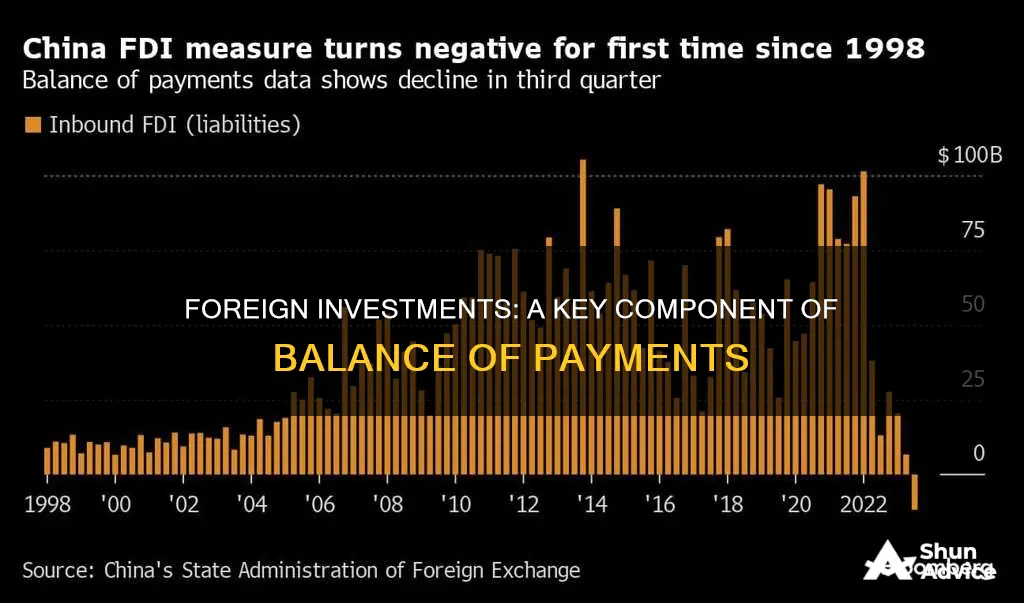
Foreign investments play a significant role in the balance of payments (BoP) of a country, and understanding their inclusion is crucial for analyzing a nation's economic health. The Balance of Payments (BoP) is a record of all economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world over a specific period. It includes various accounts, such as the current account, capital account, and financial account, each capturing different types of transactions. When a country attracts foreign direct investment (FDI) or holds assets abroad, these transactions are recorded in the BoP. This paragraph will explore how foreign investments are accounted for in the BoP and their impact on a country's economic indicators.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Foreign investments are not directly included in the Balance of Payments (BoP) but are accounted for in the Capital Account. |
| Impact on BoP | Foreign investments can influence the BoP indirectly through the Capital Account, which records changes in ownership of assets and liabilities. |
| Reporting | These investments are typically reported in the International Investment Position (IIP), which provides a snapshot of an economy's external assets and liabilities. |
| Types | Foreign direct investments (FDI), portfolio investments, and other investment flows. |
| Data Source | Data on foreign investments is often obtained from national statistical agencies, central banks, and international organizations like the World Bank. |
| Frequency | Data is usually reported annually or quarterly, depending on the country's reporting standards. |
| Global Trends | Foreign investment flows have been increasing globally, with significant variations across regions and countries. |
| Policy Implications | Foreign investments can impact a country's economic growth, employment, and overall development. |
| Risks | Potential risks include currency fluctuations, political instability, and regulatory changes. |
| Recent Trends | There has been a shift towards more sustainable and responsible investment practices, with a focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. |
What You'll Learn

Balance of Payments (BoP) Framework
The Balance of Payments (BoP) framework is a comprehensive system used by countries to record and analyze their international economic transactions over a specific period, typically a year. It provides a detailed breakdown of a country's economic interactions with the rest of the world, including goods, services, income, and financial flows. One of the key components of the BoP is the Current Account, which focuses on transactions that occur in the short term, such as exports and imports of goods and services, and unilateral transfers.
When it comes to foreign investments, they are indeed included in the BoP framework, specifically under the Capital Account. The Capital Account records transactions that are not part of the Current Account and are often associated with long-term economic activities. Foreign direct investments (FDI) and portfolio investments are the primary types of foreign investments that are captured in the BoP. FDI refers to investments made by a resident of one country into business enterprises in another country, while portfolio investments involve the purchase and sale of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives.
In the BoP, foreign investments are recorded as capital inflows or outflows, depending on the direction of the investment. When a foreign investor purchases assets in a country, it is recorded as a capital inflow, increasing the country's capital account balance. Conversely, if a domestic investor invests abroad, it is considered a capital outflow, reducing the country's capital account. These transactions are crucial for understanding the flow of capital and the overall financial position of a country in the global economy.
The inclusion of foreign investments in the BoP provides valuable insights into a country's economic relationships and its integration into the global financial system. It helps policymakers and economists assess the stability and attractiveness of a country's investment environment. By analyzing the capital account, they can identify potential risks, such as large capital outflows, and make informed decisions regarding monetary and fiscal policies. Moreover, the BoP data on foreign investments can be used to negotiate trade agreements, attract foreign direct investment, and promote economic growth.
In summary, the Balance of Payments framework plays a vital role in tracking and understanding a country's international economic activities, including foreign investments. The Capital Account is specifically designed to capture these transactions, providing essential data for economic analysis and decision-making. By including foreign investments in the BoP, countries can better manage their financial affairs, attract foreign capital, and ensure a more sustainable and balanced economic development path.
Ethereum to Ripple: A Guide to Converting Your Crypto
You may want to see also

Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and BoP
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a significant role in the Balance of Payments (BoP), and understanding its impact is crucial for economists and policymakers. When a company or individual from one country invests in a business or asset in another country, it is considered FDI. These investments can take various forms, such as acquiring a stake in a foreign company, establishing a new production facility, or merging with a local business. The inclusion of foreign investments in the BoP is an essential aspect of international financial accounting.
In the context of the BoP, FDI is a critical component of capital account transactions. It reflects the flow of capital across international borders and provides insights into a country's economic integration and development. When a foreign investor puts money into a local business, it increases the recipient country's capital inflow, impacting the BoP positively. This investment can contribute to economic growth, job creation, and technological advancement in the host country.
The impact of FDI on the BoP is twofold. Firstly, it can lead to a significant improvement in the current account, as FDI often generates exports and imports, thus increasing the trade balance. Secondly, FDI can influence the financial account, as investors may seek to protect their investments by converting local currency into a more stable one, impacting the exchange rate and capital flows. This process can have both short-term and long-term effects on a country's economic stability and growth.
Moreover, the inclusion of FDI in the BoP allows for a comprehensive analysis of a country's external economic relationships. It helps identify the sources and destinations of capital flows, providing valuable information for investment promotion and economic planning. By studying these patterns, governments can make informed decisions regarding trade policies, tax regulations, and incentives to attract or retain foreign investors.
In summary, Foreign Direct Investment is an integral part of the Balance of Payments, offering insights into a country's economic health and global integration. Understanding the dynamics of FDI and its impact on the BoP is essential for policymakers to make strategic decisions that promote sustainable economic development and maintain a stable financial environment.
Invest Hard Cash: Strategies for Smart Financial Growth
You may want to see also

Portfolio Investment and Capital Flows
The Balance of Payments (BoP) is a comprehensive record of a country's international transactions, providing a detailed snapshot of its economic interactions with the rest of the world. When it comes to foreign investments, the question of whether they are included in the BoP is an important one, as it directly impacts the understanding of a country's financial position and the flow of capital.
Portfolio investment, a key component of international capital flows, refers to the investment in financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and other securities. These investments are typically made by investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to foreign markets. When a foreign investor purchases a share of a domestic company or buys a bond issued by a foreign government, it is considered portfolio investment. This type of investment is crucial for capital formation and can significantly influence a country's economic growth.
Capital flows associated with portfolio investment are an essential aspect of the BoP. These flows involve the movement of financial resources across borders, often driven by market forces and investment opportunities. As investors buy or sell securities, there is a corresponding transfer of funds, which is recorded in the BoP. For instance, if a foreign investor purchases domestic stocks, it results in an inflow of capital, increasing the country's financial assets. Conversely, if a domestic investor sells foreign bonds, it leads to an outflow, reducing the country's financial liabilities.
The inclusion of foreign investments in the BoP is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a comprehensive view of a country's external assets and liabilities. By accounting for portfolio investments, the BoP offers a more accurate representation of a nation's economic health and its integration into the global financial system. This information is crucial for policymakers, investors, and economists who rely on accurate data to make informed decisions.
Secondly, tracking portfolio investment and capital flows helps identify patterns and trends in international financial markets. It allows for the analysis of capital movements, which can reveal the attractiveness of different markets and the factors driving investment decisions. This knowledge is invaluable for understanding the dynamics of global capital, the impact of economic policies, and the potential risks and opportunities associated with international investments.
In summary, portfolio investment and the associated capital flows are integral components of the BoP. By including foreign investments in the BoP, economists and analysts can gain a comprehensive understanding of a country's international financial position, the flow of capital, and its integration into the global economy. This detailed approach to recording economic transactions ensures that policymakers and investors have access to accurate and relevant information, enabling them to make strategic choices in an increasingly interconnected world.
Recording Cash Investments: A Quickbooks Guide
You may want to see also

Foreign Currency Reserves and BoP
Foreign currency reserves play a crucial role in a country's economy, particularly in the context of the Balance of Payments (BoP). These reserves are an essential component of a nation's external assets and are held by the central bank or monetary authority. The primary purpose of foreign currency reserves is to ensure financial stability, maintain the value of the domestic currency, and support the country's exchange rate. When a country's BoP is analyzed, the inclusion of foreign investments becomes a critical aspect to consider.
In the BoP, foreign investments are indeed included and are categorized under the capital account. This account records transactions related to the acquisition or disposal of non-resident assets and the changes in ownership of these assets. Foreign investments can take various forms, such as direct investment, portfolio investment, and other investment categories. Direct investment involves the establishment of a long-term interest in an enterprise located in a foreign country, while portfolio investment refers to the purchase and sale of securities and other financial assets.
The inclusion of foreign investments in the BoP is significant as it provides a comprehensive view of a country's economic transactions with the rest of the world. It helps in understanding the flow of capital, the impact of foreign investment on the domestic economy, and the overall financial stability of the nation. By analyzing these investments, economists and policymakers can assess the potential risks and benefits associated with international financial activities.
Foreign currency reserves are often used to manage and stabilize the value of a country's currency in the foreign exchange market. When a country's currency depreciates, the central bank may intervene by selling its foreign currency reserves to support the domestic currency. Conversely, during periods of currency appreciation, the central bank might buy foreign assets to maintain or increase its reserves. This strategic use of reserves can influence the BoP and the overall economic health of the country.
In summary, foreign investments are an integral part of a country's BoP, providing valuable insights into international financial transactions. The management of foreign currency reserves is a critical tool for maintaining economic stability and influencing the exchange rate. Understanding the relationship between foreign investments, currency reserves, and the BoP is essential for policymakers and economists to make informed decisions regarding a country's financial strategy and global economic integration.
Invested Wealth: When to Use It and Why
You may want to see also

BoP Impact of Multinational Corporations
The Balance of Payments (BoP) is a crucial tool for understanding a country's economic transactions with the rest of the world. It records all international economic transactions, including those involving goods, services, income, and financial flows. When considering the impact of multinational corporations (MNCs) on a country's BoP, it is essential to recognize the role of foreign investments.
Foreign investments, such as direct foreign investment (FDI) and portfolio investment, can significantly influence a country's BoP. FDI occurs when a foreign entity acquires a significant stake in a domestic company, often leading to the establishment of a subsidiary or branch office. This type of investment can have a substantial impact on the BoP as it involves capital inflows, which are recorded as a credit in the current account. These inflows can contribute to a country's economic growth, create jobs, and enhance its infrastructure. For instance, an MNC investing in a developing country's manufacturing sector may lead to increased production capacity, improved technology transfer, and the creation of local employment opportunities, all of which can positively affect the BoP.
Portfolio investment, on the other hand, involves the purchase and sale of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. When an MNC or foreign investor buys domestic financial assets, it results in capital inflows, similar to FDI. These inflows can stabilize a country's currency and provide access to international capital markets. However, it is important to note that portfolio investment can also lead to capital outflows when foreign investors sell their holdings, potentially impacting the BoP negatively.
The impact of foreign investments on the BoP is not limited to the immediate financial transactions. MNCs often bring advanced technologies, management practices, and access to global markets, which can have long-term effects on a country's economy. For example, an MNC investing in a developing country's energy sector might introduce new drilling techniques, leading to increased oil production and exports. This, in turn, could result in a higher trade surplus and a more positive BoP outcome.
In summary, foreign investments, particularly FDI and portfolio investment, play a significant role in shaping a country's BoP. These investments can lead to capital inflows, economic growth, technology transfer, and improved trade balances. Understanding the dynamics of these investments is essential for policymakers and economists to assess the overall economic health and stability of a nation in the context of the BoP.
Where the Ultra-Wealthy Put Their Money
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Balance of Payments is a record of all economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world over a specific period, typically a year. It provides a comprehensive overview of a country's international financial position.
Yes, foreign investments are an essential component of the BoP. When a foreign entity invests in a domestic market, it is recorded as an investment account entry in the BoP. This includes direct investments, portfolio investments, and other investment categories.
FDI is a significant aspect of the investment account in the BoP. It represents the acquisition of a lasting interest in an enterprise resident in the economy of another country. FDI can be inward (foreign investment in the domestic country) or outward (domestic investment abroad). These transactions are carefully tracked and reported in the BoP to provide an accurate picture of a country's international investment position.
Absolutely. Portfolio investments, such as stocks, bonds, and other securities, are also part of the investment account in the BoP. These transactions involve the buying and selling of financial assets across international borders. The BoP records these flows to monitor the movement of capital and assess the impact on a country's financial stability and growth.







