Short-term investments are a crucial aspect of financial management, and understanding their classification as operating activities is essential for businesses. Operating activities are those that are directly related to the core business operations and revenue generation. In this context, short-term investments refer to the strategic allocation of funds in financial instruments with a maturity period of less than one year. These investments can include money market funds, treasury bills, and short-term bonds. By exploring the nature of short-term investments and their integration into operating activities, businesses can optimize their financial strategies and make informed decisions regarding their short-term liquidity and capital allocation.
What You'll Learn

Short-term investments definition and classification
Short-term investments are a crucial component of a company's financial strategy, and understanding their definition and classification is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. These investments are typically made with the intention of holding them for a short period, often less than a year, and are considered highly liquid assets. The primary purpose of short-term investments is to provide a source of funds that can be quickly converted into cash without significant loss of value.
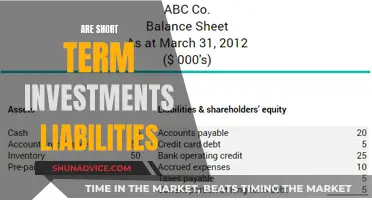
In financial terms, short-term investments are generally classified as a component of a company's current assets. This classification is based on the liquidity and accessibility of these investments. Current assets are those that a company expects to convert into cash or use up within one year or one operating cycle, whichever is longer. Short-term investments fall into this category because they can be readily sold or liquidated to meet short-term financial obligations or operational needs.
The definition of short-term investments can vary slightly depending on the industry and specific accounting standards. However, a common characteristic is that these investments are made with a low-risk profile and are intended to generate a modest return. Examples of short-term investments include treasury bills, certificates of deposit (CDs), and money market funds. These instruments are often used by companies to manage their cash flow, provide a safe haven for excess cash, and earn a small return in the short term.
From an accounting perspective, short-term investments are recorded at fair value, which is the price that would be received to sell the investment in an arm's-length transaction. This fair value is then classified as a current asset on the company's balance sheet. The classification as a current asset is crucial for financial reporting, as it provides a clear picture of a company's liquidity and ability to meet its short-term financial commitments.
In summary, short-term investments are an essential part of a company's financial management, providing a means to maintain liquidity, manage cash flow, and earn a modest return. Their classification as current assets is fundamental to financial reporting, ensuring that stakeholders have a comprehensive understanding of the company's financial health and ability to meet its short-term obligations. Understanding the definition and classification of short-term investments is key to accurate financial analysis and decision-making.
Unveiling the Potential: Is Short-Term Investment an Asset?
You may want to see also

Operating activities vs. investing activities
Operating activities and investing activities are two crucial components of a company's financial statements, particularly the cash flow statement. Understanding the distinction between these activities is essential for investors and analysts to assess a company's financial health and performance. When it comes to the question of whether short-term investments are an operating activity, it is important to clarify the definitions and implications of these terms.
Operating activities refer to the core revenue-generating processes of a business. This includes day-to-day operations such as sales, production, and administrative tasks that directly contribute to the company's primary income. These activities are fundamental to the company's ongoing business and are often associated with the generation of cash flow from the company's main operations. For example, a manufacturing company's operating activities would involve the production and sale of goods, which directly impact its cash position.
Investing activities, on the other hand, involve the allocation of resources to long-term assets and investments. This category includes the purchase and sale of long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, as well as investments in other companies or financial instruments. Investing activities are not directly related to the company's primary revenue-generating processes but are essential for its long-term growth and financial strategy. For instance, a company might invest in new machinery for expansion or acquire another business to diversify its operations.
Short-term investments, in this context, typically refer to highly liquid assets that can be easily converted into cash within a year or less. These investments are often used as a means of managing cash flow and can include money market funds, treasury bills, or short-term bonds. While short-term investments are not considered operating activities, they can be classified under investing activities. Companies may engage in short-term investments to generate a return on their excess cash while maintaining liquidity for ongoing operations.
In summary, operating activities are the day-to-day revenue-generating processes that drive a company's core business. Short-term investments, while not an operating activity, are a strategic financial move to manage cash flow and generate returns. Investing activities encompass a broader range of decisions related to long-term asset allocation and financial strategy. Understanding these distinctions is vital for evaluating a company's financial performance and making informed investment decisions.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: A Balance Sheet Guide
You may want to see also

Impact of short-term investments on cash flow
Short-term investments can significantly impact a company's cash flow, and understanding this relationship is crucial for financial management and decision-making. When a business engages in short-term investments, it typically involves the allocation of funds into assets that are expected to be converted back into cash within a year or less. These investments are often made to optimize cash flow and generate returns in the short term.
The impact on cash flow is twofold. Firstly, short-term investments can provide a source of liquidity, allowing companies to access their funds quickly if needed. This is particularly important for businesses that require immediate access to cash to meet operational expenses or unexpected financial obligations. By having a portion of their assets in short-term investments, companies can ensure they have the necessary cash reserves without tying up long-term capital.
Secondly, these investments can influence cash flow through their potential returns. Short-term investments often include options like money market funds, certificates of deposit, or short-term bonds. These instruments offer relatively low-risk opportunities to generate income. As the investments mature and are sold, the cash generated can be reinvested or used to fund other business activities, thus positively impacting cash flow. This strategic use of short-term investments can help companies maintain a healthy cash flow position while still utilizing their capital effectively.
However, it is essential to consider the trade-off between liquidity and potential returns. While short-term investments provide quick access to cash, they may offer lower yields compared to longer-term investments. Companies must carefully evaluate their investment strategies to balance the need for liquidity with the desire to maximize returns. Effective management of short-term investments can lead to improved cash flow management and overall financial stability.
In summary, short-term investments play a vital role in shaping a company's cash flow dynamics. They offer a means to enhance liquidity and provide a steady source of cash, especially during periods of financial uncertainty. By strategically allocating funds into these investments, businesses can ensure they have the necessary financial flexibility while also generating returns that contribute to their overall cash flow health. Understanding the impact of short-term investments is key to making informed financial decisions and managing cash flow effectively.
Maximize Your Short-Term Cash: Top Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

Accounting treatment for short-term investments
Short-term investments are typically classified as financial activities rather than operating activities in accounting. These investments are generally considered highly liquid and are expected to be converted into cash or sold within one year or the operating cycle of the business, whichever is longer. The primary purpose of holding short-term investments is to generate a return on cash that is not immediately needed for business operations.
In accounting, short-term investments are reported on the balance sheet at fair value, which is the price at which the investment could be sold in the current market. This fair value measurement is based on the principle of matching the timing of cash flows, ensuring that the financial statements reflect the economic substance of the investment. When a short-term investment is sold or matures, the gain or loss is recognized in the income statement, impacting the net income for the period.
The accounting treatment for short-term investments involves several key steps. Firstly, the investment must be classified as a financial asset at fair value through profit or loss. This classification is appropriate when the investment is held for trading or is a derivative financial instrument. For other short-term investments, they are classified as available-for-sale financial assets, and their fair value is marked to market each reporting period. Any unrealized gains or losses are reported in other comprehensive income, except for certain circumstances where they may be reclassified to the income statement.
When a short-term investment is sold, the difference between the selling price and the initial investment cost is recognized as a gain or loss in the income statement. This gain or loss is calculated as the difference between the selling price and the carrying amount of the investment. The carrying amount is typically the fair value of the investment at the beginning of the period. It is important to note that any realized gains or losses on short-term investments are considered operating items and are included in the net income of the reporting period.
Additionally, companies should disclose the nature and extent of their short-term investments in the notes to the financial statements. This disclosure provides transparency and helps users of the financial statements understand the company's investment strategy and the potential risks associated with these investments. It is crucial to maintain accurate records and regularly review the classification and valuation of short-term investments to ensure compliance with accounting standards and provide reliable financial reporting.
Debt Securities: Unlocking the Investment-Finance Connection
You may want to see also

Risks and benefits of short-term investments
Short-term investments are a crucial aspect of financial management, especially for businesses, as they can significantly impact a company's liquidity, cash flow, and overall financial health. When considering whether short-term investments are an operating activity, it's essential to understand the risks and benefits associated with these financial decisions.
One of the primary benefits of short-term investments is their ability to provide a quick return on investment. These investments typically involve purchasing assets that can be easily converted into cash within a short period, often a year or less. This characteristic allows businesses to access their capital quickly, which is particularly useful for taking advantage of short-term opportunities or managing unexpected financial obligations. For instance, a company might invest in short-term government bonds or money market funds to ensure it has the necessary funds for day-to-day operations or to capitalize on a sudden business expansion.
However, short-term investments also carry certain risks. One of the main risks is the potential for loss due to market volatility. Short-term investments are often more sensitive to market fluctuations compared to long-term investments. If the market value of these investments decreases, the business may face a loss, especially if the investments are sold before the intended maturity date. This risk is particularly relevant for investments in stocks, bonds, or other securities that are subject to market forces.
Another risk associated with short-term investments is the potential for missed opportunities. By investing in short-term assets, a business might forgo the potential benefits of longer-term investments. Long-term investments often provide higher returns over time, but they require a longer commitment and may not offer the same level of liquidity as short-term investments. Balancing short-term and long-term investments is crucial for a comprehensive financial strategy.
Despite these risks, short-term investments can be a valuable tool for businesses to manage their cash flow and financial stability. They provide a means to diversify investment portfolios, ensuring that a company's assets are not overly exposed to any single investment. Additionally, short-term investments can help businesses maintain a positive cash flow position, which is essential for day-to-day operations and long-term growth.
In conclusion, short-term investments are indeed an operating activity, offering both benefits and risks. Businesses must carefully consider their investment strategies, weighing the potential returns against the risks of market volatility and missed opportunities. A well-diversified portfolio, including a mix of short-term and long-term investments, can help mitigate these risks and contribute to a company's overall financial success.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: Are They Current Assets?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Operating activities are those that are directly related to the core business operations and revenue generation. Short-term investments, such as treasury bills, money market funds, or highly liquid assets, are typically classified as financial activities rather than operating activities. These investments are used to manage cash flow, provide liquidity, and earn a modest return, but they are not part of the primary business operations.
Short-term investments are generally reported in the current assets section of a company's balance sheet. They are considered highly liquid and can be easily converted into cash within one year. These investments are valued at fair value, and any changes in value are reflected in the income statement as part of other comprehensive income or net income, depending on the accounting standards followed.
No, short-term investments are not a source of revenue or profit for a business. They are primarily used for managing cash and maintaining liquidity. The returns generated from these investments are usually minimal and are often reinvested or used to cover short-term financial obligations. Operating activities, on the other hand, involve the day-to-day business processes that generate revenue and contribute to the company's long-term profitability.