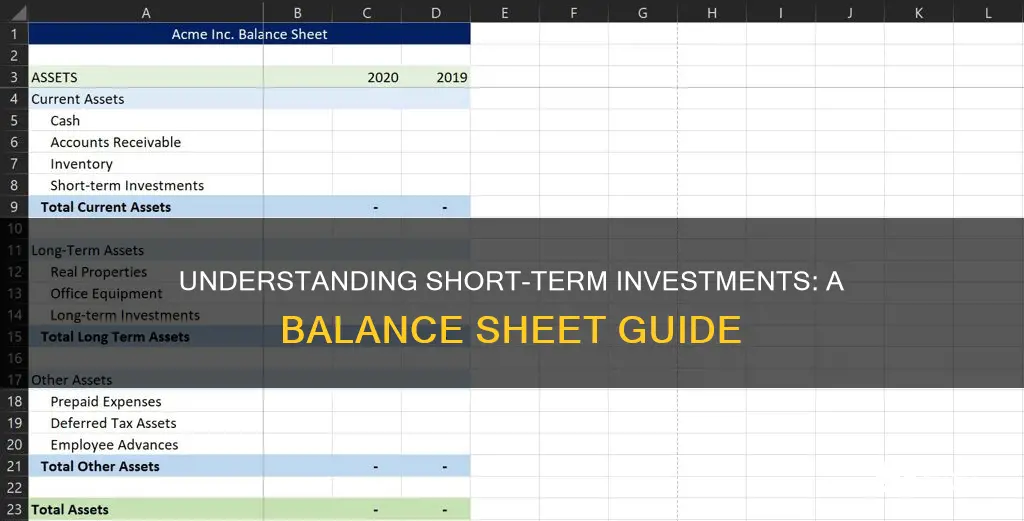
Short-term investments are a crucial component of a company's balance sheet, representing assets that are expected to be converted into cash or sold within one year. These investments can include marketable securities, such as stocks, bonds, and treasury bills, which are highly liquid and easily convertible into cash. They provide a way for companies to manage their cash flow, generate returns, and maintain financial flexibility. Understanding short-term investments is essential for assessing a company's liquidity, financial stability, and overall investment strategy.
What You'll Learn
- Cash and Cash Equivalents: Short-term investments in highly liquid assets like cash, bank deposits, and short-term government securities
- Marketable Securities: Easily convertible into cash within a year, including stocks, bonds, and treasury bills
- Trade Accounts Receivable: Money owed to the company by customers for goods or services sold on credit, typically due within a year
- Short-Term Investments in Derivatives: Financial instruments with values tied to underlying assets, often used for hedging or speculation
- Prepaid Expenses: Payments made for goods or services to be received in the near future, such as insurance premiums or rent

Cash and Cash Equivalents: Short-term investments in highly liquid assets like cash, bank deposits, and short-term government securities
When discussing short-term investments on a company's balance sheet, one of the most critical components is Cash and Cash Equivalents. These are highly liquid assets that are readily convertible into cash with minimal impact on their market value. This category is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a clear picture of a company's liquidity, indicating how quickly it can access and utilize its assets to meet short-term obligations. Secondly, it offers insight into a company's financial health and stability, as it demonstrates the company's ability to manage its cash flow effectively.
Cash and Cash Equivalents primarily include:
- Cash: This is the most basic and widely accepted form of liquidity, representing the physical currency and funds held in the company's bank accounts.
- Bank Deposits: These are funds held in demand deposit accounts or money market accounts, which can be easily withdrawn or transferred without significant loss of value.
- Short-term Government Securities: These are highly liquid investments, such as treasury bills and short-term bonds issued by the government. They are considered low-risk and are often used to maintain liquidity while still earning a modest return.
The value of these short-term investments is crucial for financial reporting and analysis. It is typically reported in the current assets section of the balance sheet, as it is expected to be converted into cash within one year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer. This classification ensures that investors and creditors can quickly assess the company's ability to meet its short-term financial commitments.
In summary, Cash and Cash Equivalents represent a company's most liquid assets, providing a safety net for short-term obligations and offering a clear indication of financial stability. These assets are essential for maintaining a healthy cash flow and ensuring that the company can navigate its financial commitments efficiently. Understanding this component is vital for investors and analysts to make informed decisions regarding the company's financial health and future prospects.
Maximizing Profits: A Beginner's Guide to Short-Term Rental Investing
You may want to see also

Marketable Securities: Easily convertible into cash within a year, including stocks, bonds, and treasury bills
Marketable securities are a crucial component of short-term investments on a company's balance sheet. These are financial assets that can be quickly converted into cash within a year or less. They are highly liquid and provide a safe and accessible way for companies to manage their short-term financial obligations and take advantage of potential investment opportunities.
The primary characteristic of marketable securities is their short-term nature, which makes them an essential tool for businesses to maintain a healthy cash flow. These investments are typically low-risk and highly liquid, allowing companies to access their funds quickly when needed. Marketable securities are often used as a temporary store of value, providing a safe haven for excess cash that the company does not immediately require for its day-to-day operations.
These securities include a variety of financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, and treasury bills. Stocks represent ownership in a company and can be easily bought and sold on the stock market. Bonds, on the other hand, are debt instruments where the issuer borrows money from investors and promises to pay back the principal amount along with regular interest payments. Treasury bills are short-term debt securities issued by governments, offering a low-risk investment option.
When a company purchases marketable securities, it gains immediate access to cash, which can be used for various purposes. This includes funding short-term projects, managing accounts payable, or taking advantage of new business opportunities. The liquidity of these investments ensures that the company can quickly convert them back into cash without incurring significant losses, making them an attractive option for conservative investors.
In summary, marketable securities are a vital part of a company's short-term investment strategy, offering a safe and accessible way to manage cash flow. With their ability to be quickly converted into cash, these securities provide businesses with financial flexibility and a means to optimize their short-term financial position.
Unraveling the True Nature of Short-Term vs. Long-Term Investments
You may want to see also

Trade Accounts Receivable: Money owed to the company by customers for goods or services sold on credit, typically due within a year
Trade Accounts Receivable (TAR) is a crucial component of a company's short-term assets and plays a significant role in its financial health. It represents the money owed to a business by its customers for goods or services sold on credit. This account is essential for businesses that operate on a credit basis, allowing them to manage their cash flow and sales effectively. TAR is typically due to be collected within one year, making it a short-term investment or asset for the company.
When a company sells products or services to customers on credit, it records the sale as revenue but defers the collection of payment until a later date. This initial sale and subsequent credit period are crucial for the company's cash flow and financial stability. TAR is a dynamic account, constantly changing as sales are made and payments are received. It reflects the company's ability to extend credit and manage its customer relationships effectively.
The amount in Trade Accounts Receivable is calculated by subtracting the total payments received from the total sales made on credit during a specific period. This calculation provides a clear picture of the outstanding balances owed by customers. It is a critical metric for businesses to monitor, as it directly impacts their short-term liquidity and financial performance. Efficient management of TAR is essential to ensure the company can meet its short-term obligations and maintain a healthy cash flow.
In the context of short-term investments, TAR serves as a bridge between sales and cash receipts. It represents the company's commitment to provide credit to customers and the customers' obligation to repay the debt. Effective management of TAR involves setting up credit policies, monitoring customer payments, and implementing strategies to minimize bad debt. This ensures that the company's short-term investments in TAR are secure and contribute positively to its overall financial health.
Regular review and analysis of TAR are vital for businesses to identify potential issues early on. This includes monitoring customer payment patterns, assessing creditworthiness, and implementing appropriate collection strategies. By doing so, companies can maintain a healthy TAR balance, ensuring that short-term investments are protected and that the business can continue to operate smoothly. Proper management of Trade Accounts Receivable is a key aspect of financial management, enabling businesses to optimize their short-term financial resources.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: A Brainly Guide
You may want to see also

Short-Term Investments in Derivatives: Financial instruments with values tied to underlying assets, often used for hedging or speculation
Short-term investments in derivatives are a type of financial instrument that plays a crucial role in the realm of finance, offering both opportunities and risks to investors. These derivatives are unique financial contracts whose value is derived from, or 'linked to', an underlying asset, index, or security. The key characteristic that sets derivatives apart is their ability to provide exposure to an asset without directly owning it, making them versatile tools for various financial strategies.
In the context of short-term investments, derivatives can be employed for several purposes. One common use is hedging, where investors use derivatives to protect their portfolios from potential losses due to adverse market movements. For instance, a company might use a derivative contract to lock in a specific price for a commodity it plans to purchase in the future, thus mitigating the risk of price fluctuations. This strategy is particularly valuable for businesses aiming to stabilize their cash flow and manage financial risks.
Another application of short-term derivatives is speculation. Investors often use derivatives to bet on the future direction of an underlying asset's price. For example, a trader might purchase a call option, which gives them the right to buy a specific stock at a predetermined price, hoping that the stock's value will rise, allowing them to profit from the difference. This speculative approach can be a high-risk, high-reward strategy, as the potential gains are significant, but so are the potential losses if the market moves against the investor's prediction.
The value of these derivatives is directly tied to the performance of the underlying asset, which can be a stock, commodity, currency, or even an index. For instance, a stock option's value is derived from the underlying stock's price, and a commodity future's value is based on the future price of the commodity. This linkage to underlying assets provides investors with a means to gain exposure to specific markets or sectors without the need for direct investment in those assets.
In summary, short-term investments in derivatives offer a flexible and powerful tool for investors to manage risk, speculate on market movements, and gain exposure to various assets. However, it is essential to approach these instruments with a clear understanding of their complexities and potential risks, as they can be highly leveraged and sensitive to market volatility.
Understanding Long-Term Investment Strategies: Key Factors to Consider
You may want to see also

Prepaid Expenses: Payments made for goods or services to be received in the near future, such as insurance premiums or rent
Prepaid expenses are an essential component of a company's balance sheet, representing payments made for goods or services that will be received in the near future. These expenses are recorded as assets on the balance sheet because they provide a future economic benefit to the company. The key characteristic of prepaid expenses is that they are not yet consumed or utilized by the business but are expected to provide value within the next accounting period.
When a company pays for services or purchases goods in advance, it increases its prepaid expenses. For example, if a business pays an annual insurance premium in advance, the entire amount is initially recorded as a prepaid expense. This is because the insurance coverage is a future benefit, and the payment represents an asset that the company will utilize over the coming months or years. Similarly, prepaying rent for the next quarter would also be classified as a prepaid expense, indicating a future obligation that provides a service or use to the company.
The treatment of prepaid expenses on the balance sheet is crucial for financial reporting and analysis. It ensures that the company's financial statements accurately reflect the economic resources it possesses and the obligations it has incurred. By recognizing prepaid expenses, businesses can provide a more comprehensive view of their financial position, as it accounts for future benefits and obligations. This is particularly important for short-term investments, as it allows investors and stakeholders to understand the company's immediate financial commitments and potential cash inflows.
In the context of short-term investments, prepaid expenses can play a significant role in a company's liquidity and cash flow management. As these expenses are expected to be utilized or consumed within a relatively short period, they can impact the company's short-term financial obligations and cash requirements. For instance, if a business has prepaid insurance premiums, it may need to allocate funds from its short-term investments to cover the initial costs associated with the insurance coverage until the premiums are fully utilized.
Properly identifying and managing prepaid expenses is essential for maintaining accurate financial records and making informed business decisions. Companies should ensure that prepaid expenses are recorded at fair value and that any changes or adjustments are made accordingly. Regular review and analysis of prepaid expenses can help businesses optimize their cash flow, identify potential risks, and make strategic investments while ensuring compliance with accounting standards.
Long-Term Investments: Separating Fact from Fiction
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Short-term investments, also known as marketable securities, are financial assets that a company expects to convert into cash or liquidate within one year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer. These investments are highly liquid and can be easily converted into a known amount of cash. Examples include treasury bills, certificates of deposit, and short-term government bonds.
Short-term investments provide companies with a way to manage their cash flow and liquidity. They offer a safe and relatively stable investment option, allowing businesses to generate a small return while keeping their capital accessible for day-to-day operations and potential short-term opportunities. These investments are crucial for maintaining financial stability and ensuring a company can meet its short-term obligations.
The presence of short-term investments can influence a company's financial ratios, particularly liquidity ratios. For instance, the current ratio, which measures a company's ability to pay short-term liabilities, may be positively affected by these investments. However, it's important to note that the quality and liquidity of these investments also play a role in assessing a company's financial health.
While short-term investments are highly liquid, not all of them are considered cash equivalents. Cash equivalents are assets that can be readily converted into cash with minimal risk and loss of value. Short-term investments, such as treasury bills, are often considered cash equivalents because they are low-risk and have a maturity period of less than 90 days. However, other short-term investments may not meet the criteria for cash equivalents.
Short-term investments are typically reported at fair value in the balance sheet. If the investment is held for trading or is a financial asset at fair value through profit or loss, it is classified as a current asset. If it is a financial asset at fair value through other comprehensive income, it is classified as a non-current asset. The changes in the value of these investments during the period are also disclosed in the income statement or notes to the financial statements.