Passive investing is a long-term strategy for building wealth by buying securities that mirror stock market indexes and holding them for long periods. It is a popular investment strategy that aims to maximise returns by minimising the costs of buying and selling securities. Passive investing is typically done by investing in a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that mimics the index's holdings. This strategy is less expensive and complex than active management, and it often produces superior after-tax results over medium to long time horizons.
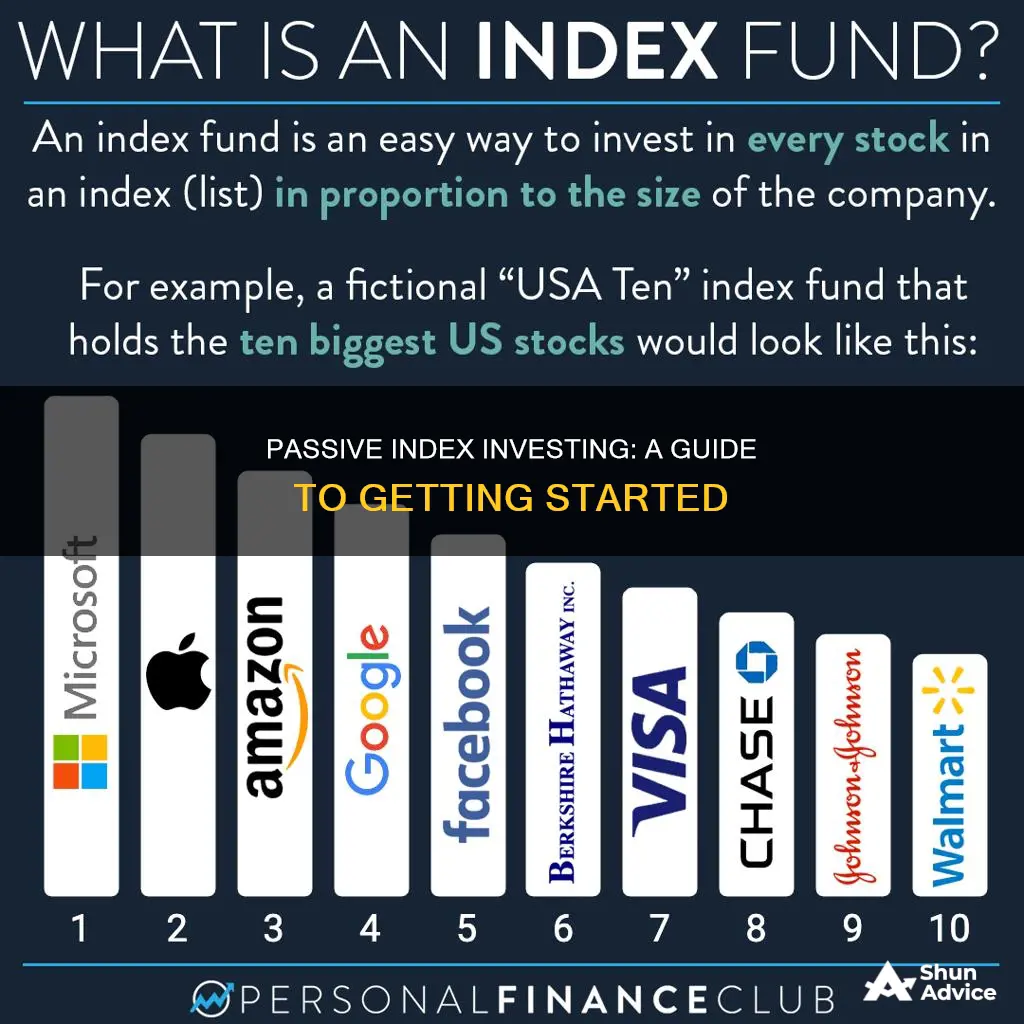
The most common type of passive investing is index investing, where investors seek to invest in a portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets that replicate a particular market index. Index funds are a type of passive fund whose investment securities are automatically selected to match an index or part of the market. They offer low-cost returns that are aligned with the market through mirroring benchmark investments.
Passive investing has several benefits, including lower fees, lower risk, and steady returns. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, as it may not provide above-market returns and has limited investment options.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Investment strategy | To build wealth over the long term |
| Buying and selling | Less frequent buying and selling of investments |
| Investment type | Broad-based market index or benchmark |
| Investment goals | To match the returns of a specific market index or benchmark |
| Investment funds | Mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) |
| Investment costs | Lower transaction costs and management fees |
| Investment horizon | Long-term |
| Investment risk | Lower risk due to a diverse portfolio |
| Investment research | Less research required |
| Investment selection | No need to select individual securities |
| Investment changes | Limited ability to make short-term changes |
| Investment returns | May not achieve above-market returns |
What You'll Learn
- Passive index investing is a long-term strategy
- It involves buying securities that mirror stock market indexes
- Passive investing is typically done by investing in a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF)
- Passive investing aims to reduce costs and simplify portfolio construction
- Passive investing is tax-efficient

Passive index investing is a long-term strategy
Passive investing is a long-term strategy for building wealth. It involves buying securities that mirror stock market indexes like the S&P 500 or the FTSE 100 and holding them for the long term. This strategy aims to maximise returns by minimising the costs of buying and selling securities.
Passive investing is typically done by investing in a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that mimics the index's holdings. This means investors don't have to actively hunt for investments, reducing the costs of selecting investments. Passive investing is also less complex and often produces superior after-tax results over medium to long time horizons.
The key to this strategy is to hold securities for relatively long periods, allowing wealth to build gradually over time. By avoiding frequent trading, passive investors reduce costs in the form of transaction fees, commissions, and taxable capital gains.
Passive investing is a popular strategy, particularly for investors with limited time, experience, or interest in actively managing their investments. It is also attractive for those seeking a hands-off approach with lower fees and greater tax efficiency.
There are several ways to implement passive investing, including index funds and ETFs. Index funds are a common choice for passive investors as they simply track the rise and fall of chosen companies or assets within an index. ETFs, on the other hand, offer more flexibility as they can be traded during market hours like stocks.
Overall, passive investing as a long-term strategy offers a straightforward approach to investing, providing diversification and reduced costs for investors.
Investing Before Elections: Cash or Risk?
You may want to see also

It involves buying securities that mirror stock market indexes
Passive investing is a long-term strategy for building wealth. It involves buying securities that mirror stock market indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and holding them for a long time. This approach aims to maximise returns by minimising the costs of buying and selling securities.
Index investing is a common form of passive investing. With index investing, investors seek to replicate and hold a broad market index or a specific sector. Index funds are created to track the performance of these indexes. These funds incorporate securities that closely mimic those found in an index, allowing investors to bet on its performance for a fee.
For example, the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) closely mirrors the S&P 500 Index. This means that investors can gain exposure to a broad, diversified portfolio of the 500 largest US companies by purchasing shares of this fund.
Index funds are typically mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Mutual funds pool money from investors to buy a portfolio of stocks or bonds, while ETFs are traded on exchanges like individual stocks. ETFs offer more trading strategies, such as timing share trades and using limit or stop-loss orders.
Passive investing has several benefits. It is a low-maintenance strategy, as investors do not need to constantly track the performance of their investments. It also offers steady returns, lower fees, lower capital gains taxes, and lower risk due to the diversification of asset classes and industries.
However, there are also some drawbacks to passive investing. One is the lack of flexibility, as investors are locked into the holdings of the index, regardless of market conditions. Another disadvantage is the potential for underperformance compared to actively managed funds, as passive funds aim to match the market average rather than outperform it.
Smart Ways to Invest a Windfall of $300K
You may want to see also

Passive investing is typically done by investing in a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF)
Passive investing is a long-term strategy for building wealth by purchasing securities that mirror stock market indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and holding them for extended periods. This approach is typically executed through investment in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that replicate the composition of a chosen market index.
Mutual funds and ETFs are both types of investment funds that pool money from numerous investors to purchase a diverse range of assets. However, they differ in certain structural and operational aspects.
Mutual funds are typically bought and sold at the end of the trading day and are priced after the market closes, based on the net asset value of the fund. They are considered less tax-efficient due to higher turnover and more frequent capital gains distributions. Mutual funds also tend to have higher management fees, as they are actively managed by fund managers who make allocation decisions and conduct trades to optimise the fund's performance.
On the other hand, ETFs are traded on stock exchanges throughout the day, just like individual stocks. This intraday trading feature provides investors with greater flexibility and control over their investments. ETFs are often passively managed, aiming to replicate the performance of a specific index. They have lower expense ratios, increased transparency, and greater tax efficiency compared to actively managed funds. The passive nature of ETFs means they have lower management fees since there is no active decision-making involved.
When considering passive investing, it is essential to understand the differences between mutual funds and ETFs to make an informed decision that aligns with your investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferences for control and flexibility.
Transferring Cash Investments: Charles Schwab to Schwab
You may want to see also

Passive investing aims to reduce costs and simplify portfolio construction
Passive investing is a long-term strategy for building wealth. It involves buying securities that mirror stock market indexes and holding them for a long time. This type of investing aims to reduce costs and simplify portfolio construction.
Passive investing seeks to reduce the costs of selecting investments by simplifying the portfolio construction process. It also reduces fees triggered by frequent trading. Index mutual funds, which are commonly used in passive investing, are larger on average than actively managed funds, so economies of scale help lower relative costs.
Passive investing typically involves investing in a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that mimics the index's holdings. This means that investors do not need to actively research and select individual securities. Instead, they buy and sell the investments that their target benchmark trades. This simplifies the process of constructing a portfolio.
In addition, passive investing often employs a long-term, buy-and-hold approach, where securities are held for relatively long periods. This strategy aims to build wealth gradually and reduce costs in the form of transaction fees, commissions, and taxable capital gains.
By simplifying the portfolio construction process and reducing fees, passive investing can be a cost-effective and less complex approach to investing.
Invest to Own: Saving for a Down Payment
You may want to see also

Passive investing is tax-efficient
Passive investing is a strategy that aims to maximise returns by minimising the costs of buying and selling securities. It is typically done by investing in a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that mimics the index's holdings. This approach is less expensive and complex than active management and often produces superior after-tax results over medium to long time horizons.
Index funds, a common form of passive investing, are also tax-efficient because they do not require costly research to pick securities, and they tend to be less expensive to operate than actively managed funds. The buy-and-hold strategy of index funds also means they generate low or no taxable capital gains annually for shareholders.
Trading with Investing.com: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Passive index investing is a long-term investment strategy that focuses on buying and holding a diverse range of investments, typically seeking to match the returns of a specific broad-based market index or benchmark. It aims to build wealth gradually over time by relying on the market to provide positive returns.
Passive index investing offers several benefits, including lower fees, lower risk, and steady returns. It is also a lower-maintenance strategy as there is no need to constantly track the performance of your investments. Additionally, passive investing can be tax-efficient due to the buy-and-hold approach, which results in lower capital gains taxes.
To start passive index investing, you can invest in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that follow a passive investment strategy. These funds aim to track a specific market index or benchmark. You will need to open a brokerage account that allows you to buy and hold passive investment funds.







