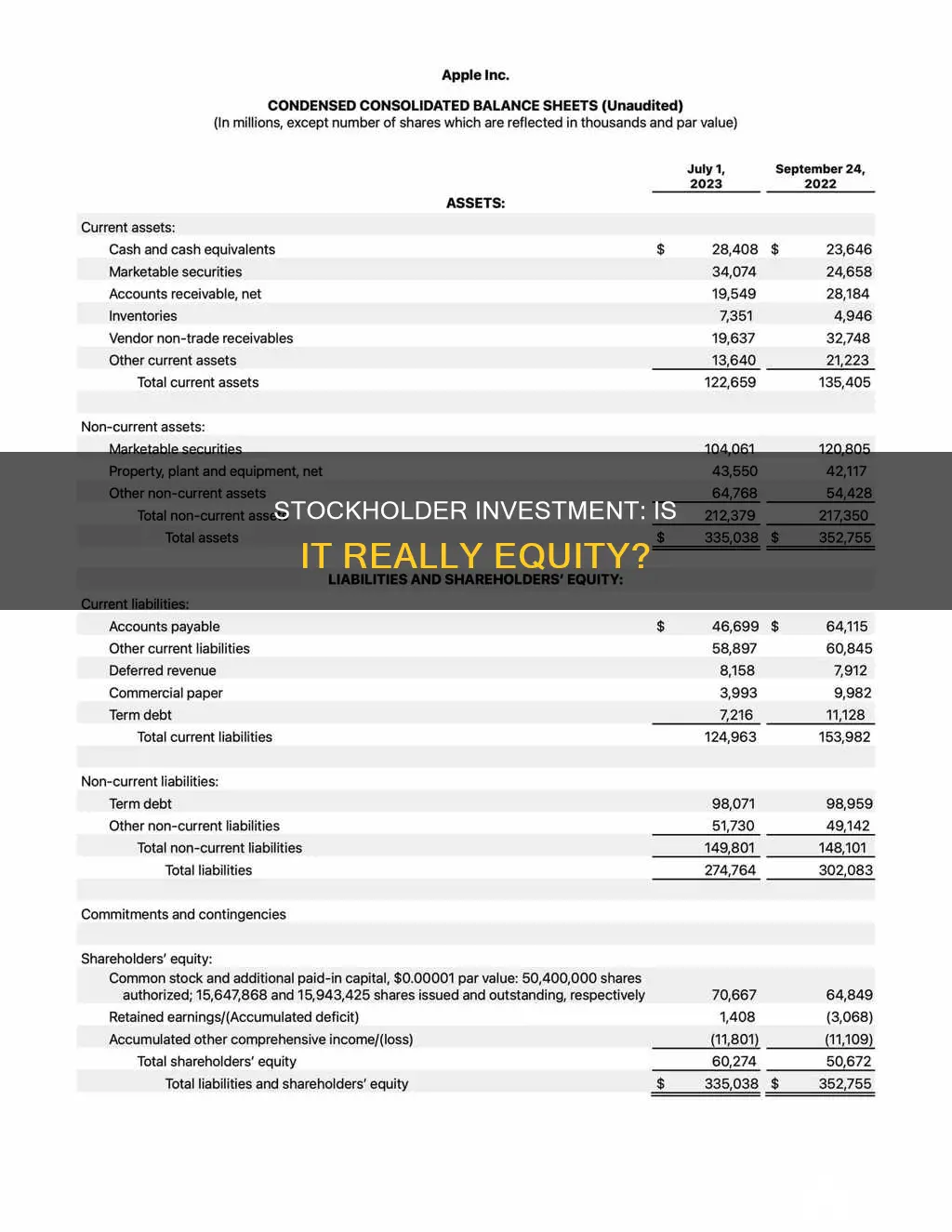
Stockholder investment is considered equity. Stockholders' equity, also known as shareholders' equity, represents the value of a company's assets after all its liabilities have been settled. It is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets, or by summing up share capital and retained earnings and then subtracting treasury shares. Stockholders' equity is a useful metric for investors to determine a company's financial health and stability. It can indicate whether a company has enough assets to cover its liabilities or if it is at risk of bankruptcy.
What You'll Learn
- Stockholder equity is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets
- It can also be calculated by adding share capital and retained earnings, then subtracting treasury stock
- Positive stockholder equity indicates a company's financial health
- Negative stockholder equity may suggest a company is at risk of bankruptcy
- Stockholder equity is useful for judging the funds retained within a business

Stockholder equity is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets
Stockholder equity, also known as shareholder equity, is a company's net worth. It is the amount of money that would be returned to stockholders if the company's assets were liquidated and all its debts paid off. Stockholder equity is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets.
Calculating Stockholder Equity
The formula for calculating stockholder equity is:
> Stockholder Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
This formula is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. All the information required to calculate stockholder equity is available on a company's balance sheet.
To calculate stockholder equity, you need to:
- Locate the company's total assets on the balance sheet for the period.
- Total all liabilities, which should be listed separately on the balance sheet.
- Locate the total stockholder's equity and add this number to the total liabilities.
- The total assets will equal the sum of liabilities and total stockholder equity.
Types of Assets
Total assets include both current and non-current assets. Current assets are those that can be converted to cash within a year, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. Non-current assets are long-term assets that cannot be converted to cash or consumed within a year, such as investments, property, equipment, and intangibles like patents.
Types of Liabilities
Total liabilities include both current and long-term liabilities. Current liabilities are debts typically due for repayment within one year, such as accounts payable and taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are obligations due for repayment over periods longer than one year, such as bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations.
Uses of Stockholder Equity
Stockholder equity is a useful metric for analysts and investors to determine a company's financial health and net worth. It is also used to calculate the return on equity (ROE), which measures how well a company's management uses its equity from investors to generate profits.
Positive vs. Negative Stockholder Equity
Stockholder equity can be either positive or negative. Positive stockholder equity means the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities. Negative stockholder equity means the company's liabilities exceed its assets, which may indicate impending bankruptcy or balance sheet insolvency.
Components of Stockholder Equity
Stockholder equity has three main components: share capital, retained earnings, and treasury shares. Share capital refers to the money invested in the company through share offerings. Retained earnings are the profits accumulated by the company over time through its operations, which are reinvested into the company. Treasury shares are issued by the company and later reacquired; their cost is deducted from stockholder equity.
BlackRock Investment Management: A Force to be Reckoned With?
You may want to see also

It can also be calculated by adding share capital and retained earnings, then subtracting treasury stock
Stockholder investment is considered equity. Stockholders' equity, also known as shareholders' equity, is the remaining assets available to shareholders after all liabilities are paid. It is calculated as a firm's total assets less its total liabilities. Alternatively, it can be calculated by adding share capital and retained earnings, then subtracting treasury stock.
Share capital refers to amounts received by the reporting entity from transactions with its owners. It is also known as contributed capital or paid-in capital. Share capital is divided into two separate accounts: common stock and preferred stock. Common stock represents residual ownership in a company, and in the event of liquidation or dividend payments, common stockholders are only paid after preferred shareholders. Preferred stockholders are those who enjoy certain privileges over common stockholders, such as priority in receiving dividends.
Retained earnings refer to the cumulative earnings of a company minus dividends distributed to shareholders. They are the profits that are not distributed as dividends to stockholders but are instead allocated for reinvestment in the business. Retained earnings can be used for funding working capital, fixed asset purchases, or debt servicing, among other things.
Treasury stock refers to previously outstanding stock that has been bought back from stockholders by the issuing company. The result is that the total number of outstanding shares on the open market decreases. Treasury stock is not included in the distribution of dividends or the calculation of earnings per share. It is also known as treasury shares or reacquired stock.
The formula for calculating stockholders' equity is as follows:
Stockholders' Equity = Share Capital + Retained Earnings - Treasury Stock
This formula is known as the investor's equation. It sums up the retained earnings of the business and the share capital, then subtracts the treasury shares.
Stockholders' equity is an important metric for determining a company's financial health and net worth. A positive stockholders' equity indicates that a company has enough assets to cover its liabilities, while a negative stockholders' equity may signal an impending bankruptcy, especially if there is also a large debt liability.
Time Management: Can You Handle Your Investments Personally?
You may want to see also

Positive stockholder equity indicates a company's financial health
Stockholder equity, also known as shareholders' or owners' equity, is the remaining assets available to shareholders after all liabilities are paid. It is calculated as a firm's total assets minus its total liabilities. Alternatively, it can be calculated as the sum of share capital and retained earnings minus treasury shares.
Positive stockholder equity indicates that a company's assets exceed its liabilities, meaning it has enough assets to cover its liabilities. This is a positive sign of a company's financial health.
Stockholder equity is frequently used by analysts and investors to determine a company's general financial health. It is also referred to as the book value of the company.
Stockholder equity is influenced by several components:
- Share Capital - Amounts received by the company from transactions with shareholders.
- Retained Earnings - Amounts earned through income that are not distributed as dividends but instead are reinvested in the business.
- Net Income and Dividends - Net income increases retained earnings, while dividend payments reduce retained earnings.
Positive stockholder equity indicates that a company is in a healthy financial position, with its assets exceeding its liabilities. This can provide reassurance to investors and analysts that the company is financially stable and has the ability to cover its debts.
However, it is important to note that stockholder equity alone may not provide a complete picture of a company's financial health. Investors and analysts often use other tools and metrics in conjunction with stockholder equity to accurately analyse a company's financial performance and make informed investment decisions.
How Investment Management Interviews Differ: What to Expect
You may want to see also

Negative stockholder equity may suggest a company is at risk of bankruptcy
Stockholder equity, also known as shareholders' equity, is an account on a company's balance sheet. It represents the residual value of assets minus liabilities. In other words, it is the owners' claim on the assets of a company after debts have been settled.
Stockholder equity is calculated by taking the company's total assets and subtracting its total liabilities. It can also be calculated by taking the sum of share capital and retained earnings, less treasury stock.
Stockholder equity is a critical measure when investing in a stock as it reveals a company's net worth. If a company has negative stockholder equity, it means that its debts exceed its assets. This is a warning sign for investors as it suggests the company is financially distressed and could be at risk of bankruptcy.
In the event of liquidation, equity holders are last in line behind debt holders to receive any payments. This means that, in the case of negative stockholder equity, shareholders will receive nothing when assets are liquidated and used to pay debts.
Negative stockholder equity can be caused by several factors, including accumulated losses over several periods, large dividend payments, or excessive debt incurred to cover losses.
While negative stockholder equity is a red flag, it is not always a definitive indicator of a company's financial health. For example, young companies may start with negative equity as they borrow money to invest in their business. These companies can still succeed and grow if they can generate profits and pay down their debt.
Therefore, when considering an investment in a company with negative stockholder equity, it is important to dig deeper into the company's financials and assess its path forward.
Managing Investments: Qualifications for Success
You may want to see also

Stockholder equity is useful for judging the funds retained within a business
Stockholder equity, also known as shareholder equity, is a useful metric for judging the funds retained within a business. It is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets, or by taking the sum of share capital and retained earnings, less treasury stock.
Stockholder equity is the remaining assets available to shareholders after all liabilities are paid. It is often referred to as the book value of the company and it comes from two primary sources: the money originally and subsequently invested in the company through share offerings, and the retained earnings (RE) the company accumulates over time through its operations.
Retained earnings are a key component of stockholder equity. They are the company's net income from operations and other business activities that are retained by the company as additional equity capital. Retained earnings are thus a part of stockholder equity, representing returns on total stockholder equity reinvested back into the company. These earnings, reported as part of the income statement, accumulate and grow larger over time. At some point, accumulated retained earnings may exceed the amount of contributed equity capital and can eventually grow to be the main source of stockholder equity.
Investing Pension Lump Sum in India: A Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Stockholder equity refers to the amount of money or assets a shareholder invests in a business. It is also referred to as shareholder equity or a company's book value.
Stockholder equity can be calculated by subtracting a company's liabilities from its assets. It can also be calculated by taking the sum of share capital and retained earnings and deducting treasury stock.
Positive stockholder equity indicates financial health, suggesting the company has more assets than liabilities and is able to pay off its liabilities.
Negative stockholder equity suggests that a company's liabilities exceed its assets, indicating potential bankruptcy.
Stockholder equity accounts for total assets and total liabilities, so cash and cash equivalents would only represent a small piece of a company's financial picture.







