Descriptive statistics play a crucial role in the realm of investment services, offering a comprehensive overview of financial data. It involves the process of summarizing and presenting raw data in a meaningful way, providing investors with valuable insights. This statistical approach enables professionals to understand trends, patterns, and relationships within investment portfolios, market trends, and risk assessments. By employing measures such as measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (range, standard deviation), descriptive statistics empower investors to make informed decisions, optimize asset allocation, and manage risk effectively.
What You'll Learn
- Measures central tendency: Mean, median, mode help summarize investment data
- Data distribution: Understanding skewness, kurtosis, and variability in investment returns
- Data visualization: Charts and graphs aid in interpreting investment trends and patterns
- Data reliability: Assessing the accuracy and consistency of investment data
- Data comparison: Statistical methods enable comparison of investment performance across different assets

Measures central tendency: Mean, median, mode help summarize investment data
Descriptive statistics play a crucial role in the field of investment services, providing a concise summary of investment data to help investors and analysts make informed decisions. Among the various measures of central tendency, the mean, median, and mode are essential tools for understanding the typical performance or value of an investment portfolio. These measures offer a snapshot of the central value, helping investors gauge the overall health and direction of their investments.
The mean, often referred to as the average, is calculated by summing up all the investment values and then dividing by the number of data points. For instance, if an investor has a portfolio with monthly returns over a year, the mean return would represent the average monthly gain or loss. This measure is particularly useful for investors as it provides a quick overview of the typical return, allowing them to assess the potential risk and reward of their investments. A higher mean return might indicate a more aggressive investment strategy, while a lower mean could suggest a more conservative approach.
Median, on the other hand, is the middle value in a dataset when it is ordered from smallest to largest. In the context of investment, the median return can be a more robust indicator of the central tendency, especially when the data exhibits a skewed distribution. For example, if a portfolio has a few months with significantly higher returns, the mean might be pulled upwards, providing an inaccurate representation of the typical performance. The median, in this case, would offer a more balanced view, making it a valuable tool for investors to understand the central value without being influenced by outliers.
Mode, the third measure of central tendency, identifies the most frequently occurring value in a dataset. In investment analysis, the mode can be useful for identifying the most common investment strategy or the prevalent market condition. For instance, if an analyst is studying the investment choices of a group of investors, the mode might reveal the most popular asset class or investment style. This information can be valuable for understanding market trends and making strategic investment decisions.
In summary, the mean, median, and mode are powerful tools for summarizing investment data and understanding central tendencies. These measures enable investors and analysts to quickly assess the typical performance, risk, and market trends associated with their investments. By utilizing these statistical techniques, investors can make more informed choices, adapt their strategies, and potentially improve their overall investment outcomes.
Exploring Long-Term Investment Strategies: Building Wealth for the Future
You may want to see also

Data distribution: Understanding skewness, kurtosis, and variability in investment returns
Descriptive statistics play a crucial role in investment services, providing a comprehensive understanding of data distribution and its characteristics. When analyzing investment returns, investors and analysts aim to gain insights into the patterns, trends, and behaviors of the data. This is where descriptive statistics come into play, offering a structured approach to summarizing and interpreting the information.
One key concept in descriptive statistics is understanding data distribution. Skewness and kurtosis are essential measures that describe the shape and characteristics of the distribution of investment returns. Skewness measures the asymmetry of the distribution, indicating whether the data is skewed to the left or right. A positive skewness suggests that the distribution has a longer tail on the right side, implying that extreme values or outliers are more frequent on the positive side. On the other hand, negative skewness indicates a longer left tail, suggesting that extreme negative returns are more common. Investors can use this information to assess the risk associated with different investment strategies.
Kurtosis, another critical measure, describes the 'tailedness' of the distribution. It quantifies the sharpness or flatness of the distribution's tails compared to a normal distribution. High kurtosis indicates a distribution with sharp, heavy tails, suggesting the presence of extreme values or outliers. Low kurtosis, on the other hand, implies a flatter distribution with less extreme values. Understanding kurtosis helps investors identify the volatility and risk associated with investment returns, especially in the presence of market anomalies or rare events.
Variability in investment returns is another aspect that descriptive statistics can help quantify. Measures such as range, interquartile range (IQR), and standard deviation provide insights into the spread or dispersion of the data. The range represents the difference between the highest and lowest values, offering a quick glimpse of the extreme values in the dataset. IQR, calculated as the difference between the third and first quartiles, provides a robust measure of variability, ignoring outliers. Standard deviation, a fundamental concept in statistics, measures the average distance of data points from the mean, indicating the overall volatility of investment returns.
By analyzing these descriptive statistics, investors can make informed decisions regarding portfolio construction, risk management, and strategy selection. Understanding the distribution of investment returns allows for a more nuanced assessment of potential risks and rewards. For instance, a highly skewed distribution with high kurtosis might indicate a concentrated risk, requiring careful consideration of diversification strategies. Conversely, a symmetric distribution with low kurtosis could suggest a more stable investment with lower volatility.
In summary, descriptive statistics provide a powerful toolkit for investors to explore and interpret investment data. Skewness, kurtosis, and measures of variability offer valuable insights into the characteristics of investment returns, enabling investors to make data-driven decisions and manage risks effectively. This understanding of data distribution is essential for building robust investment strategies and ensuring long-term success in the financial markets.
Understanding Term Sheets: A Guide to Investment Agreements
You may want to see also

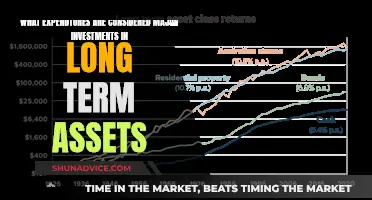
Data visualization: Charts and graphs aid in interpreting investment trends and patterns
Data visualization is a powerful tool in the field of investment services, offering a clear and concise way to interpret complex data and identify trends. Charts and graphs are essential components of this process, providing a visual representation of investment data that can be easily understood and analyzed. By presenting data in a graphical format, investors and analysts can quickly grasp the underlying patterns and make informed decisions.
One of the primary benefits of data visualization is its ability to simplify large datasets. Investment data often involves vast amounts of information, making it challenging to identify key trends and patterns. Through the use of charts and graphs, investors can condense this data into a more manageable format. For example, a line graph can illustrate the performance of an investment portfolio over time, allowing investors to spot upward or downward trends and make strategic adjustments. Similarly, a bar chart can compare the returns of different investment vehicles, aiding in the selection of the most profitable options.
Various types of charts and graphs are employed in investment analysis, each serving a unique purpose. One common type is the scatter plot, which displays individual data points and can reveal correlations between different variables. In investment services, this could be used to analyze the relationship between interest rates and stock prices, helping investors understand market dynamics. Another useful graph is the histogram, which shows the distribution of data and can identify outliers or areas of concentration. This is particularly valuable for risk assessment and portfolio optimization.
Additionally, time-series charts are invaluable for tracking investment performance over extended periods. These charts can display monthly or yearly returns, providing a comprehensive view of an investment's growth or decline. By examining these charts, investors can make long-term strategic decisions and assess the impact of market fluctuations. Furthermore, the use of color-coding and interactive elements in data visualization tools can enhance the user experience, allowing for a more intuitive exploration of investment data.
In summary, data visualization through charts and graphs is an indispensable skill for professionals in the investment industry. It enables them to communicate complex ideas effectively and make data-driven decisions. By presenting investment data in a visually appealing and understandable manner, investors can identify trends, assess risks, and optimize their portfolios. The power of data visualization lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights, ultimately contributing to the success of investment strategies.
Unlocking the Long-Term Benefits: Is a Mortgage an Investment Worth Making?
You may want to see also

Data reliability: Assessing the accuracy and consistency of investment data
Data reliability is a critical aspect of investment services, as it directly impacts the accuracy and consistency of financial data used for decision-making. When assessing the reliability of investment data, several key factors come into play. Firstly, data accuracy is essential; it involves ensuring that the information collected is free from errors, omissions, and biases. This means verifying the source of the data, employing proper data entry procedures, and implementing quality control measures to minimize human error. For instance, in the context of stock market data, accurate recording of share prices, trading volumes, and financial indicators is vital for investors to make informed choices.
Consistency in data is another crucial element of reliability. Consistent data ensures that the information remains dependable and comparable over time and across different sources. This involves establishing standardized data collection methods, maintaining uniform recording practices, and ensuring that the data is consistent with the defined parameters of the investment strategy. For example, if an investment firm tracks the performance of various funds, consistent data collection and reporting will enable accurate comparisons, helping investors understand the relative performance of different investment options.
To assess data reliability, investment firms employ various techniques. One common approach is to use statistical methods to identify outliers and anomalies in the data. These methods can help detect data entry errors or unusual events that might affect the overall consistency of the dataset. Additionally, cross-referencing data from multiple sources can enhance reliability. By comparing and validating data from different systems or providers, investment firms can ensure that the information is accurate and consistent.
Another strategy to enhance data reliability is to implement robust data validation processes. This includes setting up data validation rules and checks to ensure that the information adheres to predefined criteria. For instance, data validation can be used to verify that financial figures fall within expected ranges or meet specific industry standards. Regular data audits and reviews are also essential to identify and rectify any discrepancies or inconsistencies in the investment data.
In summary, data reliability is a cornerstone of investment services, ensuring that financial data is accurate, consistent, and dependable. By employing statistical analysis, cross-referencing, and robust validation techniques, investment firms can maintain high standards of data integrity. This, in turn, enables investors to make well-informed decisions based on reliable information, fostering trust and confidence in the investment process.
Markatale Securities: Unraveling the Short-Term Investment Mystery
You may want to see also

Data comparison: Statistical methods enable comparison of investment performance across different assets
The comparison of investment performance across various assets is a critical aspect of financial analysis, and statistical methods play a pivotal role in this process. Descriptive statistics, in the context of investment services, provide a comprehensive overview of the data, allowing investors and analysts to make informed decisions. When comparing investments, the primary goal is to assess the relative performance of different assets, be it stocks, bonds, real estate, or alternative investments. This comparison is essential for investors to diversify their portfolios, manage risk, and optimize returns.
Statistical techniques, such as mean, median, and standard deviation, are powerful tools for data comparison. The mean, often referred to as the average, represents the central tendency of a dataset. In investment analysis, calculating the mean return of various assets over a specific period enables investors to identify the overall performance of each investment category. For instance, if you are comparing the performance of tech stocks and healthcare ETFs, the mean return for each asset class can provide a quick snapshot of their historical profitability.
Median, on the other hand, is useful when dealing with skewed data distributions. It represents the middle value in a dataset when it is ordered. In investment analysis, the median return can help identify the performance of assets that are not significantly influenced by outliers or extreme values. This is particularly valuable when assessing the consistency of investment returns over time.
Standard deviation is a measure of volatility and risk. It quantifies the dispersion of data points around the mean. In the context of investment comparison, standard deviation can highlight the variability in returns for different assets. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility, which may be a concern for risk-averse investors. By comparing standard deviations, investors can assess the risk exposure associated with various investment options.
Additionally, statistical methods like correlation and regression analysis are invaluable for data comparison. Correlation analysis helps determine the relationship between the returns of different assets. A strong positive correlation between two assets suggests that their performance tends to move in the same direction, which can be useful for portfolio construction. Regression analysis, on the other hand, allows investors to predict the returns of one asset based on another, providing insights into the drivers of investment performance.
In summary, descriptive statistics and various statistical methods provide a robust framework for comparing investment performance. These techniques enable investors to make data-driven decisions, optimize portfolio allocation, and manage risk effectively. By employing these tools, investors can navigate the complex world of financial markets with greater confidence and precision.
TQQQ: A Long-Term Investment Strategy or a Short-Term Trade?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that focuses on summarizing and describing the main features of a dataset. In investment services, it involves analyzing and presenting data to provide insights and an understanding of investment performance, market trends, and risk factors. This includes calculating measures such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range to describe the central tendency, variability, and distribution of investment data.
Investment analysts employ descriptive statistics to gain a comprehensive overview of investment portfolios, market indices, or individual securities. They calculate key metrics like return on investment, volatility, and correlation to assess the performance and risk exposure of different assets. These statistics help investors make informed decisions by providing a clear picture of the investment landscape.
Descriptive statistics plays a vital role in risk management by enabling investors and analysts to quantify and assess various types of investment risks. By analyzing historical data and calculating measures like value at risk (VaR) and expected shortfall, investors can understand the potential losses associated with different investment strategies. This information is crucial for developing risk mitigation strategies and making prudent investment choices.
Descriptive statistics is an essential tool in investment research, aiding in the analysis of large datasets and market trends. Researchers use it to summarize and present key findings, such as market share, sales growth, or customer satisfaction. These statistics help investors identify patterns, make comparisons, and draw conclusions about the performance and potential of various investment opportunities.
Absolutely! In investment portfolios, descriptive statistics can be used to describe the composition of assets, such as the percentage allocation to different asset classes or sectors. It can also involve calculating the average return, standard deviation of returns, and correlation coefficients among individual securities. These statistics assist investors in understanding the diversification benefits and risk-adjusted performance of their investment portfolios.