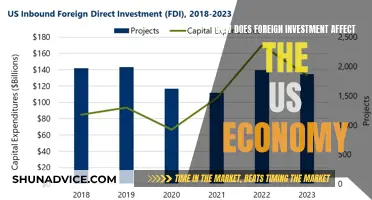
Foreign investment policy is a crucial aspect of a country's economic strategy, designed to regulate and manage the flow of capital and assets from foreign entities into the domestic market. This policy framework aims to attract international investors while ensuring that the investment process is transparent, fair, and beneficial to the host country's economic development. It involves setting guidelines and regulations that define the terms and conditions under which foreign investors can operate, including restrictions on ownership, investment limits, and specific sectors that are open to foreign investment. The primary goal is to strike a balance between promoting economic growth and maintaining national sovereignty, ensuring that foreign investments contribute positively to the host country's infrastructure, job creation, and overall economic prosperity.
What You'll Learn
- Definition and Types: Foreign investment policy outlines the rules and regulations governing various forms of international investment
- Economic Impact: Policies assess the economic effects of foreign direct investment on host countries
- Regulatory Framework: Governments establish legal structures to manage and control foreign investment
- Policy Instruments: These include incentives, restrictions, and tax measures to attract or deter foreign capital
- International Treaties: Bilateral and multilateral agreements shape foreign investment policies and standards

Definition and Types: Foreign investment policy outlines the rules and regulations governing various forms of international investment
Foreign investment policy is a crucial framework that shapes the global economy and international business dynamics. It refers to the set of guidelines, regulations, and strategies established by governments to manage and regulate the flow of capital, assets, and investments across international borders. This policy is designed to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) while also ensuring that the host country's interests and objectives are met.
The primary objective of foreign investment policy is to create a favorable environment for international investors, fostering economic growth and development. It involves a comprehensive approach to attract foreign capital, which can take various forms. These forms include portfolio investments, where investors buy and sell securities in foreign markets, and direct investments, which involve establishing operations or acquiring assets in a foreign country.
There are several types of foreign investment policies, each with its own set of rules and incentives. One common type is the 'screening' policy, where governments carefully examine and approve foreign investments based on specific criteria. This ensures that investments align with national development goals and may include sectors like infrastructure, technology, or renewable energy. Another approach is the 'negative list' policy, which allows foreign investments in all sectors except those explicitly restricted or prohibited. This provides a high level of foreign investment freedom while retaining some control over sensitive areas.
Additionally, countries may adopt 'investment promotion' policies, offering various incentives to attract foreign investors. These incentives can include tax benefits, subsidies, streamlined regulations, or special economic zones with favorable conditions. Such policies aim to enhance the competitiveness of the host country and encourage foreign companies to set up operations locally.
Understanding foreign investment policy is essential for businesses and investors navigating the global market. It provides a clear framework for international operations, helping companies make informed decisions regarding market entry, expansion, or investment opportunities. By adhering to these policies, businesses can ensure compliance with local laws and regulations, fostering successful and sustainable international ventures.
Best Cash Investments to Make Right Now
You may want to see also

Economic Impact: Policies assess the economic effects of foreign direct investment on host countries
Foreign investment policy plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of host countries. When assessing the economic impact of foreign direct investment (FDI), policymakers and researchers analyze various factors to understand the potential benefits and challenges it brings. One key aspect is the creation of jobs and the stimulation of economic growth. FDI often leads to the establishment of new businesses or the expansion of existing ones, resulting in increased employment opportunities for the local population. This can be particularly significant in regions with high unemployment rates, as it provides a means to address labor market issues and reduce poverty.
The economic effects of FDI are often associated with the transfer of capital and technology from foreign investors to the host country. This can result in improved productivity and efficiency in local industries. For instance, multinational corporations bringing in advanced machinery and expertise can enhance the capabilities of local firms, making them more competitive in the global market. Moreover, FDI can contribute to the development of infrastructure, such as transportation networks and communication systems, which are essential for economic growth and can have a long-lasting impact on the host country's overall development.
However, the economic impact of FDI is not without its challenges. One potential issue is the risk of exploitation, where foreign investors may take advantage of weaker regulations or less developed markets. This could lead to environmental degradation, labor rights violations, or the displacement of local businesses. Therefore, policies must carefully consider the balance between attracting FDI and ensuring sustainable and equitable development. This includes implementing regulations that protect the interests of the host country, its workers, and the environment while still promoting foreign investment.
Assessing the economic impact also involves studying the distribution of benefits across different sectors and regions. FDI policies might aim to direct investments towards specific industries or areas that have the potential for long-term growth and job creation. For example, investing in renewable energy projects can contribute to environmental sustainability and create new business opportunities. Additionally, policies can encourage FDI in sectors that address social and economic disparities, such as healthcare, education, or rural development.
In summary, foreign investment policies are instrumental in evaluating the economic implications of FDI. By understanding the job creation, technological transfer, and infrastructure development associated with FDI, policymakers can design strategies that maximize its benefits. Balancing the attraction of foreign capital with the need for sustainable and equitable growth is essential to ensure that the economic impact of FDI is positive and long-lasting for the host country. This requires a comprehensive approach that considers both the immediate and long-term effects of FDI on various economic indicators.
Understanding Cash Flows: Notes Receivable and Operating Cash
You may want to see also

Regulatory Framework: Governments establish legal structures to manage and control foreign investment
The regulatory framework for foreign investment is a critical component of a country's foreign investment policy, designed to provide a structured environment for international capital inflows while ensuring national interests are protected. This framework involves a set of laws, regulations, and policies that govern the entry, operation, and exit of foreign investors, aiming to strike a balance between attracting investment and maintaining control over strategic assets and industries. Governments employ various legal structures to manage foreign investment, each tailored to specific objectives and the nature of the investment.
One common approach is the establishment of investment promotion agencies or departments within government ministries. These bodies are tasked with attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) by providing information, incentives, and support to potential investors. They often offer services such as business registration assistance, tax guidance, and access to investment-ready projects, making the investment process more accessible and attractive. For instance, a country might set up a dedicated foreign investment agency that acts as a single point of contact for investors, streamlining the process and reducing bureaucratic hurdles.
In addition to promotional efforts, governments implement regulatory measures to ensure that foreign investments comply with domestic laws and regulations. This includes setting up registration and licensing requirements, which may vary depending on the sector and the level of investment. For instance, a foreign company investing in the telecommunications sector might need to obtain specific licenses and adhere to strict operational guidelines, while a small-scale investment in agriculture may be subject to less stringent regulations. These measures help governments maintain oversight and ensure that foreign investments contribute positively to the economy without compromising national interests.
Another critical aspect of the regulatory framework is the establishment of dispute resolution mechanisms. Given the potential for conflicts between foreign investors and host countries, governments create legal frameworks that provide a fair and transparent process for resolving disputes. This can include international arbitration clauses in investment treaties, which offer a neutral platform for resolving disagreements, ensuring that investors' rights are protected while also allowing for the enforcement of local laws and regulations.
Furthermore, governments may introduce special economic zones (SEZs) or industrial parks to encourage foreign investment in specific regions or sectors. These zones often offer tax incentives, streamlined regulations, and infrastructure support to attract investors. By creating dedicated areas for foreign investment, governments can better manage and control the flow of capital, ensuring that it aligns with national development goals. This approach is particularly useful for promoting industrialization, technology transfer, and job creation in specific sectors or regions.
In summary, the regulatory framework for foreign investment is a multifaceted system that combines promotional and regulatory measures to manage international capital inflows effectively. It involves a range of legal structures, from investment promotion agencies to specialized economic zones, all designed to attract and facilitate foreign investment while safeguarding national interests. By implementing these frameworks, governments can create a conducive environment for foreign investors, fostering economic growth and development while maintaining control over critical sectors of the economy.
Finding Initial Investment: Utilizing Positive Cash Flow Strategies
You may want to see also

Policy Instruments: These include incentives, restrictions, and tax measures to attract or deter foreign capital
Foreign investment policy is a crucial framework that governments employ to regulate and shape the flow of capital across international borders. It involves a strategic approach to managing foreign direct investment (FDI) and international portfolio investment, aiming to maximize benefits for the host country while mitigating potential risks. One of the primary tools in this policy toolkit is the use of policy instruments, which can be categorized into incentives, restrictions, and tax measures.
Incentives: These are designed to attract foreign investors by offering various benefits and advantages. Governments often provide tax breaks, subsidies, and grants to encourage FDI. For instance, a country might offer a reduced corporate tax rate for a specific period to entice foreign companies to invest in local operations. Additionally, incentives can include special economic zones or industrial parks with favorable conditions, such as relaxed regulations, streamlined procedures, and infrastructure support, to make these areas more attractive for foreign investors. These incentives aim to create a conducive environment, fostering economic growth and development.
Restrictions: On the other hand, governments may also implement measures to restrict or deter foreign investment in certain sectors or industries. This can be done through licensing requirements, foreign ownership limits, or sector-specific regulations. For example, a country might impose strict licensing procedures for foreign investors in sensitive areas like defense, media, or natural resources, ensuring that these sectors remain under domestic control. Restrictions can also be applied to protect local industries from potential market disruption or to address specific economic or social concerns.
Tax Measures: Tax policy is a powerful instrument in foreign investment policy. Governments can use tax incentives to promote FDI by offering reduced tax rates or tax holidays. This encourages investors to bring capital into the country and invest in specific sectors or activities. Conversely, higher tax rates or penalties can be imposed on foreign investors to discourage investment in certain areas or to deter speculative capital flows. Tax measures can also include withholding tax regulations, import/export duties, and value-added tax (VAT) policies, all of which significantly impact the profitability and overall appeal of foreign investment.
The effectiveness of these policy instruments depends on the specific economic goals and priorities of the host country. A well-designed foreign investment policy should balance the need to attract FDI for economic growth with the responsibility to protect local industries, jobs, and national interests. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the domestic economy, international investment trends, and the potential impact of policy changes on various stakeholders.
Investing via Cash App: A Guide for Under-18s
You may want to see also

International Treaties: Bilateral and multilateral agreements shape foreign investment policies and standards
International treaties play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of foreign investment policies and standards globally. These agreements, whether bilateral or multilateral, serve as the cornerstone for fostering a conducive environment for cross-border investments while also addressing the concerns and interests of participating nations. Bilateral treaties, in particular, are direct agreements between two countries, often tailored to each nation's specific needs and priorities. They establish a framework for the protection and promotion of investments, ensuring that foreign investors receive fair treatment and enjoy certain privileges within the host country's jurisdiction. These treaties typically cover various aspects, including the definition of "investor" and "investment," the scope of protection, and the mechanisms for dispute resolution. By providing a clear and mutually agreed-upon set of rules, bilateral agreements reduce uncertainty and potential conflicts, thereby encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI).
Multilateral treaties, on the other hand, involve multiple countries and often have a broader scope. These agreements aim to establish common standards and rules for foreign investment across a wider region or globally. The most prominent example is the United Nations Convention on Transnational Corporations (1986), which sets out principles for the regulation of transnational corporations and encourages cooperation among countries to promote responsible business practices. Multilateral treaties can also take the form of regional trade agreements, such as the European Union's Directive on the Protection of Investors, which harmonizes investment protection and promotion standards within the EU. These agreements facilitate the movement of capital, goods, and services, fostering economic integration and cooperation.
The impact of these international treaties is far-reaching. They influence the design and implementation of national foreign investment policies, often leading to the adoption of similar or compatible standards. For instance, a country's foreign investment policy might include provisions for national treatment, ensuring that foreign investors are not subjected to less favorable conditions than domestic investors. Treaties also often include provisions for the establishment of investment review mechanisms, allowing countries to assess the potential impact of foreign investments on their economies and industries. This process can help identify and mitigate risks associated with FDI, such as potential negative effects on local industries or environmental concerns.
Furthermore, international treaties provide a platform for resolving disputes between host countries and foreign investors. The investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS) mechanism, present in many bilateral and multilateral agreements, allows investors to seek international arbitration in cases of alleged breaches of treaty obligations. This mechanism ensures that investors have access to a fair and transparent process for resolving conflicts, which is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and attracting FDI.
In summary, international treaties, both bilateral and multilateral, are instrumental in shaping foreign investment policies and standards. They provide a legal framework that encourages cross-border investments, promotes economic cooperation, and ensures a level playing field for investors. By establishing common rules and standards, these treaties facilitate global trade and investment, contributing to the growth and development of nations involved. Understanding and effectively utilizing these treaties is essential for governments and investors alike to navigate the complex world of international business and investment.
Investment Bankers' Toolbox: Secrets to Success
You may want to see also