actual dollar value of the project but the annual return that makes the NPV equal to zero. |
| IRR and investment choices | When comparing investment options, the investment with the highest IRR is generally the best choice. |
What You'll Learn
- IRR is the annualised interest rate at which the initial capital investment must grow to reach the ending value
- IRR is used to analyse investment returns, especially when interest payments or cash dividends are not reinvested
- IRR is a useful metric for capital planning, allowing companies to compare the profitability of creating a new operation with that of expanding an existing one
- IRR is a useful tool for analysing stock buyback programs, helping companies evaluate if it is more profitable to allocate capital to buying back shares
- IRR is a useful metric for analysing insurance policies, helping individuals determine which policies are more beneficial

IRR is the annualised interest rate at which the initial capital investment must grow to reach the ending value
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a metric used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of potential investments. It is a discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis.
The IRR is calculated using the same formula as NPV, but it sets the NPV equal to zero. The formula for determining IRR is:
$$Net\ cash\ inflow\ during\ the\ period\ t = Total\ initial\ investment\ costs + The\ internal\ rate\ of\ return \times The\ number\ of\ time\ periods$$
The IRR is the annual rate of growth that an investment is expected to generate. It is the annualised interest rate at which the initial capital investment must grow to reach the ending value.
When calculating the IRR, the expected cash flows for a project or investment are given, and the NPV equals zero. This means that the initial cash investment for the beginning period will be equal to the present value of the future cash flows of that investment.
The IRR can be calculated manually or by using software such as Excel. Manual calculation involves setting the NPV equal to zero and solving for the discount rate, which is the IRR. The initial investment is considered a negative value because it represents an outflow. Each subsequent cash flow can be positive or negative, depending on the estimates of the project's future performance.
Excel provides functions such as IRR, MIRR, and XIRR to calculate the IRR. The IRR function is used when cash flows are expected at regular intervals, while the MIRR function is used when there is a finance rate involved, such as borrowing or reinvesting. The XIRR function is used for cash flows that don't have regular intervals.
The IRR is a valuable tool for companies to determine where to invest their capital. It helps them compare different investment options and select the one with the highest IRR, indicating the best potential return.
Preventing Cash Crunch in Illiquid Investments: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

IRR is used to analyse investment returns, especially when interest payments or cash dividends are not reinvested
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a metric used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of potential investments. It is a discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis.
IRR is particularly useful for analysing investment returns when interest payments or cash dividends are not reinvested. In such cases, IRR can be used to determine the investment return of various assets. This is because IRR assumes that dividends and cash flows are reinvested at the discount rate, which may not always be the case.
The formula for calculating IRR is as follows:
Net cash inflow during period t
Total initial investment costs
The internal rate of return
The number of time periods
Manually calculating IRR involves setting the NPV equal to zero and solving for the discount rate, which is the IRR. However, due to the nature of the formula, IRR cannot be easily calculated analytically and must be determined through trial and error or by using software such as Excel.
When using Excel, the IRR function can be utilised to simplify the calculation process. The steps are as follows:
- Enter all cash flows associated with the investment or project into an Excel spreadsheet, ensuring they are listed in chronological order.
- Use the IRR function in a cell where you want the IRR value to appear. The syntax for the function is: =IRR(values).
- Select all cash flows, including the initial investment, to calculate the IRR.
IRR is a valuable tool for companies and investors to assess potential investments and determine where to allocate their capital. It provides a uniform metric for comparing investments of varying types and helps identify the most attractive opportunities with the highest potential returns.
Understanding Cash Flow: Investing vs. Financing Activities
You may want to see also

IRR is a useful metric for capital planning, allowing companies to compare the profitability of creating a new operation with that of expanding an existing one
IRR, or internal rate of return, is a metric used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of potential investments. It is a useful tool for capital planning, allowing companies to compare the profitability of different projects, including the creation of new operations and the expansion of existing ones.
The IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from a project equal to zero. In other words, it is the expected compound annual rate of return that will be earned on a project or investment. When calculating IRR, the initial cash investment for the beginning period will be equal to the present value of the future cash flows of that investment.
The IRR is a useful metric for capital planning as it allows companies to compare the profitability of different projects. For example, an energy company may use IRR to decide whether to open a new power plant or renovate and expand an existing one. The project with the higher IRR is likely to be the more profitable option, and therefore the more logical decision.
It is important to note that IRR does not account for changing discount rates and is therefore not suitable for longer-term projects with varying discount rates. Additionally, IRR does not take into account the actual dollar value of the project or any anomalies in cash flows. As such, it should not be the sole metric used for investment decisions.
When making capital planning decisions, companies often compare the IRR of different projects to determine which option will provide the best return on investment. By ranking projects based on their IRR, companies can make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources.
In summary, IRR is a valuable tool for capital planning as it allows companies to compare the profitability of different projects, including the creation of new operations and the expansion of existing ones. By considering the IRR alongside other factors, companies can make more informed decisions about their capital allocation.
Cash Payments for Trading Securities: An Investment Activity?
You may want to see also

IRR is a useful tool for analysing stock buyback programs, helping companies evaluate if it is more profitable to allocate capital to buying back shares
IRR, or Internal Rate of Return, is a useful metric for evaluating the profitability of potential investments. It is a discount rate that makes the Net Present Value (NPV) of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis. This makes it a valuable tool for analysing stock buyback programs, helping companies determine if buying back shares is a more profitable option than other uses of their capital, such as creating new outlets or acquiring other companies.
A stock buyback, or share repurchase program, is when a company uses its cash to buy back its own shares from the market. This can be done to return excess cash to shareholders and boost demand for the stock, thereby increasing its price. A company might decide to do this if it believes its shares are undervalued.
When analysing a stock buyback program, the IRR would be calculated by setting the NPV equal to zero and solving for the discount rate, which is the IRR. This calculation would consider the initial investment as a negative value (an outflow) and subsequent cash flows as positive or negative depending on the estimates.
For example, let's consider a company that is evaluating a stock buyback program. The initial investment required to repurchase the shares is $500,000. The company expects to generate additional annual profits of $150,000 in the first year, $160,000 in the second year, and $170,000 in the third year. We can use the IRR function in Excel to calculate the IRR for this scenario.
By comparing the IRR of the stock buyback program with the IRR of other potential investments, the company can determine if the buyback is a more profitable option. A higher IRR indicates a more desirable investment, assuming other parameters are equal.
It is important to note that IRR analysis should not be the sole basis for decision-making. Other factors, such as qualitative considerations and a company's risk tolerance, should also be taken into account when evaluating stock buyback programs. Additionally, the IRR assumes that positive cash flows will be reinvested at the same rate, which may not always be accurate.
Understanding Investment Project Cash Flows: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

IRR is a useful metric for analysing insurance policies, helping individuals determine which policies are more beneficial
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a metric used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of potential investments. It is a discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis. In other words, it is the expected compound annual rate of return that will be earned on an investment.
The IRR is particularly useful for individuals looking to analyse insurance policies and determine which is the most beneficial. This is because the IRR does not account for the actual dollar value of the policy but instead focuses on the annual return. This is important as life insurance policies tend to have very high IRRs in the early years, often exceeding 1000%, which then decrease over time. This is because, in the early years, the lump-sum benefit outweighs the monthly premiums paid.
When analysing insurance policies, it is important to treat the premiums as the investment and the death benefit as the return. By doing so, individuals can determine which policies offer the highest IRR for the same premium, thus helping them to make more informed decisions about which policies are more beneficial for them.
However, it is important to note that the IRR has some limitations. For example, it does not account for the actual dollar value of the investment and can be misleading when comparing projects of different durations. As such, it is often used in conjunction with other metrics and analyses to make more robust decisions.
Diversifying Your Investment: Using Multiple Platforms for Your Money
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
IRR is a metric used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of potential investments. It is the annual rate of return that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from an investment equal to zero. A higher IRR indicates a more desirable investment.
The manual calculation of IRR involves dividing the future value (FV) of an investment by its present value (PV), raising it to the inverse power of the number of periods, and then subtracting one.
Mathematically, it can be represented as:
> IRR = (FV / PV)^(1 / number of periods) - 1
IRR has some limitations. It does not provide the return on the initial investment in absolute terms, and using it exclusively can lead to poor investment decisions, especially when comparing projects of different durations. It also assumes that positive cash flows will be reinvested at the same rate as the project, which may not always be accurate.







