A company's cash flow statement is a crucial indicator of its financial health and operational efficiency. One of the three main sections of a cash flow statement is cash flow from investing activities, which includes the purchase and sale of long-term assets and other business investments. An increase in inventory, for instance, is reflected in the operating section of the cash flow statement. When a company purchases inventory-related items, the inventory balance increases, representing a cash outflow. This increase in inventory is shown as a negative amount in the cash flow statement, indicating that the company has purchased more goods than it has sold. On the other hand, a decrease in inventory balance represents a cash inflow and is considered a positive amount. Proper inventory planning and risk mitigation are crucial for effective cash flow management.
What You'll Learn
- An increase in inventory is shown as a negative amount on the statement of cash flows
- Inventory generates cash flow but purchasing inventory requires a cash outlay
- An increase in inventory indicates a company has bought more goods than it has sold
- Inventory turnover improves business cash flow when items are turning over and not sitting on shelves
- A company's cash flow statement summarises the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving

An increase in inventory is shown as a negative amount on the statement of cash flows
The statement of cash flows (or CFS) is one of the three main financial statements used by companies, alongside the balance sheet and the income statement. The CFS provides an overview of a company's cash management, including how well it generates cash. It is a valuable measure of a company's strength, profitability, and long-term future outlook.
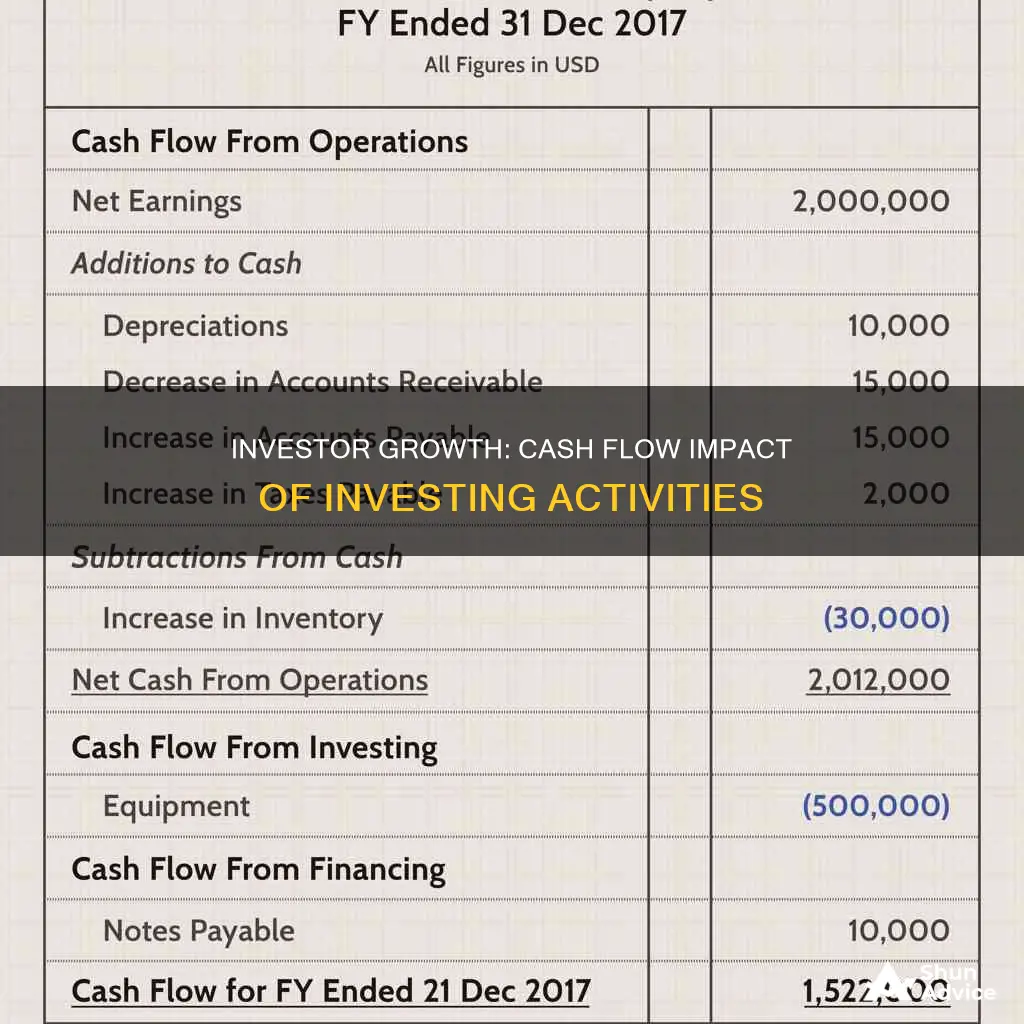
The CFS is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities include any sources and uses of cash from business activities, such as receipts from sales, payments to suppliers, and salary and wage payments. Investing activities include sources and uses of cash from a company's investments, such as purchases or sales of assets, loans, or payments related to mergers and acquisitions. Financing activities include sources of cash from investors and banks, as well as cash paid to shareholders, such as dividends or debt repayments.
An increase in inventory would be reflected in the operating section of the CFS. When a company purchases inventory-related items, it increases the inventory balance and represents a cash outflow. This outflow of cash is recorded as a negative amount on the CFS. Conversely, when items are sold, the inventory balance decreases, and the sale is recognized as a cash inflow, which is recorded as a positive amount on the CFS.
Proper inventory planning and management are crucial for effective cash flow management. Holding more inventory than needed can tie up available cash, while efficient inventory turnover improves cash flow by ensuring items are sold and not sitting unsold on shelves.
Cashing Out Your GCash Investments: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Inventory generates cash flow but purchasing inventory requires a cash outlay
Inventory management is a critical aspect of a company's cash flow. Inventory generates cash flow, but purchasing inventory requires a cash outlay, impacting the company's cash balance. An increase in inventory is shown as a negative amount in the cash flow statement, indicating that the company has purchased more goods than it has sold and represents a cash outflow. On the other hand, a decrease in inventory is positive for cash flow, as it indicates a cash inflow.
The correlation between inventory and cash flow is influenced by inventory stock levels, inventory turnover, and the chosen inventory accounting method. Proper inventory planning and risk mitigation are crucial for effective cash flow management. Inventory turnover, calculated using the cost of goods sold (COGS) or the average of beginning and ending inventory, is a key measure of business performance. High inventory turnover implies strong sales and efficient inventory control, positively impacting cash flow.
From an accounting perspective, changes in inventory are reflected in the operating section of the cash flow statement. An increase in inventory is a cash outflow, while a decrease in inventory is a cash inflow.
Investing activities, including purchases and sales of long-term assets and other business investments, are a separate section of the cash flow statement. While purchases of inventory are not typically considered investing activities, they can be classified as capital expenditures if they are for the acquisition of fixed assets.
Overall, effective inventory management is essential for optimising cash flow, ensuring that the business has sufficient stock to meet demand while avoiding excess inventory that ties up cash.
Cashing Out Your SoFi Investment: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

An increase in inventory indicates a company has bought more goods than it has sold
Inventory management is crucial for a business's cash flow. Holding more inventory than is needed for current sales forecasts and demand means using available cash to pay for surplus inventory, and converting current cash into non-cash assets. Effective inventory planning and risk mitigation can help businesses manage their cash flow more effectively.
Inventory turnover is a key measure of how well a business is doing. A high inventory turnover ratio indicates strong sales and efficient inventory control, while a low ratio suggests poor inventory control. Businesses can improve inventory turnover by implementing proper stock control, which will reduce costs and increase cash in the bank.
Inventory accounting methods also play a role in the correlation between inventory and cash flow. For example, the Last In, First Out (LIFO) and First In, First Out (FIFO) methods can impact the value of inventory on a company's balance sheet and, consequently, its cash flow.
Overall, an increase in inventory indicates that a company has purchased more goods than it has sold, resulting in a negative impact on its cash flow statement and cash balance.
Invest Your Weekly Cash Wisely: A Guide to Getting Started
You may want to see also

Inventory turnover improves business cash flow when items are turning over and not sitting on shelves
Inventory management and cash flow are closely linked. Inventory generates cash flow, but purchasing inventory requires a cash outlay that affects the company's cash balance. An increase in inventory is shown as a negative amount in the cash flow statement, indicating a cash outlay or that the business has bought more goods than it has sold.
Inventory turnover is a key measure of how well a business is doing. The inventory turnover ratio determines the number of times inventory stock is bought and sold within the company's financial year. A high inventory turnover ratio implies strong sales and requires increasingly efficient inventory control to meet high demand and respond to market needs.
A low inventory turnover ratio, on the other hand, may be a sign of weak sales or excess inventory. This could indicate a problem with a retail chain's merchandising strategy or inadequate marketing. A low inventory turnover ratio means the product is not selling well.
Businesses should aim for a high inventory turnover ratio, as this reduces the amount of capital tied up in inventory. It also helps increase profitability by increasing revenue relative to fixed costs.
To improve inventory turnover, businesses can implement proper stock control, which will help reduce the cost of goods sold, positively impacting cash flow and resulting in more cash in the bank.
Strategies for Investing Cash Without IRS Attention
You may want to see also

A company's cash flow statement summarises the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving
A company's cash flow statement is one of its most important financial statements, summarising the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving the business. It provides an overview of a company's financial health and operational efficiency, and is used by investors and creditors to assess the company's liquidity and ability to manage its expenses and debts.
The cash flow statement is usually divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
Operating Activities
This section covers the cash flow associated with the company's core business operations, including:
- Receipts from sales of goods and services
- Payments to suppliers
- Salary and wage payments
- Other operating expenses
- Changes in cash, accounts receivable, depreciation, inventory, and accounts payable
Investing Activities
This section includes the sources and uses of cash from a company's investments, such as:
- Purchases or sales of assets
- Loans made to or received from vendors or customers
- Payments related to mergers and acquisitions
- Changes in equipment, assets, or investments
Financing Activities
This section details the cash flow from financing activities, including:
- Sources of cash from investors and banks
- Cash paid to shareholders, such as dividends and stock repurchases
- Repayment of debt principal
Calculating Cash Flow
There are two methods for calculating cash flow: the direct method and the indirect method. The direct method involves listing all cash receipts and payments during the reporting period, while the indirect method starts with net income and adjusts for changes in non-cash transactions.
Inventory and Cash Flow
An increase in inventory is usually shown as a negative amount in the statement of cash flows, as it indicates that the company has purchased more goods than it has sold, resulting in an additional outflow of cash. Conversely, a decrease in inventory is considered a positive amount, as it represents a cash inflow.
A Windfall's Wise Investment: Strategies for Sudden Cash
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A cash flow statement summarises the inflow and outflow of cash, providing insights into a company's financial health and operational efficiency.
The main components of a cash flow statement are cash from three areas: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
Investing activities involve the purchase and sale of long-term assets and other business investments within a specific reporting period. They are directly related to the growth of a business and bring in profits in the long run.
An increase in inventory is reflected as a negative amount in the operating section of a cash flow statement, indicating an outflow of cash.
Inventory management has a direct impact on the cash flow of a business. Proper inventory planning and risk mitigation can help businesses manage cash flow effectively.