Short-term investments are a crucial aspect of financial management, and understanding their classification as either assets or liabilities is essential for investors and businesses alike. These investments typically involve funds that are expected to be converted into cash within one year or less. While short-term investments are generally considered assets because they represent money that can be readily available for spending or investing, they can also be viewed as liabilities in certain contexts. This dual nature arises when these investments are used to meet short-term financial obligations, effectively becoming a liability until the investment matures or is sold. This paragraph sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the complexities surrounding short-term investments and their dual roles in financial statements.
What You'll Learn
- Definition: Short-term investments are assets expected to be converted to cash within one year
- Examples: Cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and short-term loans
- Risk: Fluctuations in value and potential liquidity issues
- Taxation: Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income rates
- Management: Regular monitoring and adjustment to meet financial goals

Definition: Short-term investments are assets expected to be converted to cash within one year
Short-term investments are a crucial aspect of financial management, representing assets that are highly liquid and intended to be converted into cash within a short period, typically one year or less. This definition is essential for understanding the nature of these investments and their role in an organization's financial strategy.
In the realm of finance, short-term investments are primarily used to manage cash flow, provide liquidity, and generate a modest return on surplus funds. These investments are often made in highly liquid assets, such as money market funds, treasury bills, certificates of deposit, and marketable securities with short-term maturities. The key characteristic that sets short-term investments apart is their short-duration nature, ensuring that the investment can be readily converted into cash without significant loss of value.
For businesses and individuals, short-term investments serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they provide a means to temporarily park funds that are not immediately required for operations or other commitments. This is particularly useful for managing cash flow and ensuring that funds are available when needed. Secondly, these investments offer a low-risk avenue to generate a small return, which can be beneficial for surplus cash that is not expected to be needed in the near future.
The definition of short-term investments is crucial for financial reporting and analysis. In accounting, these investments are typically classified as current assets, as they are expected to be converted to cash within one year. This classification is important for maintaining accurate financial statements and assessing a company's liquidity and short-term financial health.
In summary, short-term investments are a strategic financial tool, providing liquidity, managing cash flow, and offering a low-risk return on surplus funds. Understanding the definition and nature of these investments is essential for effective financial management, ensuring that organizations can make informed decisions regarding their short-term financial strategies.
Long-Term Investments vs. Long-Term Debt: Understanding the Difference
You may want to see also

Examples: Cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and short-term loans
When discussing short-term investments, it's important to clarify the distinction between assets and liabilities, as this is a fundamental concept in finance. Short-term investments are typically considered assets because they are resources that a company expects to convert into cash or use up within one year. These investments are crucial for a company's liquidity and financial health, ensuring it can meet its short-term obligations.
Now, let's explore some key examples of short-term investments:
- Cash: This is the most liquid asset a company can have. Cash includes physical currency, bank deposits, and any other funds that are readily available for use. It is a critical component of a company's short-term investments because it provides the immediate financial flexibility to cover expenses, pay suppliers, and manage day-to-day operations. For instance, a company might have a cash reserve to ensure it can pay its employees on time, even if it's just for a few days.
- Marketable Securities: These are highly liquid financial instruments that can be quickly converted into cash with minimal impact on their market value. Common examples include treasury bills, short-term government bonds, and money market funds. Marketable securities are often used to generate a small return on investment while still maintaining the ability to access funds quickly. For instance, a company might invest in short-term government bonds to earn interest income without tying up its capital for an extended period.
- Accounts Receivable: This represents the money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services delivered on credit. Accounts receivable are considered a short-term asset because the company expects to collect the money within one year. It reflects the company's ability to convert its sales into cash in the near future. For example, if a company sells products to a customer on credit and expects payment within 30 days, this sale would be recorded as an account receivable until the payment is received.
- Short-Term Loans: These are loans that a company takes out for a period of one year or less. Short-term loans are used to bridge the gap between short-term liabilities and assets, providing the necessary liquidity to manage day-to-day operations. For instance, a company might take out a short-term loan to finance a large purchase, such as new equipment, and then repay it within a year when the equipment is fully operational and generating revenue.
In summary, short-term investments are essential for maintaining a company's liquidity and financial stability. Cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and short-term loans are all examples of short-term investments that provide the necessary flexibility to manage short-term obligations and take advantage of opportunities. Understanding these examples is crucial for businesses to effectively manage their financial resources and make informed decisions.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: Are They Debt or Not?
You may want to see also

Risk: Fluctuations in value and potential liquidity issues
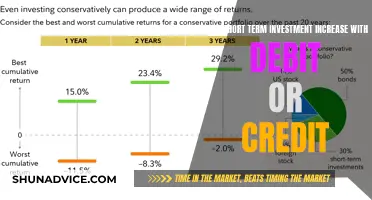
When considering short-term investments, it's crucial to understand the inherent risks associated with these financial instruments, particularly regarding fluctuations in value and potential liquidity issues. Short-term investments are typically those with a maturity of less than one year, designed to provide quick access to capital and generate returns in the near term. However, this short-term nature introduces several risks that investors should be aware of.
One significant risk is the potential for value fluctuations. Short-term investments often include various financial instruments like money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and short-term bonds. The value of these investments can change rapidly due to market dynamics and economic conditions. For instance, interest rates can fluctuate, impacting the value of fixed-income securities. If interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds may decrease as new issues offer higher yields. Conversely, in a low-interest-rate environment, the value of these investments might appreciate. Market sentiment and investor behavior also play a role; a sudden market downturn or a shift in investor preferences can lead to rapid value changes.
Liquidity is another critical aspect of short-term investments. These investments are meant to be easily convertible into cash without significant loss of value. However, certain factors can hinder liquidity. For example, some short-term investments, like certain money market funds, are considered highly liquid and can be redeemed quickly. In contrast, other investments, such as certain types of CDs or short-term corporate bonds, may have penalties for early withdrawal, making them less liquid. Additionally, during times of market stress or economic uncertainty, even highly liquid assets might experience temporary illiquidity, where selling them quickly becomes challenging.
Understanding the potential for value fluctuations and liquidity issues is essential for investors to make informed decisions. Diversification is a key strategy to mitigate these risks. By spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors, investors can reduce the impact of individual asset price movements. Regular review and monitoring of short-term investments are also crucial, especially in volatile market conditions, to ensure that the portfolio remains aligned with the investor's financial goals and risk tolerance.
In summary, short-term investments carry risks related to value volatility and liquidity. Investors should be prepared for rapid changes in the value of their holdings and consider the potential impact on their overall investment strategy. Staying informed about market trends, interest rate changes, and economic indicators can help investors navigate these risks effectively.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: Are They Cash Equivalents?
You may want to see also

Taxation: Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income rates
When it comes to short-term investments, understanding the tax implications is crucial for investors. Short-term capital gains, which are profits from the sale of assets held for a short period, are taxed at ordinary income rates. This means that if you sell an asset within a year of purchasing it, the gain realized will be taxed at the same rate as your regular income. This is a significant distinction from long-term capital gains, which are taxed at a lower rate.
The taxation of short-term capital gains is an essential consideration for investors, especially those who frequently buy and sell assets. For example, if an investor sells stocks or other assets within a year, the profit made will be subject to ordinary income tax. This can result in a higher tax burden compared to long-term gains, which are typically taxed at a more favorable rate. Understanding this tax treatment is vital for effective financial planning and can impact an investor's overall strategy.
The tax rate applied to short-term capital gains can vary depending on an individual's income level and tax bracket. In many jurisdictions, short-term gains are taxed at the same rate as regular income, which can be quite high. For instance, in the United States, short-term capital gains are often taxed at the same rate as ordinary income, which can range from 10% to 37%, depending on the taxpayer's income. This means that the tax on short-term gains can be substantial, and investors should carefully consider the potential tax implications when making investment decisions.
To illustrate, let's consider a hypothetical scenario. Suppose an investor buys 100 shares of a company at $10 each and sells them after a year at $15 per share, resulting in a profit of $500. If this profit is considered a short-term capital gain, it will be taxed at the investor's ordinary income rate. If the investor's income falls into the 25% tax bracket, they would pay $125 in taxes on this gain. This example highlights the importance of recognizing the tax treatment of short-term investments to avoid unexpected financial obligations.
In summary, short-term capital gains are an essential aspect of investment taxation. Investors should be aware that these gains are taxed at ordinary income rates, which can significantly impact their overall financial strategy. Understanding the tax implications allows investors to make informed decisions, especially when considering the frequency of buying and selling assets. It is always advisable to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure compliance with tax laws and to optimize investment returns.
Debt vs. Equity: Long-Term Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

Management: Regular monitoring and adjustment to meet financial goals
Regular monitoring and adjustment of financial strategies are crucial for effective management, especially when dealing with short-term investments and liabilities. This process involves a proactive approach to ensure that financial goals are not only met but also optimized over time. Here's a detailed breakdown of how this can be achieved:
Financial Analysis and Reporting: Management should establish a robust system for financial analysis, which includes regular reviews of investment portfolios, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. By doing so, managers can identify trends, potential risks, and opportunities. For instance, monitoring short-term investments can reveal market fluctuations, allowing for timely decisions to lock in profits or cut losses. This analytical approach provides a clear picture of the financial health and direction of the organization.
Performance Evaluation: A key aspect of management is to evaluate the performance of short-term investments regularly. This involves setting benchmarks and comparing actual returns against projected figures. By doing so, managers can quickly identify underperforming assets and make necessary adjustments. For example, if a short-term bond investment is not generating the expected returns, managers can consider selling it and reinvesting in a more profitable opportunity. This iterative process ensures that the investment strategy remains on track.
Risk Management and Mitigation: Regular monitoring enables managers to identify and assess risks associated with short-term investments. This could include market risks, credit risks, or liquidity risks. For instance, if a significant portion of the portfolio is in a single stock, a market downturn could impact the entire investment. Managers can then adjust the strategy by diversifying the portfolio, ensuring a more balanced approach. Additionally, monitoring can help in identifying potential legal or regulatory changes that might affect the investment landscape, allowing for proactive risk management.
Strategic Adjustments: Based on the insights gained from regular monitoring, management can make informed strategic adjustments. This might involve reallocating funds, changing investment vehicles, or modifying financial policies. For example, if the market is experiencing a bull run, managers might decide to increase the allocation to equity investments. Conversely, during a market downturn, a shift towards more conservative, short-term debt instruments could be considered. These adjustments ensure that the financial strategy remains agile and adaptable to changing market conditions.
Long-Term Financial Planning: While focusing on short-term investments and liabilities, management should also keep long-term financial goals in mind. This involves regularly reviewing and updating financial plans to align with the organization's overall objectives. For instance, a company might have a long-term goal to expand its operations, which would require significant capital. By monitoring financial performance and market trends, managers can make strategic decisions to ensure the availability of funds for such future endeavors. This holistic approach to financial management ensures sustainability and growth.
In summary, regular monitoring and adjustment are essential tools for management to navigate the complexities of short-term investments and liabilities. It empowers managers to make timely decisions, mitigate risks, and optimize financial strategies. By adopting a proactive approach, organizations can ensure that their financial goals are not just achievable but also consistently met, even in the face of market volatility and changing economic landscapes.
Navigating the Duality: Short-Term and Long-Term Investments Demystified
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Short-term investments are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or sold within one year or the operating cycle of the business, whichever is longer. These investments are considered highly liquid and can be easily converted into cash without significant loss of value. Liabilities, on the other hand, are obligations or debts that a company owes to others. Short-term investments are not typically classified as liabilities because they are not obligations but rather assets that the company holds for a short period.
No, short-term investments are not debt and do not represent a liability. They are financial assets that the company owns and can be easily liquidated. Liabilities, such as accounts payable, notes payable, or short-term loans, are obligations that the company must pay back within a year. Short-term investments are more about the company's financial strategy and risk management rather than a debt obligation.
Short-term investments are reported as a current asset on a company's balance sheet. They are considered highly liquid and are valued at the lower of cost or fair value. If the fair value is lower than the cost, the investment is written down to the fair value. These investments provide liquidity and can be used to meet short-term financial obligations or take advantage of investment opportunities.
While short-term investments are generally considered low-risk compared to other investment options, they still carry some level of risk. The primary risk is the potential loss of value if the investment is sold at a lower price than its purchase cost. Additionally, there might be market risk if the investment is in volatile markets. However, short-term investments are typically chosen for their safety and ease of conversion into cash, making them a popular choice for conservative investors.
Yes, short-term investments can be an effective tool for managing cash flow. Companies often use these investments to optimize their cash balances and take advantage of potential investment opportunities. By holding short-term investments, businesses can maintain liquidity while potentially earning a return. This strategy helps in managing cash flow, especially during periods of low cash reserves or when waiting for long-term investments to mature.