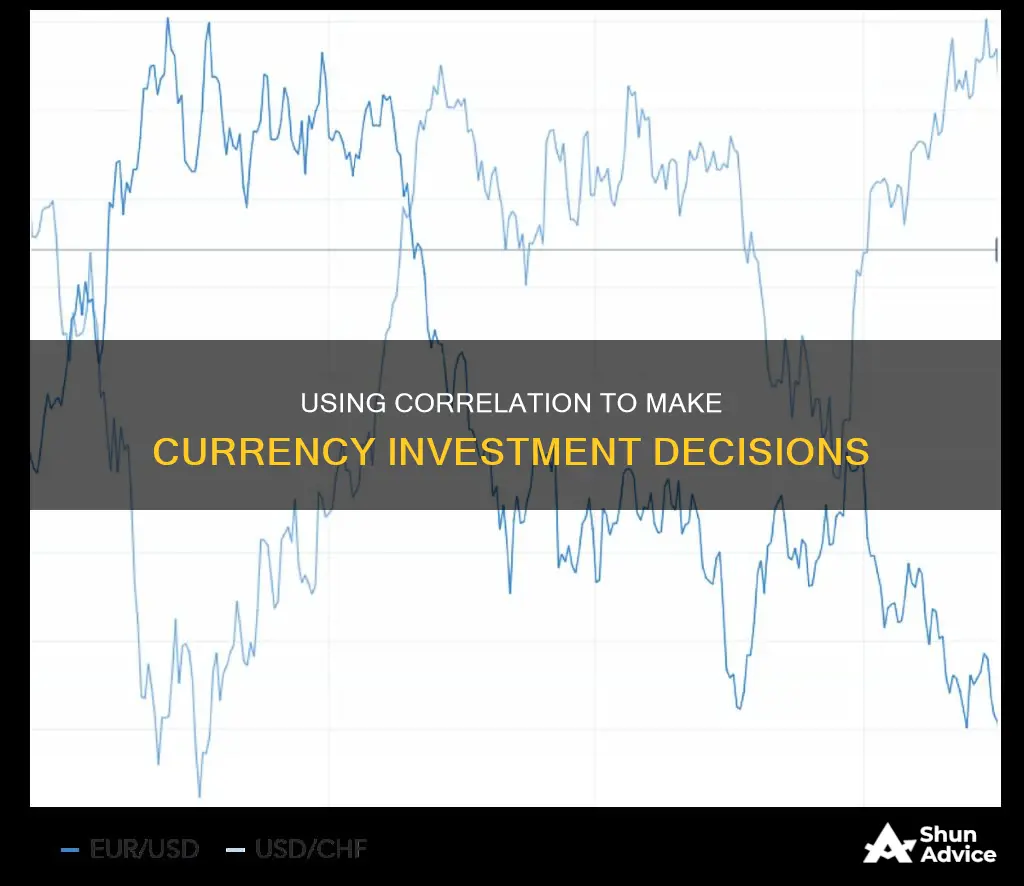
Currency correlation is a statistical measure of the relationship between two currency pairs and how they move in relation to each other. It is important for traders to understand currency correlation as it can affect their level of risk when trading in the forex market. Currency pairs are priced in pairs, meaning no single pair trades independently of the others. Currency correlation can be positive, negative, or neutral. A positive correlation means that the values of two variables move in the same direction, while a negative correlation means they move in opposite directions. A neutral correlation means the relationship between the currency pairs is completely random. Currency correlation can be used to inform investment decisions by helping investors avoid conflicting positions, diversifying risk, and hedging positions.
What You'll Learn
- Positive correlation: Two currency pairs move in the same direction
- Negative correlation: Two currency pairs move in opposite directions
- No correlation: The movement of the currency pairs is random
- Avoid conflicting positions: Correlation can help you avoid entering positions that cancel each other out
- Diversify risk: Currency pairs with imperfect positive correlation can be used to diversify your risk

Positive correlation: Two currency pairs move in the same direction
Positive correlation in currency trading refers to when two currency pairs move in the same direction. For example, if EUR/USD goes up, GBP/USD might also go up.
The EUR/USD and GBP/USD are the most correlated currency pairs. Over one month, the EUR/USD and GBP/USD had a very strong positive correlation of 0.95. This implies that when the EUR/USD rallies, the GBP/USD also rallies 95% of the time. Over the past six months, the correlation was weaker (0.66), but in the long run (one year), the two currency pairs still have a strong correlation.
Another example of a positive correlation is NZDUSD vs AUDUSD. This is because both New Zealand and Australia are closely tied economies that trade together.
Positive correlations can be used to potentially increase profits. For example, since GBP/USD and EUR/USD are positively correlated, a trader might place a long trade on both to utilise the relationship.
It is important to note that even if two currency pairs are positively correlated, the magnitude of their movements may differ. For example, one pair may move up 100 pips while another moves down 70 pips. Therefore, while they are positively correlated, the size of the movement is different.
Additionally, correlations can change over time. For example, USD/CAD and USD/CHF had a strong positive correlation over the past year, but the relationship deteriorated significantly in the previous month. This could be due to a number of reasons, such as a rally in oil prices or changes in monetary policy.
Where the Ultra-Wealthy Put Their Money
You may want to see also

Negative correlation: Two currency pairs move in opposite directions
A negative correlation between two currency pairs means that they move in opposite directions. For example, if EUR/USD goes up, USD/CHF might go down. This is also known as an inverse correlation.
Negative correlations can be utilised for hedging purposes. For instance, if a trader holds a short position in EUR/USD and a long position in USD/CHF, the risks in each trade may be offset by the other, as these two currency pairs often move in opposite directions.
A strong negative correlation between two currency pairs can also be used to create a hedge. For example, the GBP/USD and EUR/GBP have a strong negative correlation of -90, meaning they move in opposite directions most of the time. Buying or selling both creates a hedge, as gains on one position will be offset by losses on the other.
Negative correlations can also be used to assess the value of a currency pair. For example, CAD pairs are highly correlated to crude oil prices (WTI). If WTI prices rise, there may be an expectation that CAD prices will also increase.
It's important to note that negative correlations can change over time due to various factors such as economic conditions, monetary policy, and geopolitical events. Therefore, it's crucial to monitor up-to-date correlation data when making investment decisions.
Renting: Is Cash Payment an Investment Strategy?
You may want to see also

No correlation: The movement of the currency pairs is random
When deciding how to invest in currencies, it is important to understand the concept of correlation. Correlation refers to the relationship between two currency pairs and how they move in relation to each other. The correlation coefficient, which ranges from \-1 to +1, indicates the degree to which two currency pairs are likely to move in the same, opposite, or completely random directions. A correlation coefficient of zero implies that the relationship between the currency pairs is completely random, or that there is no correlation.
In the context of no correlation, the movement of the currency pairs is unpredictable and has no apparent connection. This means that the values of the currency pairs fluctuate in no particular pattern. For example, if EUR/USD goes up, there is no clear indication of how GBP/USD will move. The changes in one currency pair's value do not cause corresponding changes in the other.
No correlation between currency pairs can occur when the currencies involved in each pair are different or when the economies of the countries involved are distinct and separate. For instance, EUR/JPY and AUD/USD have no matching currencies, and the economies of the Eurozone, Japan, Australia, and the US are all separate. As a result, the correlation between these pairs tends to be lower, and their movements are less likely to influence each other.
It is important to note that even in cases of no correlation, there may still be indirect or complex economic factors at play that influence the movements of the currency pairs. Additionally, the lack of correlation does not mean that the currency pairs will never move in the same or opposite directions; it simply indicates that there is no predictable pattern or relationship between their movements.
Traders should be cautious when dealing with currency pairs that have no correlation. While it may seem that diversifying investments across uncorrelated pairs reduces risk, unexpected movements in one pair could still impact the other. Therefore, it is crucial to continuously monitor and analyze the market, staying up-to-date with any changes in correlations and economic conditions that may influence currency movements.
Understanding Investment Cash Flows: A Timeline Perspective
You may want to see also

Avoid conflicting positions: Correlation can help you avoid entering positions that cancel each other out
Currency correlation is a statistical measure of the relationship between two securities. It is important to understand how different currency pairs move in relation to each other, especially if you are trading more than one pair at the same time.
Currency pairs that have a strong positive correlation will move in the same direction. For example, if EUR/USD goes up, GBP/USD might also go up. On the other hand, currency pairs with a strong negative correlation will move in opposite directions. For instance, if EUR/USD goes up, USD/CHF might go down.
By understanding these relationships, you can avoid entering positions that cancel each other out. For example, if you know that EUR/USD and USD/CHF move in opposite directions almost 100% of the time, then having a portfolio with long positions in both EUR/USD and USD/CHF is the same as having no position at all. This is because when EUR/USD rallies, USD/CHF will undergo a sell-off, and vice versa.
On the contrary, if you consider EUR/USD and NZD/USD, it is like doubling the same position due to the strong positive correlation between the two pairs. So, if you are bullish on the EUR/USD, you can also go long on NZD/USD to increase your exposure to the same directional move.
Correlation coefficients can range from -1 to +1, with -1 being a perfect negative correlation and +1 being a perfect positive correlation. A coefficient of zero implies that the relationship between the currency pairs is completely random.
It is important to note that correlations can change over time due to various factors such as economic conditions, monetary policy, and geopolitical events. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor up-to-date correlation data and not rely solely on long-term correlations.
By understanding and monitoring currency correlations, you can make more informed trading decisions, manage your risk, and avoid entering conflicting positions that may cancel each other out.
Finding Initial Investment: Utilizing Positive Cash Flow Strategies
You may want to see also

Diversify risk: Currency pairs with imperfect positive correlation can be used to diversify your risk
Diversify Risk with Currency Correlation
Currency correlation is a statistical measure of how two currency pairs move in relation to each other. It is an important concept for traders to understand as it can directly impact their trading results, often without their knowledge.
A positive correlation means that the values of two variables move in the same direction, while a negative correlation means they move in opposite directions. A correlation coefficient of +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, with the pairs moving in the same direction 100% of the time. Conversely, a coefficient of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, with the pairs moving in opposite directions 100% of the time.
For instance, the EUR/USD and GBP/USD currency pairs have a strong positive correlation, meaning they tend to move in the same direction. On the other hand, the EUR/USD and USD/CHF pairs have a strong negative correlation, so they tend to move in opposite directions.
Currency pairs with imperfect positive correlation, such as AUD/USD and EUR/USD, can be used to diversify your risk. For example, to express a bearish outlook on the USD, instead of buying two lots of EUR/USD, you could buy one lot each of EUR/USD and AUD/USD. The imperfect correlation between these two pairs allows for more diversification and marginally lowers risk. Additionally, the central banks of these currencies have different monetary policies, so in the event of a dollar rally, the impact on the Australian dollar may differ from that on the euro.
By understanding currency correlation, traders can make more informed decisions when holding multiple currency pairs in their trading accounts. This knowledge can help them diversify their risk, hedge positions, and increase their profit potential.
Robin Hood Investing: A Beginner's Guide to Trading
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Currency correlation is a statistical measure of the extent to which two currency pairs are related in value and move together. It indicates whether currencies tend to move in the same direction, in opposite directions, or with no discernible pattern.
You can calculate correlation using Microsoft Excel. First, find a charting package that provides past or current currency prices. Export this data to Excel, then use the formula =CORREL(range 1, range 2).
Correlation can help you avoid entering conflicting positions, diversify your risk, and hedge your positions. For example, by knowing the correlation between two currency pairs, you can avoid taking positions that cancel each other out or double your risk.