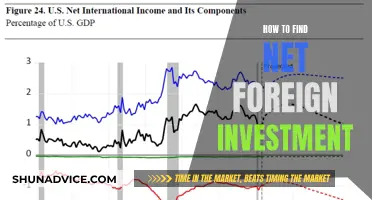
Horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI) is a strategic approach where a company invests in a foreign market by acquiring or establishing a subsidiary in a different country that operates in the same industry as its parent company. This type of investment aims to expand market share, gain access to new resources, and diversify operations globally while maintaining a similar business model and product or service offering. Horizontal FDI is often driven by the desire to secure a competitive advantage, reduce costs, and increase efficiency by leveraging the strengths of the host country's market.
What You'll Learn
- Market Expansion: FDI in foreign markets to increase sales and customer reach
- Resource Acquisition: Accessing natural resources, raw materials, or skilled labor abroad
- Technology Transfer: Sharing technological advancements and know-how across borders
- Local Integration: Establishing local operations and supply chains for market penetration
- Economic Development: FDI as a catalyst for host country economic growth and job creation

Market Expansion: FDI in foreign markets to increase sales and customer reach
Horizontal Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is a strategic approach for businesses aiming to expand their operations globally. This type of FDI involves a company investing in a similar or identical business in a foreign market, often with the goal of increasing sales, market share, and customer reach. By engaging in horizontal FDI, companies can leverage their existing strengths and capabilities to tap into new markets efficiently.
The primary objective of this investment strategy is to replicate the success of the parent company in a different geographical location. It allows businesses to quickly establish a presence in a new market, especially when entering a region with a high demand for their products or services. For instance, a technology company might invest in setting up a software development center in a foreign country to cater to the local market's needs, ensuring that the product is tailored to the specific requirements of the new region.
One of the key advantages of horizontal FDI is the ability to maintain control over the production process and quality standards. By investing in a similar business, the parent company can ensure that its products or services are delivered consistently across different markets. This approach also enables the company to retain its brand identity and reputation, which is crucial for building customer trust and loyalty in new territories.
When expanding through horizontal FDI, companies can benefit from the local knowledge and expertise of the acquired business. This includes understanding the cultural nuances, consumer preferences, and market dynamics, which are essential for successful market penetration. By combining the parent company's global resources with the local insights, the investment can lead to more effective marketing strategies, improved product offerings, and a faster time-to-market.
In summary, horizontal FDI is a powerful tool for businesses seeking to expand their global footprint. It provides a structured approach to market entry, allowing companies to quickly increase sales and customer reach while maintaining control over their operations. This strategy is particularly beneficial for industries where product standardization is possible, and where the company's existing business model can be adapted to suit the foreign market's needs.
Cash Investments: Impacting Stockholders Equity Positively
You may want to see also

Resource Acquisition: Accessing natural resources, raw materials, or skilled labor abroad
Horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI) is a strategic approach for companies aiming to expand their operations globally by acquiring resources, assets, or businesses in a different country. This type of investment is primarily focused on resource acquisition, which can be categorized into three key areas: natural resources, raw materials, and skilled labor.
In the context of natural resources, horizontal FDI often involves the exploration and exploitation of resources in a foreign country. This could include investing in oil and gas fields, mining operations, or renewable energy projects. For instance, a company might establish a subsidiary in a country rich in oil reserves to secure a steady supply of crude oil for its refining operations back home. This strategy ensures a consistent supply of raw materials, which is crucial for the production process and can provide a competitive edge in the market.
Raw materials, such as metals, chemicals, and agricultural products, are essential for manufacturing and production processes. Horizontal FDI in this sector involves setting up production facilities or acquiring local companies in countries with abundant raw materials. For example, a car manufacturing company might invest in a steel mill in a country with vast iron ore deposits, ensuring a reliable source of raw materials for its car production. This approach not only secures the necessary inputs for production but also can lead to the development of local industries and economies.
Skilled labor is another critical aspect of horizontal FDI. Many companies seek to establish a global presence by hiring and training local talent in the host country. This strategy allows businesses to tap into a skilled workforce, often at a lower cost compared to their home country. For instance, a software development company might set up a development center in a country with a large pool of IT professionals, enabling them to access a talented workforce for software development and IT services. This approach not only benefits the company but also contributes to the local economy by creating job opportunities and fostering professional development.
In summary, horizontal FDI is a powerful tool for companies to secure resources, raw materials, and skilled labor on a global scale. By investing in natural resources, raw material production, and local talent, businesses can ensure a steady supply of inputs, maintain competitive advantages, and contribute to the economic growth of the host country. This strategic approach allows companies to expand their operations, reduce costs, and establish a strong presence in the international market.
Investment Firm Apps: Choosing the Right One
You may want to see also

Technology Transfer: Sharing technological advancements and know-how across borders
Technology transfer is a critical aspect of international business, especially in the context of horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI). It involves the exchange of technological knowledge, skills, and innovations between companies or countries, often with the goal of enhancing productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness. This process is particularly important in today's globalized economy, where businesses seek to expand their operations and tap into new markets by leveraging advanced technologies.
In the context of horizontal FDI, technology transfer can take various forms. One common approach is when a multinational corporation (MNC) acquires or merges with a local company in a foreign market. This acquisition allows the MNC to integrate its advanced technologies and expertise into the acquired business, thereby transferring knowledge and capabilities to the new subsidiary. For instance, a technology company based in the United States might acquire a software development firm in Europe, enabling the transfer of cutting-edge software engineering practices and tools to the European company.
Another method is through strategic partnerships and joint ventures. When two or more companies from different countries collaborate, they can combine their technological strengths to create new products or services. This collaboration often results in the sharing of intellectual property, research and development (R&D) facilities, and technical expertise. For example, a pharmaceutical company in Japan might partner with a research institute in the United States to develop a new drug. The Japanese company contributes its expertise in clinical trials and market knowledge, while the US institute provides advanced research capabilities, leading to a successful technology transfer and potential product launch in multiple markets.
International research and development (R&D) centers are also significant vehicles for technology transfer. Many MNCs establish R&D hubs in various countries to tap into local talent pools and cultural insights. These centers facilitate the exchange of ideas and innovations between different regions, fostering a global network of technological advancements. For instance, a car manufacturer might set up an R&D center in South Korea to develop advanced autonomous driving systems, benefiting from the country's strong engineering and technology sectors.
Furthermore, technology transfer can occur through licensing agreements and technology licensing. Companies can grant licenses to use their proprietary technologies to foreign entities, allowing for the transfer of know-how without direct ownership. This approach is common in industries like telecommunications and media, where companies license their patents and software to local businesses, enabling them to adopt and adapt advanced technologies to their specific needs.
In summary, technology transfer is a powerful mechanism for horizontal FDI, enabling businesses to expand globally while sharing and acquiring technological advancements. It promotes economic growth, fosters innovation, and strengthens international trade relationships. By facilitating the exchange of knowledge and expertise, technology transfer plays a vital role in shaping the global business landscape and driving economic development across borders.
Preparing a Cash Flow Statement: Investing Activities Guide
You may want to see also

Local Integration: Establishing local operations and supply chains for market penetration
Local integration is a crucial aspect of horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI), especially when aiming for market penetration and long-term success in a new country. This strategy involves setting up local operations and integrating into the host country's supply chain to ensure a seamless and efficient business process. Here's a detailed breakdown of the process:
- Market Research and Local Presence: The first step is to conduct extensive market research to understand the local business environment, consumer behavior, and competition. This research will guide the decision-making process regarding the type of local operations to establish. Setting up a local presence can be achieved through various means, such as forming a joint venture with a local company, acquiring an existing business, or creating a new subsidiary. This step is essential to gain a deeper understanding of the market and build a strong foundation for future operations.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Horizontal FDI often involves integrating into the local supply chain to ensure cost-effectiveness and efficiency. This includes identifying local suppliers and partners who can provide raw materials, components, or services at competitive prices. By optimizing the supply chain, companies can reduce costs, improve product quality, and ensure timely delivery. It also allows for better control over the production process, especially when dealing with perishable goods or those requiring specific local conditions.
- Local Operations and Infrastructure: Establishing local operations is a significant part of the integration process. This may involve building manufacturing facilities, distribution centers, or offices, depending on the nature of the business. The infrastructure should be designed to meet local regulations and standards while also being efficient and sustainable. Local operations enable companies to have more control over production, quality control, and customer service, which is crucial for market penetration.
- Talent Acquisition and Training: Building a skilled local workforce is essential for the success of any FDI project. Companies should focus on hiring and training local talent to fill various roles within the organization. This includes management, technical positions, and support staff. By investing in local talent, the company can ensure a steady supply of skilled workers, reduce recruitment costs, and foster a sense of ownership among employees. Training programs can also be designed to upskill the workforce, ensuring they are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to contribute to the company's goals.
- Supply Chain Network Expansion: As local operations become established, the focus shifts to expanding the supply chain network. This involves identifying and partnering with additional local suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers to create a robust and reliable supply chain. The goal is to ensure a consistent flow of goods and services, even as the business grows and expands its market reach. Regular reviews and performance evaluations of the supply chain partners should be conducted to maintain quality and efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance and Local Partnerships: Navigating local regulations and legal requirements is essential for a successful FDI project. Companies should establish a robust compliance framework to ensure they adhere to all relevant laws and standards. Building strong relationships with local government bodies and industry associations can provide support and guidance. Additionally, forming strategic alliances with local businesses or industry leaders can open doors to new opportunities and help establish a solid foothold in the market.
Local integration is a complex process that requires careful planning, market understanding, and a commitment to long-term success. By establishing local operations and integrating into the supply chain, companies can effectively penetrate new markets, gain a competitive edge, and build a sustainable business presence. This approach also contributes to the host country's economic development by creating jobs, transferring knowledge, and fostering local entrepreneurship.
A Guide to Investing Cash in Australia
You may want to see also

Economic Development: FDI as a catalyst for host country economic growth and job creation
Horizontal Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a pivotal role in fostering economic development and transforming the trajectory of host countries. This type of investment involves a company expanding its operations into a new market, often by acquiring or merging with an existing business in the target country. The primary objective is to replicate and maintain the company's existing business model and practices in the new location, rather than creating a new venture.
In the context of economic development, horizontal FDI serves as a powerful catalyst for growth and job creation. When a multinational corporation (MNC) invests in a new market horizontally, it brings with it a range of benefits. Firstly, it introduces advanced technologies, management practices, and expertise to the host country, which can significantly enhance the productivity and efficiency of local businesses. This transfer of knowledge and skills can lead to improved product quality, increased output, and better resource utilization, ultimately boosting the host country's economic performance.
The impact of horizontal FDI on job creation is particularly noteworthy. As the MNC establishes a presence in the host country, it creates employment opportunities for local workers. This can range from direct jobs within the MNC's operations to indirect jobs created through the supply chain and supporting services. The influx of new jobs can help reduce unemployment rates, especially among the youth and less-skilled labor force, and contribute to a more dynamic and vibrant labor market. Moreover, the wages and salaries earned by these employees can stimulate local consumption, further boosting the economy.
Additionally, horizontal FDI often leads to the development of ancillary industries and supporting services, which further enhances job creation. Local suppliers, distributors, and service providers may emerge to cater to the needs of the MNC, creating a network of interdependent businesses. This ecosystem of supporting industries can generate additional employment opportunities and foster a more diverse and resilient economy.
In summary, horizontal FDI is a powerful tool for economic development, offering a range of benefits that extend beyond the immediate investment. It facilitates technology transfer, improves productivity, and creates numerous job opportunities. By attracting horizontal FDI, host countries can experience significant economic growth, improved standards of living, and a more robust and sustainable development trajectory. Understanding and promoting this type of investment can be a strategic approach for governments and policymakers to drive economic transformation and prosperity.
Foreigners' Guide: Investing in ETFs: A Step-by-Step Process
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to the acquisition or establishment of a business in a foreign country that operates in the same industry as the investor's existing business. It involves expanding into a new market by replicating the investor's existing business model, products, or services.
Horizontal FDI is when a company invests in a similar or identical business in a different country, often to access new markets or expand its customer base. In contrast, vertical FDI involves investing in companies that operate at different stages of the production or supply chain, such as acquiring a supplier or a distributor.
Horizontal FDI can provide several advantages, including increased market share, improved economies of scale, access to new customer segments, and the ability to leverage existing brand recognition and expertise. It allows companies to diversify their operations and reduce risks associated with relying solely on domestic markets.
An example of horizontal FDI could be a multinational corporation expanding its manufacturing operations to a new country. If the company already has a successful manufacturing facility in its home country, it might set up a similar plant in the new market to produce the same products, targeting local consumers or exporting to other regions.
While horizontal FDI offers opportunities, it also comes with challenges. These may include cultural and regulatory differences, competition from local firms, managing supply chains across borders, and potential political risks. Companies must carefully consider these factors and conduct thorough market research before making such investments.