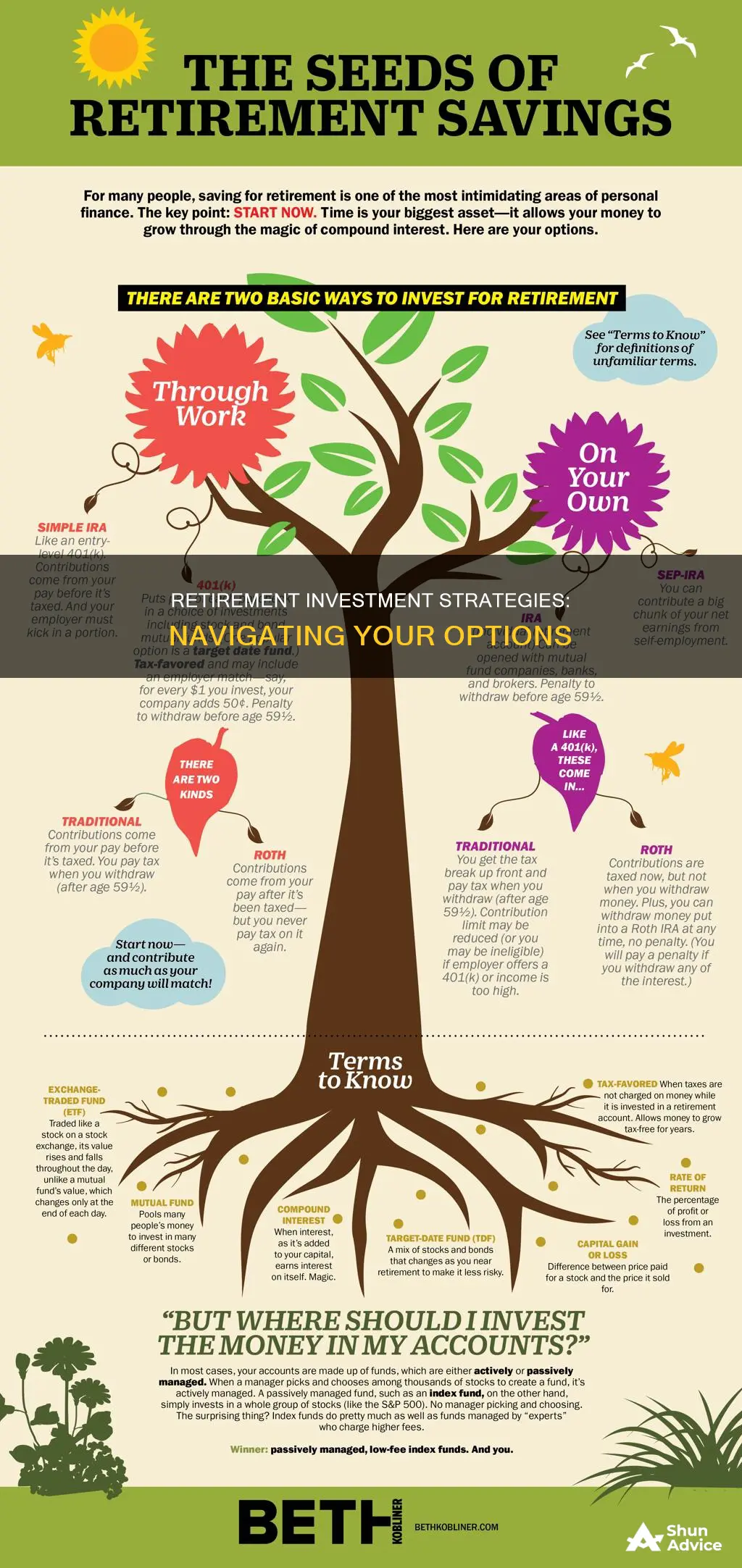
There are many ways to invest for retirement, and it's important to start as early as possible to take advantage of compound interest. A common method is to use tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, which offer tax-deferred or tax-free growth. It's also crucial to understand asset allocation, or how much money to put into stocks, bonds, and cash. Robo-advisors and target-date funds can help with this by automatically rebalancing your portfolio over time. Annuities, dividend-paying stocks, rental properties, and real estate investment trusts (REITs) are also popular investment options for retirement. When selecting investments, it's important to consider your risk tolerance, time horizon, and overall financial goals.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Start saving for retirement | As early as possible |
| Understand | Your options |
| Calculate | Your net worth |
| Keep | Your emotions in check |
| Pay attention to | Fees |
| Get | Professional help |
| Diversify | Your portfolio |
| Be aware of | Tax implications |
| Consider | Estate planning |
What You'll Learn

Understand your retirement account options
Understanding your retirement account options is a crucial step in planning for your retirement. There are various types of accounts to consider, each with its own advantages and suitability depending on your circumstances. Here is a detailed overview of the different retirement account options available to you:
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
These accounts offer tax benefits, allowing your savings to grow tax-free or tax-deferred. The most common examples are 401(k) plans and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs). 401(k)s are employer-sponsored defined-contribution plans, which means you can contribute a portion of your salary before taxes are deducted. IRAs also offer tax advantages and can be set up through a bank, brokerage firm, or other financial institutions. Both 401(k)s and IRAs have annual contribution limits, and you should be aware of any applicable rules and restrictions.
Defined-Benefit Plans
Also known as pensions, these plans are funded by employers and guarantee a specific retirement benefit based on factors like salary history and duration of employment. However, defined-benefit plans are becoming less common, especially in the private sector.
Traditional and Roth Accounts
Both 401(k)s and IRAs can be either traditional or Roth accounts. Traditional accounts may allow you to deduct your contributions from your taxes now, and you will pay taxes when you make withdrawals in retirement. On the other hand, Roth accounts are funded with after-tax money, and withdrawals in retirement are typically tax-free.
Annuities
Annuities are insurance contracts that provide consistent, long-term income payments during retirement. They are often chosen for the safety and security they offer. There are different types of annuities, including fixed, variable, and index annuities, each with its own risks and benefits. It is important to carefully consider the costs and features of annuities before selecting this option.
Dividend-Paying Stocks
Some investors opt for dividend-paying stocks, which provide steady, consistent income in the form of dividends. Companies that pay dividends share a portion of their profits with investors, usually in the form of monthly, quarterly, or annual payments. While dividend payments are not guaranteed, they tend to be sustained as missing payments may indicate financial instability.
Real Estate and Rental Properties
Investing in real estate or rental properties can provide a consistent income stream, but it comes with additional responsibilities and expenses. Alternatively, you can invest in a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT), which is a group of income-generating properties that have historically paid higher dividends.
Qualified Longevity Annuity Contracts (QLACs)
QLACs are a type of annuity specifically designed to ensure regular income payments in the later stages of life. They help extend the deadline for required minimum distributions (RMDs) from tax-advantaged retirement accounts, potentially reducing your tax liability and keeping your Medicare premiums lower.
Brokerage Accounts
Online brokerage accounts offer flexibility but typically do not provide any tax advantages. They can be a good option for investing outside of retirement accounts, but it's important to consider the tax implications.
Remember, the availability and suitability of these options depend on your personal circumstances, including your age, risk tolerance, and financial goals. It is always a good idea to consult with a financial professional or advisor to determine which retirement account options are best for you.
Retirement Planning: A Smart Investment Strategy for the Future
You may want to see also

Start saving early
Starting to save for retirement early is one of the most important things you can do to ensure a comfortable retirement. The earlier you start, the more time your money has to grow, and the less you'll have to save overall.
Compound interest is a crucial factor in growing your retirement savings. The longer your money is invested, the more it will grow, even while you sleep. For example, if you invest $1,000 in a bond that earns 3% interest per year, at the end of the first year, your investment will grow by $30. The next year, you'll earn interest on the original $1,000 plus the previous year's interest, so your investment will grow by $30.90. This process continues, and your money will grow more and more each year.
The power of compound interest means that if you start saving early, you'll be able to save less overall to reach your retirement goals. For example, if you want to have a retirement nest egg of roughly $2.38 million by age 67, assuming an average annualized return of 8%, you would need to save $475 per month if you start at age 21. However, if you wait until age 32 to start saving, you would need to save $1,390 per month to reach the same goal.
Starting early with retirement savings also gives you more flexibility in your investment choices. When you start saving early, you have the time to take on higher-risk, higher-reward investments. These investments can give you a more significant financial cushion when you retire and increase the probability of your investments weathering market fluctuations.
Additionally, starting early with retirement savings can help you reduce your income taxes. When you contribute to a 401(k) or similar retirement plan, that money is often deducted from your paycheck before taxes, so you'll pay less in taxes overall. The longer you save, the more tax benefits you'll receive.
Finally, starting early with retirement savings gives you more control over your future. By building a nest egg, you won't have to depend on Social Security, Medicare, or anyone else to take care of you in retirement. You'll be self-sufficient and able to make your own choices about when and how to retire.
Retirement Windfall: Strategies for Investing a Lump Sum
You may want to see also

Calculate your net worth
To effectively invest for retirement, it's important to understand your net worth, which is the difference between what you own (your assets) and what you owe (your liabilities). This can give you a good idea of where you stand financially and help you make informed decisions about your retirement investments. Here are four to six paragraphs outlining how to calculate your net worth:
Understanding your net worth is crucial for making informed financial decisions, especially when planning for retirement. Net worth is a quantitative concept that measures the value of an individual's or entity's financial position. It is calculated by subtracting all liabilities from all assets. Assets include anything of monetary value that you own, such as cash, investments, real estate, vehicles, etc. Liabilities, on the other hand, are financial obligations that deplete your resources, such as loans, mortgages, credit card debt, and other debts. By regularly calculating your net worth, you can track your financial progress and make necessary adjustments to achieve your retirement goals.
When calculating your net worth, it's important to include all your assets. These can be further categorised into liquid assets, which are easily convertible into cash, such as savings and investment accounts, and fixed assets, which are less liquid but still have monetary value, such as your home, vehicles, or other personal property. By valuing all your assets, you can get a comprehensive understanding of your financial position. For example, if you own a house worth $200,000 and have a mortgage loan of $150,000, your net worth would include the remaining $50,000 of equity in the house.
On the other hand, it's crucial to also account for all your liabilities. This includes any money owed to another person or entity, such as credit card debt, student loans, auto loans, and mortgage payments. Even if you are using your home as an asset, its mortgage should still be considered a liability. By subtracting your total liabilities from your total assets, you can determine your net worth. It is recommended to do this calculation regularly, such as once a year, to track your financial progress over time.
Your net worth can be either positive or negative. A positive net worth indicates that your assets exceed your liabilities, suggesting good financial health. On the other hand, a negative net worth means your liabilities exceed your assets, which may be a cause for concern. To improve your net worth, you can focus on reducing liabilities while increasing or maintaining your assets. This can be achieved through various strategies, such as budgeting, debt reduction techniques, or increasing your income.
Calculating your net worth is a powerful tool for understanding your financial standing and making informed decisions about your retirement investments. It allows you to set realistic retirement goals and adjust your savings and investment strategies accordingly. Additionally, tracking your net worth over time can help you identify areas where you can cut back on expenses or increase your investments to ensure a comfortable retirement. By doing so, you can take control of your financial future and work towards achieving your retirement goals.
Boston Dynamics: The Future of Robotics
You may want to see also

Understand asset allocation
Understanding asset allocation is a crucial part of investing for retirement. Asset allocation refers to the mix of different investment assets in your portfolio, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. The right asset allocation is essential for long-term investors and can help you meet your financial goals.
Risk Tolerance and Investment Timeline
Your risk tolerance, or how much investment risk you are willing to take, is a critical factor in determining your asset allocation. If you have a low-risk tolerance, you will likely invest more in low-risk assets like bonds and cash, which offer lower potential returns but reduce the potential for losses. On the other hand, if you have a higher-risk tolerance, you may allocate more to the stock market, which is a high-risk, high-reward investment.
Your investment timeline is also crucial. Generally, younger investors can take on more risk because they have more time to recover from potential losses. As you get closer to retirement, it is typical to shift towards more conservative investments to protect your savings.
Diversification
Diversification is a key component of asset allocation. By diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes, you can manage risk and potentially enhance returns. Diversification can occur not only across asset classes but also within them. For example, within stocks, you can invest in different types, such as small-cap, large-cap, international, etc. Similarly, within bonds, you can invest in corporate, municipal, or government bonds.
Asset Allocation Models and Funds
There are various asset allocation models that provide a framework for allocating your investments. These include the Income Portfolio (focusing on bonds), the Balanced Portfolio (a mix of stocks and bonds), and the Growth Portfolio (emphasizing stocks).
Additionally, you can utilise asset allocation funds, which are mutual or exchange-traded funds that invest in a mix of asset classes. These funds periodically adjust their allocations based on market conditions and investment strategies. Target-date funds are a type of asset allocation fund that becomes more conservative as you approach retirement.
Age-Based Allocation
While age is a significant factor, it is not the sole determinant of your asset allocation. Your innate risk tolerance and financial goals should also be considered. As a general guideline, the Rule of 100 and the Rule of 110 suggest that you subtract your age from 100 or 110, respectively, to determine the percentage of stocks to hold. However, these rules do not account for individual risk tolerance and circumstances.
- 20-year-old investor: 100% stocks, 0% bonds
- 30-year-old investor: 90% stocks, 10% bonds
- 40-year-old investor: 80% stocks, 20% bonds
- 50-year-old investor: 70% stocks, 30% bonds
- 60-year-old investor: 60% stocks, 40% bonds
- 70-year-old investor: 50% stocks, 50% bonds
Professional Guidance
Determining the right asset allocation can be complex, and it is crucial to ensuring it aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Financial advisors can provide valuable guidance in creating a financial plan for your retirement and helping you adjust your asset allocation as needed. They can assist in designing a savings plan that matches your needs and goals, both in the lead-up to and during retirement.
Student Debt vs. Stock Market: Where Should Your Money Go?
You may want to see also

Consider a robo-advisor
Robo-advisors are one of the fastest-growing sectors of the investment world. They are automated advisors that can build an investment portfolio based on your needs, such as your retirement age and risk tolerance. They are a low-cost option, typically charging well below what a traditional financial advisor would charge for similar services.
Robo-advisors use algorithms to mimic the decision-making and considerations of a human financial advisor. They select investments that meet your needs, whether you require money in the short term or are investing for retirement.
Select a robo-advisor
Robo-advisors compete based on features and management fees. When selecting a robo-advisor, compare them based on the following traits:
- Management fees: The industry standard is 0.25% annually, but some robo-advisors charge more or less.
- Funds' expense ratios: ETFs charge investors a percentage of the amount invested. Any number below 0.10% is excellent.
- Number of funds offered: A higher number of funds may allow for a more customized portfolio.
- Tax-loss harvesting: This technique sells losing investments to reduce taxes and boost long-term gains. It is a premium feature not offered by all robo-advisors.
- Automatic portfolio rebalancing: Some robo-advisors can do this with minimal impact on your taxes.
- Goal-planning tools: These tools can help you stay on track with your retirement goals.
- Option for a human advisor: Some robo-advisors give you access to human advisors for an extra fee.
Fill out an information sheet and risk questionnaire
After selecting a robo-advisor, you will need to provide basic information, such as your name and address, to set up your account. You will also need to complete a questionnaire that assesses your risk tolerance, including how much risk you are willing to take to achieve a certain level of return. Be as honest as possible about your goals and risk tolerance to allow the robo-advisor to tailor your portfolio effectively.
Determine how much you can invest
Based on your goal, the robo-advisor will construct a portfolio of funds to help you achieve it. It will consider your risk tolerance, income, and timeline. For example, if you are investing for retirement with a long-term horizon, the portfolio is likely to be higher-risk and higher-return, with more stocks than bonds.
Deposit money regularly
You can set up regular contributions to your retirement plan, taking advantage of dollar-cost averaging. This strategy averages your purchase prices over time and can be optimal if you don't closely follow the market.
Retire comfortably
By setting up your account and contributing regularly, you are on your way to a comfortable retirement. As your income grows, consider adding more to your robo-advisor account to build your wealth.
Robo-advisors are a cost-effective way to get a high-quality investment experience. They use the same decision-making tools as human advisors but at a lower cost, as financial decision-making is automated. This can save investors money, which can then be invested.
Robo-advisors like Wealthfront, Betterment, and Schwab Intelligent Portfolios are highly rated and offer a range of features, including tax-loss harvesting, automated portfolio rebalancing, and goal-planning tools.
Russia: Invest or Avoid?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The earlier you start investing for retirement, the more time your money has to grow. Starting early also gives you more time to recover from losses, so you can try higher-risk/higher-reward investments.
You can save for retirement in tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s and individual retirement accounts (IRAs). These accounts provide tax-deferred or tax-free growth, making them ideal tools for retirement investing.
Asset allocation is a strategy that helps you choose how much money to put in stocks, bonds, and cash when investing for retirement. A simple asset allocation model, such as a two- or three-fund portfolio based on mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), can make it easy to invest and save for retirement.







