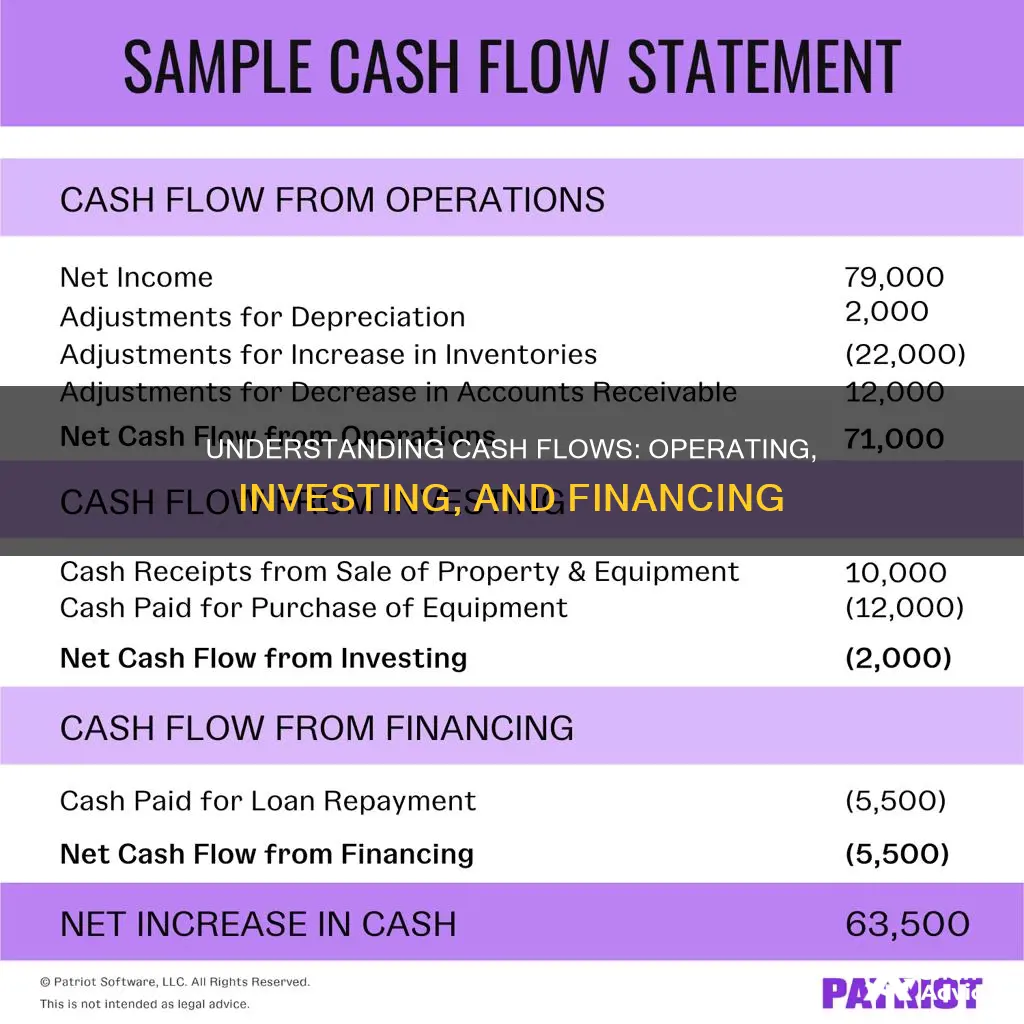
The statement of cash flows is one of the three key financial statements, alongside the income statement and the balance sheet. It presents the sources and uses of cash in three distinct categories: cash flows from operating activities, cash flows from investing activities, and cash flows from financing activities. This statement is important as it allows users to assess a company's strategy, ability to generate profit, and stay in business. It also provides a detailed picture of what happened to a business's cash during a specified period, known as the accounting period.
What You'll Learn
- Operating activities include revenue and expenses, such as sales, salaries and inventory
- Investing activities include cash flow from the purchase or sale of assets, like property or patents
- Financing activities detail cash flow from debt and equity financing
- Non-capital financing activities include borrowing money and repaying principal and interest
- Capital and related financing activities include acquiring and disposing of capital assets

Operating activities include revenue and expenses, such as sales, salaries and inventory
Operating activities are the functions of a business directly related to providing its goods and services to the market. They are the company's core business activities, such as manufacturing, distributing, marketing, and selling a product or service. Operating activities are the daily activities of a company involved in producing and selling its product, generating revenues, and conducting general administrative and maintenance activities.
Revenue and expenses are key components of operating activities. Revenue is generated through sales, which can include selling the company's own in-house manufactured products or products supplied by other companies, as in the case of retailers. Companies that primarily sell services may also sell products to generate additional revenue. For example, a spa business may sell health and beauty products in addition to providing services such as massages.
Expenses incurred in operating activities include the costs of manufacturing, advertising, and marketing the company's products or services. Manufacturing costs include all direct production costs, such as the cost of goods sold (COGS). Operating costs related to advertising and marketing include expenses for promoting the company and its products or services through various media outlets, trade shows, and public events.
Other expenses that fall under operating activities are salaries and inventory. Salaries are paid to employees, including those involved in the production and distribution of goods, as well as managers who oversee operations. Inventory expenses include the cost of purchasing materials from suppliers and paying for labour to produce the final product.
Operating activities are crucial for a company's financial success, as they generally provide the majority of its cash flow and determine its profitability. These activities are reflected in the company's financial statements, particularly the income statement and cash flow statement.
Invest Smarter: Toolbox Investments 101
You may want to see also

Investing activities include cash flow from the purchase or sale of assets, like property or patents
Investing activities are a crucial component of a company's cash flow statement, offering insights into its investment strategies and capital allocation decisions. This section of the statement reflects the cash inflows and outflows stemming from investment-related activities, including the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets such as property, plant, and equipment, and investments in marketable securities.
Investing activities encompass a diverse range of transactions, such as purchasing physical assets, investing in securities, or selling securities or assets. These activities can generate either negative or positive cash flow. When a company buys assets, it leads to negative cash flow, as money is spent on these purchases. Conversely, selling assets results in positive cash flow, as income is generated from these sales.
The purchase of fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, is a significant investing activity. These are known as capital expenditures (CapEx) and represent a company's investment in future operations. CapEx investments are necessary to maintain and expand a company's operations, but they also reduce cash flow. As such, companies with substantial capital expenditures are typically in a growth phase.
Another notable investing activity is the acquisition of other businesses or companies. This involves investing cash in purchasing another business entity, which can be a substantial investment and impact a company's cash flow position.
It is important to note that negative cash flow from investing activities is not always a negative indicator of a company's financial health. In some cases, it may signal that the company is making strategic investments in assets, research, or long-term development activities that are crucial for its sustainability and future growth.
The calculation of cash flow from investing activities involves adding or subtracting the relevant cash inflows and outflows. The formula is: Cash flow from investing activities = CapEx/purchase of non-current assets + marketable securities + business acquisitions – divestitures (sale of investments).
Free Cash Flow: Investment Costs and Their Inclusion
You may want to see also

Financing activities detail cash flow from debt and equity financing
Financing activities detail a company's cash flow from debt and equity financing. This section of the cash flow statement provides investors with insight into the company's financial strength and how well its capital structure is managed. It includes transactions involving debt, equity, and dividends.
The financing activities section of the cash flow statement details the money coming in and going out of the company. Money comes in from the issuance of debt or equity, and it goes out when paying back loans, buying back shares, or paying dividends. By looking at this section, stakeholders can understand how a company deals with debt, equity, and dividends.
Financing activities include the issuance and repayment of debt, the issuance and repayment of equity, the payment of dividends, and capital lease obligations. Companies that require capital will raise money by issuing debt or equity, and this will be reflected in the cash flow statement.
The cash flow from financing activities is the net amount of funding a company generates in a given time period. It includes all changes in accounts related to debt and equity.
A positive number for cash flow from financing activities means more money is flowing into the company than flowing out, which increases the company's assets. Conversely, negative CFF numbers can indicate that the company is servicing debt, but it can also mean that the company is retiring debt or making dividend payments and stock repurchases, which investors may view as positive actions.
The choices companies make regarding financing activities, such as issuing bonds or paying off loans, reveal their strategy for maintaining liquidity and capital. For example, a company may choose to fund its business entirely with equity, with a combination of debt and equity, or by recapitalising the business and changing its capital structure.
Understanding financing activities is crucial for assessing a company's financial health and stability. It provides insight into how businesses raise capital, repay lenders, and achieve good investment returns. These activities impact the company's cash flow, financial health, and long-term growth potential.
Understanding DCF Methods for Analyzing Investment Decisions
You may want to see also

Non-capital financing activities include borrowing money and repaying principal and interest
Non-capital financing activities are a crucial aspect of a company's financial operations, encompassing transactions that involve borrowing money and repaying the principal and interest. This section of the cash flow statement provides valuable insights into the company's financial management and overall health.
When a company engages in non-capital financing activities, it primarily focuses on short-term and long-term borrowing. This includes taking out short-term and long-term loans from financial institutions, such as banks. These loans provide the company with the necessary funds to run its operations, invest in new projects, or expand its business. However, it is essential to distinguish non-capital financing activities from capital and related financing activities, which involve borrowing specifically for the acquisition, construction, or improvement of capital assets.
The impact of non-capital financing activities on a company's financial statements is significant. When a company borrows money, it experiences a cash inflow, which is reflected in its cash flow statement. This inflow increases the company's assets and equity. On the other hand, when the company repays the principal and interest on these borrowings, it results in a cash outflow, reducing its assets and equity. The cash flow statement captures these outflows, providing a clear picture of the company's financial position.
It is worth noting that interest payments made on borrowings are typically recorded separately in the operating activities section of the cash flow statement. This separation highlights the difference between the core operations of the business and its financing activities. Additionally, the repayment of principal and interest on borrowings should not be confused with the repayment of debt, which falls under capital and related financing activities.
Non-capital financing activities also extend beyond borrowing and repayment. They include transactions such as the issuance of stocks or shares to investors, resulting in a cash inflow for the company. Conversely, when a company repurchases its own shares or distributes dividends to shareholders, it leads to a cash outflow. These transactions are essential for managing the company's capital structure and maintaining a healthy financial position.
In summary, non-capital financing activities encompass a range of financial transactions that involve borrowing, repayment, and capital raising through debt or equity. By analysing this section of the cash flow statement, investors and creditors can assess the company's financial strength, management capabilities, and overall attractiveness as an investment opportunity.
A Beginner's Guide to Investing with E-Trade
You may want to see also

Capital and related financing activities include acquiring and disposing of capital assets
Cash inflows from capital and related financing activities include:
- Proceeds from issuing or refunding bonds and other short and long-term borrowings used to acquire, construct and improve capital assets.
- Cash receipts from contributions made by other governments, organisations or individuals for the specific purpose of defraying the cost of acquiring, constructing or improving capital assets.
- Cash receipts of capital grants awarded to the agencies.
- Cash receipts from sales of capital assets and proceeds from insurance on capital assets that are stolen or destroyed.
- Cash receipts from special assessments or property and other taxes levied for capital purposes.
- Cash receipts from state appropriations to acquire, construct and improve capital assets.
Cash outflows from capital and related financing activities include:
- Cash payments to acquire, construct, or improve capital assets.
- Cash payments for principal and interest on borrowings to acquire, construct and improve capital assets.
- Other principal payments to vendors who have extended credit to an agency directly for the purpose of acquiring, constructing or improving capital assets.
Capital and related financing activities are one of the sections of a company's cash flow statement. The cash flow statement is one of the three key financial statements, reporting the cash generated and spent during a specific period of time. The other two financial statements are the income statement and the balance sheet. The cash flow statement acts as a bridge between the income statement and balance sheet by showing how cash moved in and out of the business.
Life Insurance Investments: Strategies for Financial Growth
You may want to see also