Life insurance is a financial product that provides peace of mind and financial security for loved ones after the policyholder passes away. However, some types of life insurance policies can also be used as an investment tool to provide financial benefits to the policyholder during their lifetime. This has led to a debate about whether life insurance should be considered primarily as a form of coverage or as an investment.
On the one hand, life insurance is designed to pay out a sum of money to beneficiaries after the policyholder's death, helping to cover burial costs, unpaid debts, and other financial losses. Term life insurance, which covers the policyholder for a set period, is often recommended for those who want to ensure their loved ones are financially protected without incurring high premiums.
On the other hand, permanent life insurance policies, such as whole life insurance, can include a cash value component that grows over time and can be borrowed against or withdrawn. This feature blurs the line between life insurance and investment, as it allows policyholders to access funds for expenses like college tuition or a down payment on a house.
So, while life insurance is traditionally associated with coverage and protection, certain types of policies can also serve as a form of investment, providing financial benefits both during and after the policyholder's lifetime.
What You'll Learn

Whole life insurance as an investment tool
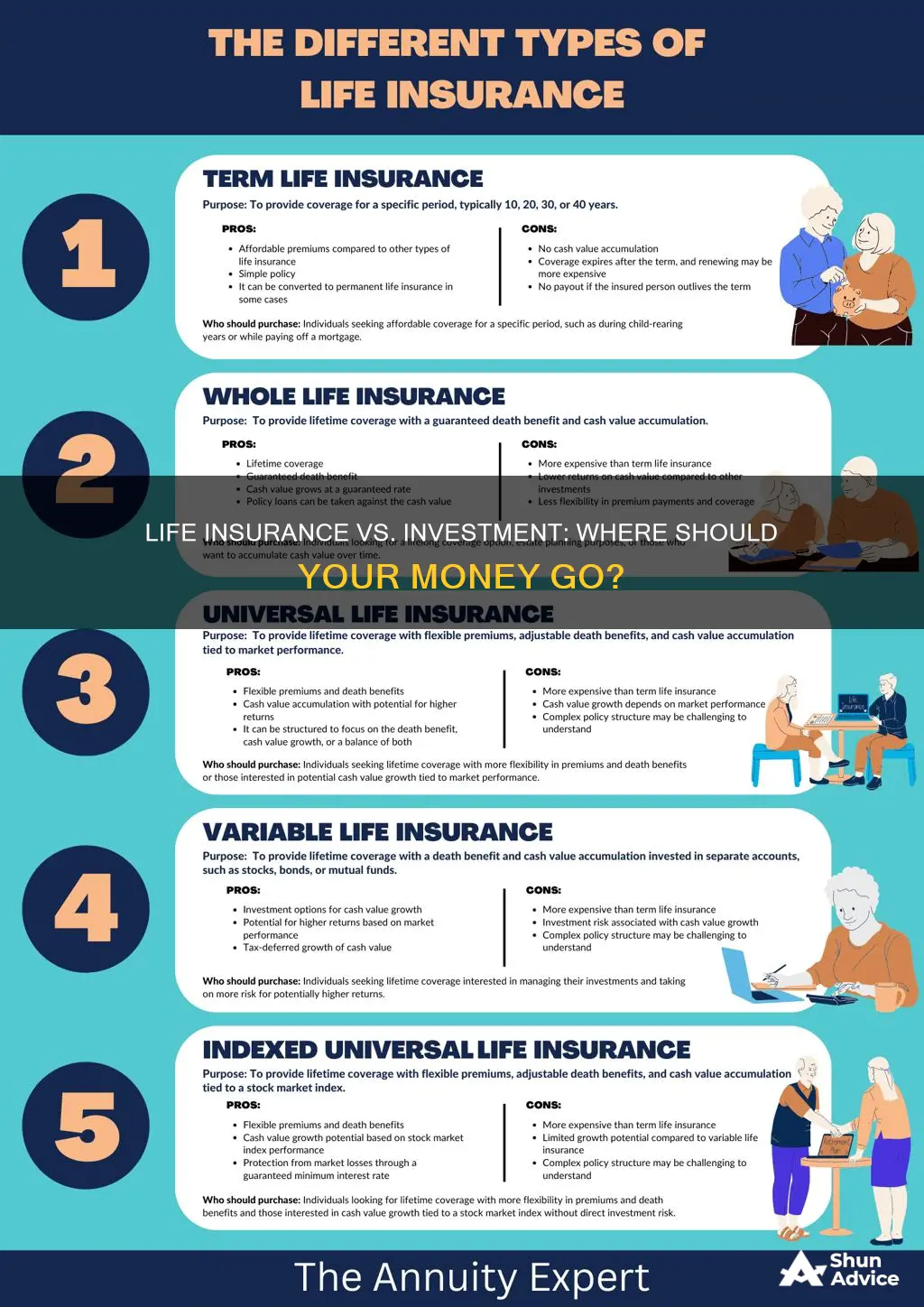
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that lasts for the entire life of the policyholder. It is often purchased for its death benefit, but it can also be used as an investment tool. Whole life insurance policies allow the holder to accumulate cash value in a tax-deferred account, which can be used to generate income during retirement, pay for large expenses, or create generational wealth. The cash value grows at a fixed rate that is guaranteed by the insurer and is not subject to market changes. This makes whole life insurance a stable investment option for those seeking to diversify their portfolios.
One of the main benefits of using whole life insurance as an investment tool is the ability to access the cash value while the policyholder is still alive. Policyholders can take out loans against the cash value, make withdrawals, or use the policy as collateral for a loan. These options provide flexibility and can help cover unexpected expenses or supplement retirement income. Additionally, the cash value grows tax-deferred, meaning policyholders don't pay taxes on the interest earned as long as the funds remain in the policy.
However, there are also some drawbacks to consider when using whole life insurance as an investment tool. Whole life insurance policies tend to be more expensive than term life insurance policies due to the built-in cash value. The cash value can also be slow to grow, as it takes time for a higher percentage of the premium to go towards the cash value. Additionally, policyholders have limited control over their investment portfolio, as the insurance company chooses where to invest the cash value.
Overall, while whole life insurance may not be the best investment option for everyone, it can be a valuable tool for those seeking stable, long-term investments with guaranteed returns. It is important for individuals to carefully consider their financial goals and needs before deciding if whole life insurance is the right investment tool for them.
Understanding Managed Investment Trusts: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Universal life insurance as an investment option
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers lifetime coverage as long as you pay your premiums. It is also known as 'jumbo' life insurance due to its high coverage level, with death benefits ranging from $1 million to $150 million and beyond.
Universal life insurance has a cash value element that can be invested in a variety of ways, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The cash value grows over time, earning interest set by the insurer, and can be borrowed against or withdrawn. However, there are some risks associated with this type of insurance. The interest rate on the cash value is not guaranteed and can change frequently, and if the investments underperform, your cash value can decrease and your premiums could increase. Additionally, there may be tax implications on withdrawals from the policy.
One of the key advantages of universal life insurance is its flexibility. Policyholders can adjust their premiums and death benefits to some extent. The ability to lower or skip payments without the policy lapsing provides valuable peace of mind, but careful account management is required to ensure the policy remains adequately funded.
Universal life insurance can be a useful investment option for those seeking permanent life insurance with the added benefit of an interest-bearing cash value component. It is particularly suitable for those who want the flexibility to adjust their premiums and death benefits and are comfortable with the associated risks. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential risks and costs before purchasing this type of insurance.
India's Guide to Investing in Renewable Energy Sources
You may want to see also

Variable universal life insurance for investing
Variable universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a death benefit alongside a savings component, known as the cash value. This coverage can last your entire life as long as you continue to pay the insurance costs.
Variable universal life insurance is similar to universal life insurance, but instead of earning a specific crediting rate on the cash-value component, it allows you to put some or all of the cash value into a "variable account" made up of investment funds. This gives you a degree of control over where you allocate the cash value portion of your policy, allowing for greater earning potential, but also market risk.
Variable universal life insurance offers flexible premium payment options, and the potential to earn higher-than-average returns compared to other types of permanent life insurance. It also allows you to maintain a certain level of self-directed control over how your cash value is invested and to allocate according to your individual risk tolerance.
However, there are some disadvantages to variable universal life insurance. It can be more complex than other forms of life insurance and may involve higher fees. There is also a risk that you could experience a decrease in your cash value due to poor performance of your investment options.
Variable universal life insurance can serve as a resource for retirement and tax planning due to its market-based cash value growth potential and tax advantages. The returns earned on any cash value are tax-free, and there are no required minimum distributions. You can also take out tax-free policy loans, although any outstanding loans will reduce your death benefit.
Variable universal life insurance may be a good option for those who want permanent life insurance protection, have a higher risk tolerance for investing, and prefer to manage investments themselves. However, it is important to carefully assess the risks before purchasing this type of policy.
Sugar Baby's Guide to Smart Investing
You may want to see also

Indexed universal life insurance for investment growth
Indexed universal life insurance (IUL) is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a death benefit and a cash value component. It is a form of universal life insurance, which provides flexible premiums and death benefits. IUL policies are complex financial products that are suitable for those seeking a combination of life insurance coverage and investment growth potential.
How IUL Works
IUL policies allow policyholders to allocate their cash value between a fixed-rate account and an equity-indexed account. The fixed-rate account offers a guaranteed interest rate, while the equity-indexed account links the cash value growth to the performance of a chosen stock market index, such as the S&P 500. Policyholders can decide how much of their cash value goes into each account.
The cash value in an IUL policy can grow tax-deferred, and the gains are not directly invested in the stock market, reducing risk. Additionally, IUL policies offer flexible premiums, and the death benefit may also be adjustable.
Advantages of IUL for Investment Growth
- Control over premiums and coverage: IUL policies allow policyholders to increase or decrease their premium payments and adjust their coverage amount to suit their financial situation and needs.
- Potential for market-linked returns: By linking the cash value to the performance of a stock index, IUL policies offer the potential for higher returns compared to traditional fixed-rate accounts.
- Protection from market downturns: IUL policies have a "floor," which is a minimum guaranteed rate that protects the investment from market downturns. Even if the market performs poorly, the policyholder's investment is protected from losses.
- Tax advantages: The cash value in an IUL policy grows tax-free, and the death benefit is also tax-free for beneficiaries.
- No contribution limits: IUL policies, unlike retirement accounts, do not have any contribution limits, allowing high-net-worth individuals to invest as much as they want.
- Liquidity: Policyholders can access the cash value in their IUL policy through policy loans and withdrawals, providing flexibility for emergency expenses or investment opportunities.
Disadvantages of IUL for Investment Growth
- Complexity: IUL policies are complex financial products with multiple moving parts, making them difficult to understand for those without a strong financial background.
- Fees and charges: IUL policies often come with various fees, such as premium loads, surrender charges, administrative expenses, and mortality charges, which can eat into the returns over time.
- Limited upside potential: IUL policies typically have caps on how much the investment can grow, and participation rates may further limit the returns.
- Potential tax implications: Withdrawing funds from an IUL policy that exceed the policy basis may result in income tax liabilities. Additionally, there may be tax consequences if the policy is surrendered or if there is an outstanding loan against the policy upon the policyholder's death.
- Risk: The stock market may not perform as projected, and if the index linked to the policy underperforms, the investment returns may be lower than expected.
Indexed universal life insurance can be a good investment option for those seeking a combination of life insurance coverage and investment growth potential. It offers flexibility, tax advantages, and the potential for market-linked returns. However, it is important to carefully consider the complexities, fees, and potential risks associated with IUL policies before making a decision.
Saving's Leakage and Planned Investment: A Balancing Act
You may want to see also

Term life insurance as an investment alternative
Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that covers you for a set period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. During this period, your beneficiaries will receive a lump-sum death benefit if you pass away. However, if you outlive the policy, there is no payout. Term life insurance is often preferred due to its simplicity, affordability, and fixed premiums.
When considering term life insurance as an investment alternative, it is important to understand its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some key points to consider:
Advantages of Term Life Insurance:
- Affordability and Cost-Effectiveness: Term life insurance is generally less expensive than permanent life insurance. This is because it only covers a specific period and lacks a cash value component. The younger and healthier you are when you purchase a term life policy, the lower your premiums are likely to be.
- Flexible Term Lengths: You can choose a term length that aligns with your financial responsibilities, such as a 10, 15, 20, or 30-year policy. This allows you to ensure coverage during important periods, such as paying off a mortgage, funding education, or covering income during your working years.
- High Coverage Amounts: Due to its affordability, term life insurance allows individuals to purchase higher coverage amounts, ensuring their families can maintain their standard of living, cover debts, and manage daily expenses in the event of an unexpected death.
- Conversion Options: Many term life insurance policies offer the option to convert to permanent life insurance later on, even if your health has declined, without requiring a new medical exam.
- Financial Protection for Dependents: Term life insurance primarily provides financial protection for your loved ones, covering essential expenses such as mortgage payments, education, and daily living expenses if you pass away during the policy term.
- Simplicity and Transparency: Term life insurance offers clear coverage for a set premium over a defined period, without the complexity of investments or cash values.
Disadvantages of Term Life Insurance:
- Limited Coverage: Unlike permanent life insurance, term life insurance only covers you for a specific period. If you outlive the policy term, there is no payout, and you will need to purchase a new policy or extend your coverage, which may be more expensive.
- No Cash Value: Term life insurance does not have a cash value component, so there is no opportunity to accumulate cash value over time or borrow against the policy.
- Increasing Premiums with Age: While premiums are fixed during the policy term, they may increase significantly if you need to renew or extend your coverage after the initial term, especially if your health has declined.
When considering term life insurance as an investment alternative, it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages. Term life insurance offers financial flexibility, the potential for higher returns by investing the difference in premiums, and the ability to customize your coverage. However, it lacks the lifelong coverage and cash value component offered by permanent life insurance.
Free Cash Flow: Private Equity's North Star
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance is a financial product that pays out a sum of money to your beneficiaries after you die.
Term life insurance covers you for a set period, such as 20 or 30 years, and is typically cheaper than permanent coverage. Permanent life insurance covers you for your entire life as long as premiums are paid and can include a cash value component that grows tax-free and can be borrowed against or withdrawn.
Life insurance can offer a financial benefit to loved ones when you pass away, but it can also be a financial asset during your life. The cash value component of permanent life insurance policies can be borrowed against, used as collateral for a loan, or withdrawn. However, any unrepaid funds from loans or withdrawals will lower the death benefit. Life insurance can also be used to provide financial stability for lifelong dependents, diversify an investment portfolio, and supplement retirement income. On the other hand, permanent life insurance can be more expensive than term life insurance, and the cash value may take a while to grow. Additionally, there may be tax implications if you withdraw more than the policy basis or surrender your policy.







