Equity mutual funds are a type of investment fund that pools money from investors to buy a portfolio of stocks. They are professionally managed and primarily invest in the stock market. The stocks are selected by a team of professionals who aim to deliver maximum returns from the investments while controlling the risk. Equity mutual funds are an attractive option for investors who want to diversify their portfolio and aim for long-term growth.
Characteristics of Equity Mutual Funds
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Description | A type of investment fund that pools money from investors to trade primarily a portfolio of stocks, also known as equity securities. |
| Management | Professionally or actively managed by a fund manager or a team of professionals. |
| Investment | Invests in a diverse mix of stocks from many different companies. |
| Risk | Higher volatility and risk of loss compared to bonds or cash. |
| Returns | Potential for higher or superior long-term returns. |
| Benefits | Diversification, professional management, and higher returns. |
| Tax | Returns are generated through capital gains and dividends, which are taxed differently. |
| Types | Actively managed funds, passive funds, growth funds, value funds, and blend equity funds. |
What You'll Learn

What are equity mutual funds?
Equity mutual funds are a type of investment fund that pools money from investors to buy a portfolio of stocks, also known as equity securities. These funds are managed by professionals who conduct investment research and make decisions about which stocks to buy, hold, or sell. The aim is to generate returns for the investors, and in exchange for higher growth potential, investors experience more ups and downs in the value of their investment.
Equity funds are classified in several ways, including investment style, portfolio focus, and level of diversification. Actively managed funds have portfolio managers who actively research, analyse and select stocks with the goal of outperforming a benchmark index. They use their expertise and various strategies to make investment decisions, and the success of the fund depends largely on the fund manager's skill. Passively managed funds, on the other hand, include index funds, which aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index. These funds do not attempt to outperform the market but instead track the index as closely as possible. Due to the more hands-on approach of active funds, they typically charge higher fees than passive funds.
Equity funds are also often categorized based on the size of the companies they invest in, with large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap funds focusing on large, medium, and small companies, respectively. Large-cap funds are generally considered less volatile, while small-cap funds may offer higher growth potential but carry more risk.
Equity funds offer investors several benefits, including diversification, professional management, and the potential for superior returns. They provide investors with a well-rounded exposure to the stock market and the convenience of a single investment. Additionally, in many countries, equity mutual funds offer tax benefits that can enhance overall investment returns.
However, investing in equity funds also carries risks, mainly due to the volatility of the stock market. Market downturns, geopolitical events, or changes in investor sentiment can cause prices to decline, leading to potential short-term losses for investors. It is important for investors to be aware of these risks and focus on long-term goals.
Understanding Investment Fund Carry: What's the Deal?
You may want to see also

Benefits of equity mutual funds
Equity mutual funds are a type of investment fund that pools money from multiple investors to buy a portfolio of stocks. These funds are managed by professionals who conduct investment research and make decisions about which stocks to buy, hold, or sell within the fund's portfolio.
Diversification
Equity mutual funds offer investors a diversified portfolio by pooling their money to invest in a wide range of stocks across different sectors and industries. This diversification helps to reduce the risk associated with holding a specific stock. If one stock performs poorly, the impact on the overall fund performance is reduced as there are many other stocks in the portfolio.
Professional Management
Equity mutual funds are professionally managed by fund managers and their teams, who have expertise in markets and finance. They research and analyze various indicators such as company profitability, its ability to survive challenging economic phases, and the sector in which it operates. Based on this research, they make investment decisions to maximise returns while controlling risk.
Breadth of Product
Equity mutual funds are one of the most common types of mutual funds, so there are many different types and options available. This means investors are more likely to find a product that meets their specific portfolio needs.
Attractive Returns
Equity mutual funds offer the potential for attractive long-term returns. Historically, stocks have given investors higher returns than other asset classes such as bonds and cash. Equity funds are particularly attractive to investors with longer time horizons who can weather short-term market fluctuations in anticipation of higher returns over time.
Tax Benefits
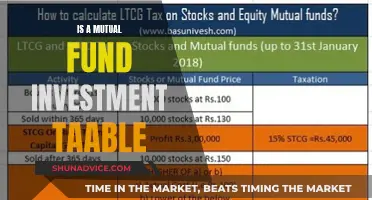
In some cases, equity mutual funds can provide tax benefits. For example, in India, Equity Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS) is a type of equity fund that offers tax-saving benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
Overall, equity mutual funds offer a convenient way to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of stocks, providing investors with the potential for higher returns than other asset classes.
How to Invest Your Roth IRA Funds
You may want to see also

Risks of equity mutual funds
Equity mutual funds are a type of investment fund that pools money from investors to buy a portfolio of stocks. They are also known as stock funds because of their focus on stocks. While investing in stocks carries more risk than some other investments, a fund can diversify with stocks from many different companies, thus offering some protection from the risk of one or more of the stocks underperforming.
Market Risk
Market risk is the primary risk affecting equity funds. It is the risk of losing value due to various factors that affect the entire stock market. Market risk can be attributed to factors such as macroeconomic trends, global economic crises, geopolitical tensions, or regulatory changes. Equity price risk is the biggest component of market risk impacting equity funds. When the market falls, all stock prices are affected, which in turn impacts the performance of an equity fund. Equity funds can also be prone to currency risk if they invest in companies operating in multiple countries.
Industry and Company-Specific Risks
Since equity funds invest in companies across different industries or sectors, they are exposed to industry-specific risks, such as unfavourable developments that adversely impact companies within a particular industry. Equity funds can also be impacted by unfavourable developments within a specific company, such as a change in management or company policy. These risks, also known as unsystematic risks, can be mitigated through diversification.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the ease with which securities can be sold at or near their valuation yield-to-maturity or true value. In the context of equity funds, this risk may be relevant for listed securities. The liquidity of investments in equities may be restricted by trading volumes and settlement periods. While securities listed on a stock exchange carry lower liquidity risk, the ability to sell these investments is limited by the overall trading volume on the stock exchanges. If a mutual fund cannot sell securities due to low liquidity, it could result in potential losses if the value of those securities declines.
Price Risk
Equity funds are subject to price risk due to company- or sector-specific events. For example, a change in government directives, economic cycles, or regulatory policies can influence stock prices and may either increase or decrease share values.
Lock-in Period and Redemption Risk
Mutual funds with a long-term and rigid lock-in period, such as ELSS (Equity Linked Saving Schemes), often come with liquidity risk. Investors may find it challenging to redeem their investments without incurring a loss during the lock-in period, especially if there is a lack of buyers in the market.
Inflation Risk
Equity mutual funds are exposed to inflation risk, which is the risk of losing purchasing power due to a rising inflation rate. If the rate of returns on investments fails to keep up with the increasing inflation rate, investors may experience a decrease in their real returns.
Investment Risk
Equity mutual funds put money into a variety of investment instruments, including debt, equity, and corporate bonds, among others. Since the prices of these instruments tend to fluctuate in response to several factors, investors may be subjected to losses. This can happen due to a fall in the NAV (Net Asset Value) of these investments.
ISA Funds: A Guide to Smart Investing
You may want to see also

Types of equity mutual funds
Equity mutual funds are a type of investment fund that pools money from investors to primarily buy a portfolio of stocks, also known as equity securities. The funds are managed by professionals who conduct investment research and make decisions on behalf of the investors.
There are two primary categories of equity funds: actively managed funds and passive funds. Actively managed funds have portfolio managers who actively research, analyse and select stocks with the goal of outperforming a benchmark index, such as the S&P 500. The success of these funds largely depends on the fund manager's skill and decision-making ability. Passive funds, on the other hand, include index funds, which aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index. Passive fund managers do not attempt to outperform the market but instead track the index as closely as possible.
Equity funds are also categorised based on their investment strategy, with two main categories: growth funds and value funds. Growth funds invest in stocks of companies expected to have rapid earnings growth, while value funds buy stocks that are considered undervalued.
Additionally, equity funds can be classified based on their focus on specific sectors or geographic regions. Sector funds invest in stocks of companies operating within a particular industry, such as technology, healthcare or finance. Geographically focused funds, also known as regional funds, buy stocks of companies based in certain areas of the world.
- Large-cap funds: Invests in stocks of large companies with a market capitalization typically exceeding $10 billion.
- Mid-cap funds: Invests in stocks of companies with market capitalization between large and small-caps, often in the growth phase of their life cycle.
- Small-cap funds: Buys stocks of companies with a small market capitalization, usually younger businesses with high growth potential.
- Domestic equity mutual funds: Own stocks in companies based in the United States.
- International equity mutual funds: Own stocks in companies based outside of the United States.
- Sector equity mutual funds: Own stocks in companies pursuing similar types of businesses or offering similar products and services.
- Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) equity mutual funds: Include ESG factors in their investment strategies, allowing investors to support companies that align with their values.
Invest Wisely: LIC Pension Fund Guide
You may want to see also

How to invest in equity mutual funds
An equity mutual fund is a professionally managed, pooled investment vehicle that invests primarily in stocks. The fund's management team determines its strategies and investable universes, which may include companies from around the world or be limited to specific regions, such as the United States.
- Understand your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon: Before investing in equity mutual funds, it is essential to define your financial objectives, such as saving for retirement, funding education, or building long-term wealth. You should also assess your risk tolerance, which refers to your ability and willingness to withstand market volatility and potential losses. The time horizon is another crucial factor and represents the length of time you plan to hold your investments.
- Choose the right fund style for you: There are different types of equity funds, including actively managed funds, passive index funds, and sector-specific funds. Actively managed funds have portfolio managers who actively research, analyze, and select stocks to outperform a benchmark index. Passive funds, on the other hand, aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. Sector-specific funds invest in stocks within a particular industry or market sector, like technology or healthcare.
- Conduct thorough research and analysis: Review the fund's prospectus, which provides detailed information about its investment objectives, strategies, risks, and fees. Additionally, study the fund's annual and quarterly reports to gain insights into its performance, holdings, and market commentary. Utilize financial news and research platforms like Morningstar or Yahoo! Finance to find fund performance data, analyst ratings, and peer comparisons.
- Compare expense ratios: The expense ratio is the annual fee charged by the fund, expressed as a percentage of assets under management. Higher expense ratios can significantly impact long-term returns, so it is essential to compare fees across different funds in the same category.
- Open an investment account: Once you have selected the equity fund(s) that align with your goals and risk profile, you need to open an investment account. You can usually open an account directly with the fund company or through a brokerage firm that offers access to multiple fund providers. Provide the required personal information, such as your name, address, and Social Security number, and fund the account by transferring money.
- Buy shares of the chosen equity fund: After funding your account, you can purchase shares of the desired equity fund. Many funds have a minimum initial investment requirement, which can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Some funds also offer automatic investment plans, allowing you to invest a fixed amount at regular intervals.
- Monitor and rebalance your investments: Regularly review the performance of your equity fund investments, keeping an eye on relevant news and market developments. Periodically rebalance your portfolio to ensure that your equity fund allocation aligns with your target asset mix and risk profile.
Remember, investing in equity mutual funds carries risks, primarily due to the volatility of the stock market. It is crucial to carefully consider your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and tax situation before investing. Consult a financial advisor to determine how equity funds fit within your overall financial strategy, and always conduct thorough research before making investment decisions.
A Beginner's Guide to Mutual Funds Abroad
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An equity mutual fund is a type of investment fund that pools money from investors to buy a portfolio of stocks. These funds are managed by professionals who conduct investment research and make decisions about which stocks to buy, hold or sell.
Equity mutual funds offer investors a professionally managed, diversified approach to investing in stocks, with the potential for attractive long-term returns. They also provide investors with broader exposure than individual stocks, helping to reduce risk.
The main risk with equity mutual funds is market risk, which means that economic downturns, geopolitical events or changes in investor sentiment can cause prices to decline. During market turbulence, equity fund prices can fluctuate significantly, potentially leading to short-term losses for investors.