Savings and investments are crucial for shaping a person's financial strategy and determining national income. They are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and functions. Saving is setting aside money for future use, while investing is buying assets with the expectation of making money. Savings provide financial security and help achieve short-term goals, while investments offer higher returns over time but come with greater risk. Both are essential for a secure future, and finding the right balance between the two is key to financial planning. Savings and investments also play a pivotal role in a country's economic health, influencing capital formation, economic growth, and national income.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition of Saving | Setting aside money that is not spent now for emergencies or future purchases |
| Definition of Investment | Buying assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or real estate with the expectation of making money |
| Purpose of Saving | Emergency fund, short-term financial goals, preparing for unexpected situations |
| Purpose of Investment | Reach long-term financial goals, e.g. children's college funds, retirement |
| Risk Factor | Saving is low-risk; Investment involves taking on some risk |
| Returns | Savings have low-interest rates; Investments have the potential for higher returns |
| Time Horizon | Saving is short-term; Investment is long-term |
| Examples of Saving | Putting money in a savings account, buying stocks, contributing to a pension plan |
| Examples of Investment | Buying stocks, bonds, mutual funds, investing in a company |
| Impact on Economy | Savings and investments influence capital formation and economic growth, increasing national income |
What You'll Learn

Savings and investments determine national income
Savings and investments are crucial in determining national income. They play a pivotal role in shaping a country's economic health and are key drivers of capital formation and economic growth. National income is influenced by various factors, including the levels of savings and investments.
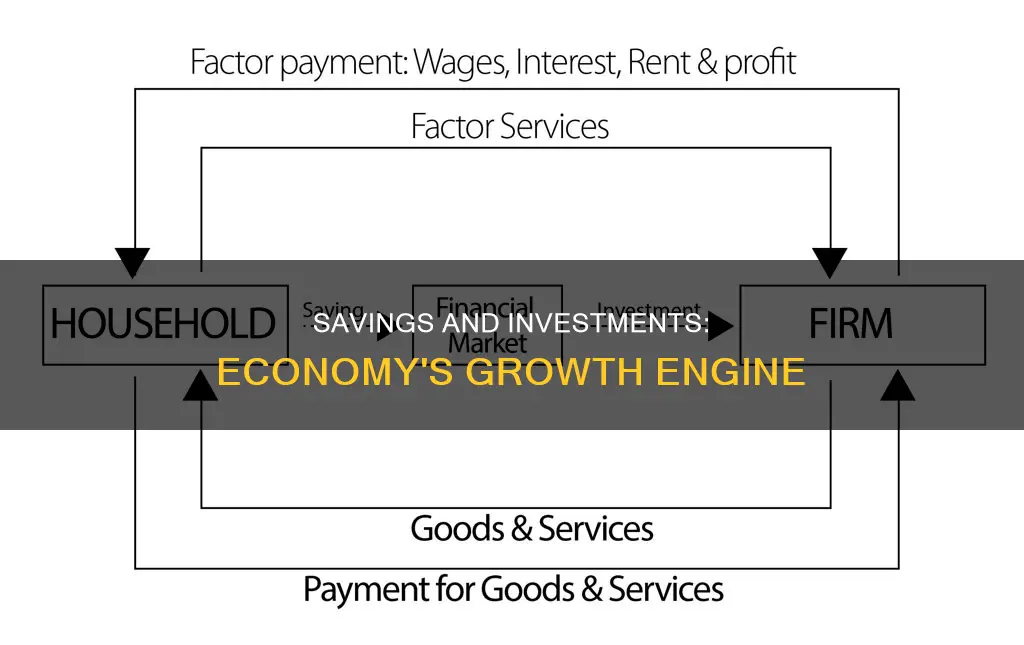
Savings, in economic terms, refer to the portion of income not spent on consumption. When individuals save, they deposit their money in banks or other financial institutions, which can then lend these savings to businesses and entrepreneurs. This process, known as capital formation, is a significant driver of economic growth. Higher levels of savings can lead to higher levels of investment, which can, in turn, increase national income.
Investments refer to the purchase of goods that are not consumed today but are used in the future to create wealth. Investments can take the form of physical assets, like machinery or infrastructure, or intangible assets, like education or skills training. They increase the productive capacity of an economy, leading to higher levels of output and income. Additionally, investments can drive technological progress, further increasing productivity and national income.
The relationship between savings, investments, and national income is complex and influenced by various factors. For example, excessively high savings and low consumption can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, slowing economic growth. Similarly, if investments are unproductive or directed towards unproductive sectors, they may not contribute to an increase in national income. Therefore, a balanced approach to savings and investments is necessary to ensure sustainable economic growth and a steady increase in national income.
In summary, savings and investments are key determinants of national income. They influence capital formation, economic growth, and the productive capacity of an economy. However, the complex relationship between these factors requires a nuanced understanding to ensure that savings and investments positively contribute to the overall economic health of a nation.
Maximizing Savings: Strategies to Double Your Money
You may want to see also

Savings and investments influence capital formation
Savings and investments are crucial in determining national income as they influence the level of capital formation and economic growth. National income is the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period, and it is a key indicator of a nation's economic health.
Savings, in economic terms, refer to the portion of income not spent on consumption. When individuals save, these savings can be deposited in banks or other financial institutions, which can then lend this money to businesses and entrepreneurs. This process, known as capital formation, is a significant driver of economic growth. Higher levels of savings can lead to higher levels of investment, which can, in turn, lead to an increase in national income.
Investments refer to the purchase of goods that are not consumed today but are used in the future to create wealth. Investments can be in the form of physical assets, like machinery or infrastructure, or in intangible assets, like education or skills training. They increase the productive capacity of an economy, leading to higher levels of output and income. Moreover, investments can also lead to technological progress, which can increase productivity and, consequently, national income.
The relationship between savings, investments, and national income is complex and influenced by various factors. For example, if savings are too high and consumption is too low, it can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, slowing economic growth. Similarly, if investments are not productive or are directed towards unproductive sectors, they may not contribute to an increase in national income. Therefore, a balanced approach to savings and investments is necessary to ensure sustainable economic growth and a steady increase in national income.
In summary, savings and investments play a pivotal role in shaping a country's financial strategy and determining its national income. They are key drivers of capital formation, influencing the productive capacity of an economy and contributing to economic growth. A well-rounded approach that includes both saving and investing can help build wealth, protect against financial shocks, and provide a solid foundation for a more secure financial future.
SSS Workers Investment and Savings: A Guide to the Program
You may want to see also

Investments increase the productive capacity of an economy
For example, when individuals save, these savings can be deposited in banks or other financial institutions. These institutions can then lend these savings to businesses and entrepreneurs, who can invest in new projects, expand their operations, or innovate their products and services. This process, known as capital formation, is a significant driver of economic growth.
The accumulation of financial capital creates greater opportunities for production and productivity by providing an additional income stream. This is particularly important for developing countries, as it can reduce their dependence on foreign investment and decrease the risk arising from volatile foreign direct investment.
Investments can also lead to technological progress, which can increase productivity and, consequently, national income. For instance, investing in education or skills training can create a more knowledgeable and skilled workforce, which can lead to innovations and improvements in production processes.
Additionally, investments in machinery or infrastructure can increase the efficiency of production processes, allowing for higher output and income. This increase in productive capacity can also have a positive impact on employment levels, as businesses may need to hire more workers to operate new machinery or manage expanded operations.
However, it is important to note that the relationship between investments and economic growth is complex and influenced by various factors. For instance, if investments are not productive or are directed towards unproductive sectors, they may not lead to an increase in national income. Therefore, a balanced approach to investments is necessary to ensure sustainable economic growth.
Exploring Private Savings and Investment Spending Dynamics
You may want to see also

Savings and investments drive economic growth
Savings and investments are essential drivers of economic growth. They play a pivotal role in determining national income, which is a key indicator of a nation's economic health. Savings and investments influence the level of capital formation and economic growth.
Savings, in economic terms, refer to the portion of income not spent on consumption. When individuals save, they deposit their money in banks or other financial institutions, which can then lend these savings to businesses and entrepreneurs. This process, known as capital formation, is a significant driver of economic growth. Higher levels of savings can lead to higher levels of investment, which can, in turn, lead to an increase in national income.
Investments refer to the purchase of goods that are not consumed immediately but are used in the future to create wealth. Investments can take the form of physical assets, like machinery or infrastructure, or intangible assets, like education or skills training. They increase the productive capacity of an economy, leading to higher levels of output and income. Additionally, investments can drive technological progress, further increasing productivity and national income.
The relationship between savings, investments, and economic growth is complex. For instance, if savings are too high and consumption is too low, it can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, slowing down economic growth. Similarly, if investments are not productive or are directed towards unproductive sectors, they may not contribute to an increase in national income. Therefore, a balanced approach to savings and investments is necessary to ensure sustainable economic growth.
The impact of savings and investments on economic growth has been studied extensively by economists. Research shows that countries with higher savings rates tend to experience faster economic growth. This is because capital accumulation provides additional income streams, creating greater opportunities for production and productivity enhancements.
In summary, savings and investments are crucial for economic growth as they drive capital formation, increase productive capacity, and enhance technological progress. A balanced approach to savings and investments is essential to sustain economic growth and improve the economic health of a nation.
Investment Options for College Savings: What Are Your Choices?
You may want to see also

The relationship between savings, investments, and national income is complex
Savings and investments are crucial in determining national income as they influence the level of capital formation and economic growth. National income is the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period and is a key indicator of a nation's economic health.
Savings, in economic terms, refer to the portion of income not spent on consumption. When individuals save, these savings can be deposited in banks or other financial institutions, which can then lend this money to businesses and entrepreneurs. This process, known as capital formation, is a significant driver of economic growth. Higher levels of savings can lead to higher levels of investment, which can, in turn, increase national income.
Investments refer to the purchase of goods that are not consumed today but are used in the future to create wealth. Investments can take the form of physical or intangible assets and increase the productive capacity of an economy, leading to higher levels of output and income. For example, investments in education or skills training can lead to technological progress, increasing productivity and, consequently, national income.
However, the relationship between savings, investments, and national income is complex and influenced by various factors. For instance, if savings are too high and consumption is too low, it can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, slowing down economic growth. Similarly, if investments are not productive or are directed towards unproductive sectors, they may not contribute to an increase in national income.
Therefore, a balanced approach to savings and investments is necessary to ensure sustainable economic growth and a steady increase in national income. This involves considering factors such as financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon to strike a balance between the two.
Savings and Planned Investments: What's the Difference?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Saving is setting aside money for future use or emergencies, while investing is buying assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate with the expectation of making money.
Savings play a crucial role in the economy as they contribute to capital formation and economic growth. They provide financial institutions with funds to lend to businesses and entrepreneurs, enabling investments in new projects, expansion, and innovation.
Investments increase the productive capacity of an economy, leading to higher output and income. They can also drive technological progress, further boosting productivity and national income.
Higher levels of savings can lead to increased investment, resulting in higher national income. However, a balance is necessary, as excessively high savings and low consumption can decrease aggregate demand and slow economic growth.
Savings and investments are key drivers of economic growth. Countries with higher savings rates tend to experience faster economic growth. Additionally, savings stimulate investment, production, and employment, leading to sustainable economic growth.