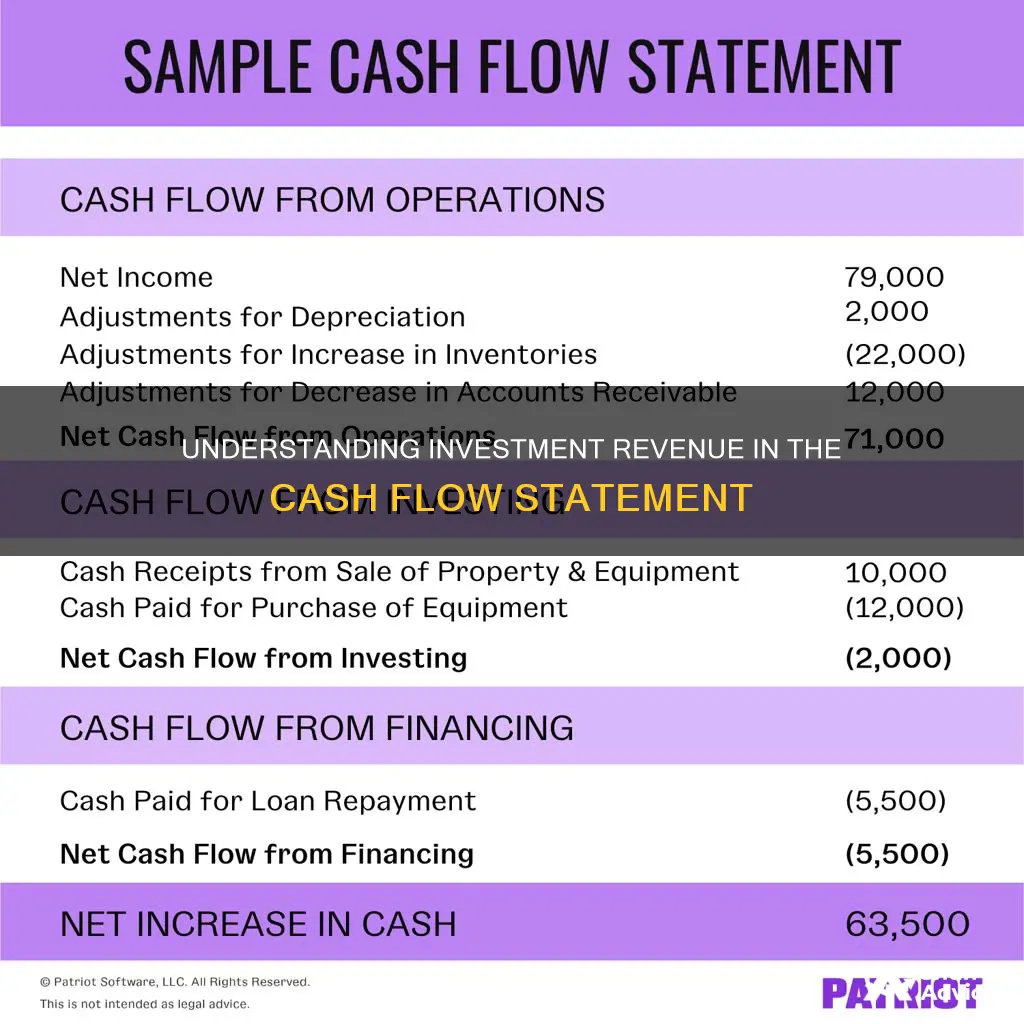
A company's cash flow statement is a financial document that provides a detailed analysis of the cash flow into and out of a business over a specific period. It is one of the three main financial statements, alongside the balance sheet and the income statement. The cash flow statement is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
Operating activities refer to the cash flow generated from a company's regular products or services, including revenue and expenses. Investing activities refer to the cash flow from purchasing or selling assets, including physical property and non-physical property. Financing activities refer to the cash flow from debt and equity financing.
The cash flow statement is an important tool for investors, creditors, business owners, and managers as it provides insights into a company's financial health, operational efficiency, and liquidity. It helps determine whether a company has enough cash to fund its operating expenses, pay down its debts, and make investments.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Investment revenue is the net cash generated from a company's investment-related activities. |
| Examples of Activities | Investments in securities, purchase of physical assets, sale of securities or assets |
| Sections of Cash Flow Statement | Investing activities is one of the three sections of a cash flow statement, the other two being operating activities and financing activities |
| Calculation Methods | Direct method, indirect method |
| Reporting Period | Monthly, quarterly, annually |
What You'll Learn

Operating cash flow
OCF is a key component of a company's cash flow statement, which provides a detailed picture of the cash flow generated by a company's operations over a specific period. The cash flow statement is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities refer to the cash flow generated by a company's core business operations, including revenue and expenses.
The direct method for calculating OCF involves tracking all transactions over a period on a cash basis, using actual cash inflows and outflows. The indirect method, which is more commonly used, starts with net income and then adds non-cash items to arrive at a cash basis figure.
A positive OCF indicates that a company's operations are generating sufficient cash to meet its reinvestment needs, such as working capital and capital expenditures. On the other hand, a negative OCF means that a company may need to seek external financing to meet its spending requirements.
OCF is an important metric for financial analysts, investors, and lenders. It provides insight into a company's overall health, profitability, and ability to generate a return on investment. A company with a healthy OCF is generally considered to be in a stronger financial position.
Strategies for Cashing Out Investments: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Investing cash flow
- Acquiring and disposing of assets
- Investing in securities
- Acquiring other companies
- Loans made to and collected from third parties
It is important to note that investing cash flow does not include short-term investments or cash equivalents, which are classified under operating activities.
The calculation of investing cash flow involves subtracting total cash outflows from total inflows related to investing activities, resulting in a net cash flow figure. This calculation provides insight into a company's capital expenditure and investment strategies, allowing stakeholders to assess its ability to invest in growth opportunities, acquire assets, and manage its long-term financial health.
A positive net cash flow from investing activities indicates that a company is generating more cash from its investing activities than it is spending. This suggests effective management of investments and strategic decisions to enhance future growth and profitability. On the other hand, negative cash flow does not always indicate poor financial health. It may signify that the company is investing in assets, research, or long-term development activities that are crucial for its health and continued operations.
Understanding Cash Flow: Investing Activities Explained
You may want to see also

Financing cash flow
The financing activities section of a company's cash flow statement includes the following:
- Issuance and repayment of debt
- Issuance and repayment of equity
- Payment of dividends
- Capital lease obligations
- Share repurchases
The formula for calculating financing cash flow is:
> CFF = CED − (CD + RP)
Where:
- CFF = Cash Flow from Financing Activities
- CED = Cash inflows from issuing equity or debt
- CD = Cash paid as dividends
- RP = Repurchase of debt and equity
Schwab's Cash Investment Options: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Cash flow from physical assets
Cash flow statements are one of the three key financial statements that provide a detailed picture of what happened to a business's cash during a specified period. They are important because they show how a company is allocating cash for the long term and indicate its ability to operate in the short and long term.
Cash flow from investing activities (CFI) is one of the sections of a company's cash flow statement. It reports how much cash has been generated or spent from various investment-related activities in a specific period. These activities include the purchase of physical assets, investments in securities, or the sale of securities or assets.
Physical assets are long-term assets that will deliver value in the future. They are also referred to as fixed assets, which are assets that last longer than a financial reporting period. Examples include property, plant, and equipment (PPE), vehicles, furniture, buildings, or land.
A positive cash flow from investing activities indicates that a company is investing in its long-term health and future growth. This is often a positive sign, even if it results in negative cash flow in the short term. For example, a company may invest in research and development (R&D) or acquire new physical assets to improve its operations and products.
On the other hand, a negative cash flow from investing activities could indicate that a company is selling off its physical assets or other investments to cover operating expenses, which is typically unsustainable in the long term.
Calculating and tracking cash flow from physical assets is crucial for understanding a company's financial health and making informed investment decisions. It helps determine the actual value of the company and provides insights into its ability to pay off debt and manage its capital structure.
Cash vs Investing: Is Holding Cash Ever Better?
You may want to see also

Cash flow from securities
Cash flow from investing activities (CFI) is one of the sections of a company's cash flow statement. It reports how much cash has been generated or spent from various investment-related activities over a specific period.
CFI is an important aspect of a company's growth and capital. It includes the acquisition and disposal of non-current assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents. Investing activities can include the purchase or sale of physical assets, such as property, or non-physical property, like patents. It also includes the purchase or sale of securities, which are a type of financial asset.
A company's cash flow statement reflects its ability to operate in the short and long term. It is one of the three main financial statements, alongside the balance sheet and the income statement. The cash flow statement bridges the gap between the income statement and the balance sheet by showing how cash moves in and out of the business.
The cash flow statement is typically divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities refer to the cash flow generated from a company's regular products or services, including revenue and expenses. Investing activities include cash flow from the purchase or sale of assets. Financing activities detail cash flow from debt and equity financing.
When it comes to cash flow from investing activities, there are a variety of transactions that can impact this section of the cash flow statement. These include:
- Purchase of fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E)
- Sale of fixed assets
- Purchase of investments, such as stocks or securities
- Sale of investment securities
- Collection of loans and insurance proceeds
It's important to note that negative cash flow from investing activities does not always indicate poor financial health. It could mean that the company is investing in assets, research, or other long-term initiatives that are crucial for the company's health and continued growth.
Cash Outflow for Land Purchase: Investing Activity?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A cash flow statement is a financial document that provides a detailed picture of the cash that entered and left a business during a specific period. It is usually broken down into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
The investing activities section includes any sources and uses of cash from a company's investments. This covers the purchase or sale of assets, loans made to or received from vendors, and payments related to mergers and acquisitions.
Revenue is the total income generated by a company from the sale of goods or services, while cash flow is the net amount of cash being transferred into and out of a company. Revenue is a measure of sales and marketing effectiveness, and cash flow is a liquidity indicator.
There are two methods for calculating cash flow: the direct method and the indirect method. The direct method involves listing all cash receipts and payments during the reporting period. The indirect method starts with net income and adjusts for changes in non-cash transactions.







