Life insurance is often viewed as a financial product to be considered only in the event of an individual's death. However, life insurance can also be used as an investment tool to provide financial security for you and your family while you are alive. This is achieved through the cash value component of certain life insurance policies, which allows you to withdraw or borrow funds for various purposes. This article will explore how to use investments to replace life insurance by examining the different types of life insurance policies that offer investment opportunities and the benefits and drawbacks of these policies.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Types of permanent life insurance | Whole life insurance, universal life insurance, variable universal life insurance, indexed universal life insurance |
| Whole life insurance features | Fixed premiums, guaranteed death benefit, predictable cash value growth |
| Universal life insurance features | Adjustable premiums, adjustable death benefit, minimum interest rate protection |
| Variable universal life insurance features | Adjustable premiums, adjustable death benefit, choice of subaccounts for cash value investment |
| Indexed universal life insurance features | Adjustable coverage, adjustable premiums, adjustable death benefit, interest rate floor and cap |
| Variable life insurance features | High-risk, high-return, range of investment subaccounts, no adjustable premiums |
What You'll Learn

Whole life insurance as an investment tool
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that lasts for the entirety of the policyholder's life. It is a popular option for those seeking to provide financial security for their loved ones after they pass away. However, whole life insurance also has features that make it a viable investment tool during one's lifetime.
Whole life insurance policies have a cash value component, which accumulates over time at a fixed rate that is guaranteed by the insurer. This cash value grows on a tax-deferred basis, meaning that any interest earned is not taxed as long as the funds remain in the policy. Policyholders can borrow against this cash value or withdraw funds for various purposes, such as paying for major expenses or supplementing retirement income.
One of the key advantages of whole life insurance as an investment tool is the ability to access funds conveniently. Policyholders can take out loans from the insurer, with the cash value serving as collateral. Additionally, the cash value can be withdrawn for income in retirement or to cover expenses like college tuition or a down payment on a house.
Another benefit of whole life insurance is the stability it offers. The premium amount remains the same throughout the policy, regardless of the policyholder's age or health condition. This fixed nature may appeal to individuals with a lower risk tolerance. Furthermore, the cash value grows at a guaranteed rate, providing predictable returns.
However, it is important to consider the drawbacks of whole life insurance. The premiums tend to be significantly higher compared to term life insurance. Additionally, the cash value can take a long time to grow, as insurers initially allocate a large portion of the premiums to fees and administrative costs. The rate of return on the cash value is also relatively low, typically ranging from 1% to 3.5%.
Whole life insurance may be a suitable investment tool for individuals who have maxed out their retirement accounts or those with lifelong dependents, such as children with disabilities. It can also help diversify an investment portfolio by providing stable returns that are not subject to market volatility.
In conclusion, while whole life insurance may not be the right choice for everyone due to its high costs and slow growth, it can serve as a valuable investment tool for individuals seeking stable and guaranteed returns, convenient access to funds, and lifelong coverage.
Investing a Large Cash Gift: Strategies for Long-Term Growth
You may want to see also

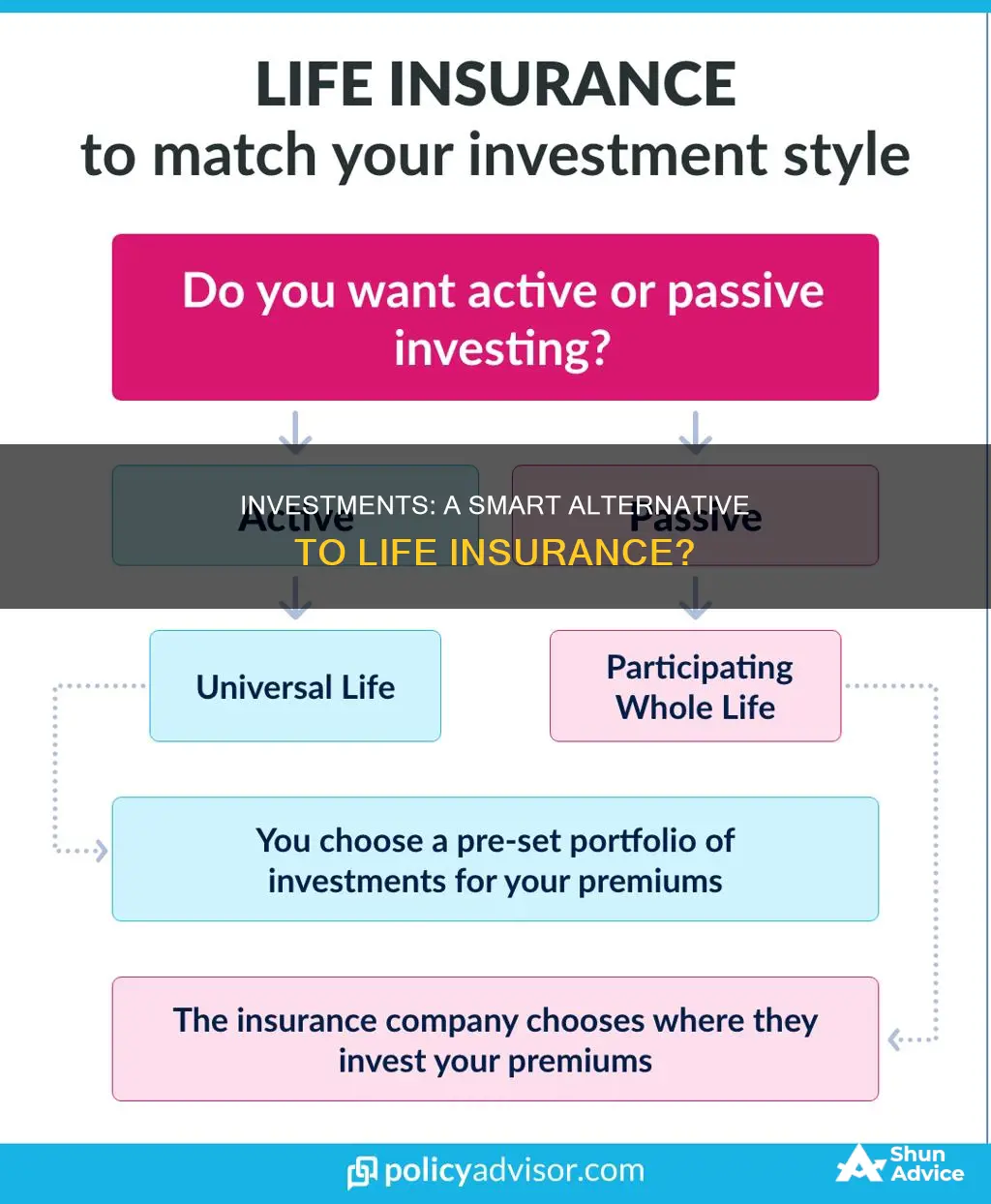
Universal life insurance for flexible coverage
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible coverage. It has a savings element, allowing policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefits. Unlike whole life insurance, which has fixed premiums, universal life insurance premiums can be raised or lowered within certain limits. This makes it a more affordable option for those seeking permanent coverage.
Universal life insurance policies consist of two components: the cost of insurance (COI) and a savings component, known as the cash value. The COI includes charges for mortality, policy administration, and other associated expenses to keep the policy active. The excess premium is added to the cash value, which accumulates interest over time. Policyholders can borrow against or withdraw the cash value, providing a source of funds during their lifetime. However, withdrawals may be taxed, and any unpaid loans or withdrawals will reduce the death benefit paid to beneficiaries.
One of the key advantages of universal life insurance is its flexibility. Policyholders can increase or decrease their coverage as their needs change, without having to purchase a new policy. This flexibility extends to the death benefit as well, allowing policyholders to adjust it according to their circumstances. Additionally, universal life insurance offers the potential for cash value growth, as the cash value earns interest based on the current market or the policy's minimum interest rate.
However, there are also disadvantages to consider. Universal life insurance requires active monitoring of the cash value. If the cash value drops too low, policyholders may have to make large payments to maintain their coverage. Additionally, the returns on the cash value are not guaranteed, and the interest rates can fluctuate. It's important to carefully review the policy details and seek advice from a financial expert before making a decision.
Calculating Initial Investment: Using IRR to Solve
You may want to see also

Variable universal life insurance for investment choice
Variable universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that combines lifelong insurance protection with flexible premiums and a cash value that can be accessed while the policyholder is alive. This type of policy is ideal for those who want to have permanent life insurance protection, have a higher risk tolerance for investing, and prefer to manage their investments.
Variable universal life insurance policies are built like traditional universal life insurance policies but allow you to invest the cash value in the market through subaccounts. These subaccounts operate like mutual funds, and you can choose from a variety of investment options, including stocks, bonds, money market securities, ETFs, and mutual funds. The return on the cash component is not guaranteed year after year, and it is possible to lose money. The growth of the cash value is tax-deferred, and policyholders may access it by taking a withdrawal or borrowing funds.
Variable universal life insurance gives you control over how to invest your cash value. You can pick the subaccounts that best fit your risk tolerance and investment objectives. It offers increased flexibility and growth potential over other life insurance options, but it is important to carefully assess the risks before purchasing it.
Variable universal life insurance policies can charge high fees because you are paying for both life insurance and investments. There may also be a surrender charge where you owe a penalty if you cancel within a certain number of years of purchasing the policy.
Venture Investing: When to Take the Plunge?
You may want to see also

Indexed universal life insurance for investment growth
Indexed universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides a death benefit alongside a cash value component. The cash value component of indexed universal life insurance can be invested to achieve growth.
How Indexed Universal Life Insurance Works
Indexed universal life insurance works similarly to universal life insurance. You pay a premium in exchange for lifelong coverage and the opportunity to build cash value over time. The premium payments go towards the cost of insurance and other fees, and the remainder is added to the cash value.
Adjustable Premiums and Death Benefit
Indexed universal life insurance premiums are adjustable. If you skip a premium payment or underpay, the cost of insurance and policy expenses are deducted from your cash value. You may also be able to adjust the death benefit amount, but this may require a medical exam.
Cash Value Earnings
The cash value in indexed universal life insurance policies can earn interest in two ways: through a fixed interest rate or by tracking the performance of stock and bond indexes. Policyholders can choose to allocate the cash value to a fixed account, an indexed account, or a combination of both.
Advantages of Indexed Universal Life Insurance
- Control: Policyholders can increase or decrease premium payments and coverage amounts to suit their needs and financial situation.
- Stock market-driven returns: The cash value grows when the market grows, and this growth is often tax-deferred.
Disadvantages of Indexed Universal Life Insurance
- Risk: The indexes may not rise as expected, resulting in lower returns than anticipated.
- Effort: Close monitoring of the policy is required, especially during periods of low returns, as additional payments may be needed to prevent the policy from lapsing.
- Capped returns: Caps and participation rates limit the ability to fully benefit from market gains.
- Fees: Indexed universal life insurance coverage fees can increase over time and may reduce the value of the policy.
Investment Bankers: Using DCF for Smart Decisions
You may want to see also

Variable life insurance for high-risk, high-reward
Variable life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance policy that lasts for the entirety of the policyholder's life, provided that the premiums are paid. It has a higher potential for earning cash compared to traditional policies as the policyholder gets to decide how to invest the cash value.
Variable life insurance policies have three primary components: a death benefit, the policy's cash value, and the investment of the cash value. The death benefit is left to the beneficiaries, while a portion of the premium payments goes towards the policy's cash value, which can be invested in certain securities, often called subaccounts, which resemble mutual funds. The cash value can be used to increase the death benefit, withdrawn as cash, or used as collateral for a loan.
Variable life insurance carries more risk compared to other life insurance policies as the cash value component is invested in assets like mutual funds, meaning it may rise or fall in value. However, investors who can assume this additional risk may prefer variable policies for their tax advantages. Returns on variable policies can provide tax-free income, and the growth of the cash value account is not taxable as ordinary income.
Variable universal life insurance is a type of variable life insurance that offers the policyholder flexibility in how much of a premium they pay. It also has a cash value structure that can be used to pay premiums.
Variable life insurance policies are complex and require more hands-on attention. They also typically have higher premiums than other cash value life insurance policies.
A Beginner's Guide to Investing with E-Trade
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are two main types of permanent life insurance that can be used as an investment: whole life insurance and universal life insurance. Whole life insurance is a permanent policy that lasts the entire life of the policyholder and offers the ability to accumulate cash value in a tax-deferred account. Universal life insurance is also a permanent plan but offers more flexibility, allowing the policyholder to increase or reduce premiums, cash value, and death benefits as needed.
Using life insurance as an investment offers several benefits, including tax advantages, asset protection, and potential income streams. The cash value in a life insurance policy grows tax-deferred, and death benefits are generally income-tax-free for beneficiaries. Life insurance policies are also protected from creditors in many states, making them a valuable tool for asset protection. Additionally, policyholders can borrow against the policy's cash value or withdraw funds to supplement their retirement income.
Some potential drawbacks of using life insurance as an investment include high costs, slow growth of cash value, low rates of return, and limited flexibility. Life insurance policies with an investment component tend to have high premiums, and it can take a significant amount of time for the cash value to accumulate. The cash value rate of return is also typically lower compared to other investments, and some types of permanent life insurance have limited flexibility in adjusting premium payments and death benefits.
To maximize the investment potential of your life insurance policy, consider the following strategies: Diversify your investment portfolio by including permanent life insurance to spread financial risks. Use life insurance to limit financial risk and provide a steady growth option. Utilize the cash value component of your policy as an additional income stream during retirement through policy loans and withdrawals. Consult a financial professional to ensure you are making informed investment decisions and maximizing your returns.







