Foreign investments play a crucial role in the economic development of developing countries, offering a multitude of benefits that can significantly impact their growth and stability. These investments can take various forms, including direct investments in businesses, portfolio investments in financial assets, and indirect investments through international trade. When foreign entities invest in developing nations, they bring capital, technology, and expertise, which can help local businesses expand, improve infrastructure, and create jobs. This influx of capital can stimulate economic activity, attract further investment, and contribute to the overall growth of the host country's economy. However, the impact of foreign investments is not without challenges, as it can also lead to concerns about dependency, environmental degradation, and the potential for exploitation. Understanding these effects is essential for policymakers to ensure that foreign investments are managed sustainably and contribute positively to the long-term development of developing countries.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Foreign investments can significantly boost the economic growth of developing countries by providing capital for infrastructure, technology, and job creation. |
| Employment and Income | These investments often lead to increased employment opportunities and higher income levels for the local population. |
| Infrastructure Development | They play a crucial role in improving transportation, energy, and communication systems, which are essential for economic development. |
| Technology Transfer | Multinational corporations bring advanced technology and expertise, facilitating technology transfer and knowledge sharing. |
| Foreign Exchange Reserves | Inflows from foreign investments can strengthen a country's foreign exchange reserves, making it easier to manage debt and stabilize the currency. |
| Attracting More Investment | Successful foreign investment projects can attract further foreign direct investment (FDI) and create a positive investment climate. |
| Environmental Impact | However, there are concerns about environmental degradation and social issues, requiring sustainable practices and regulations. |
| Debt Sustainability | Managing the debt associated with foreign investments is critical to ensure long-term economic stability. |
| Political Stability | Political stability and good governance are essential to attract foreign investors and maintain a positive investment environment. |
| Regional Disparities | The impact of foreign investments may vary across regions, requiring careful planning to address regional imbalances. |
| Local Business Development | Foreign investments can foster the growth of local businesses through partnerships and supply chain integration. |
| Education and Skills | They can contribute to the development of human capital by providing training and educational opportunities. |
| Market Access | Foreign investors often provide access to new markets, both domestically and internationally. |
| Policy Reforms | Governments may implement policy reforms to attract foreign investments, which can have long-term benefits. |
| Social Development | Investments can support social development projects, including healthcare and education initiatives. |
| Risk and Volatility | Developing countries may face risks and volatility associated with foreign investment flows. |
| Cultural Exchange | Cultural exchange and understanding can result from foreign investments, fostering international cooperation. |
What You'll Learn
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and job creation in developing nations
- Impact of portfolio investments on local businesses and infrastructure
- How remittances from abroad influence economic growth and poverty reduction?
- The role of international aid in fostering economic development
- Foreign investment's effect on the balance of payments and currency stability

Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and job creation in developing nations
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in the economic development of developing countries, particularly in the context of job creation. When foreign investors establish operations or acquire assets in these nations, it can have a significant impact on local employment opportunities. Here's an overview of how FDI contributes to job creation in developing economies:
Industry Development and Expansion: FDI often leads to the establishment of new industries or the expansion of existing ones. Foreign investors bring capital, technology, and expertise, which can help develop sectors that might have been previously underdeveloped or non-existent. For example, a foreign automotive company setting up a manufacturing plant in a developing country can create numerous jobs, from engineers and technicians to assembly workers and administrative staff. This industry development can have a ripple effect, stimulating the growth of ancillary businesses and supporting services.
Direct Employment: The most immediate impact of FDI on job creation is the direct employment it generates. Foreign companies create jobs within their operations, providing employment opportunities for the local population. These jobs can range from skilled positions requiring specialized training to unskilled labor, catering to various educational backgrounds and skill sets. As these companies grow, they may also offer training and development programs, enhancing the employability of local workers and potentially leading to career advancement.
Induced Investment and Spin-offs: FDI can attract further investment and create a multiplier effect. When foreign companies set up operations, they may require additional resources, services, and infrastructure, leading to further investment in the local economy. This includes spending on local suppliers, contractors, and supporting businesses. For instance, a foreign manufacturing company might source raw materials from local suppliers, creating jobs in agriculture or mining. Additionally, spin-off businesses may emerge, providing services or products complementary to the primary investment, further boosting employment.
Knowledge Transfer and Skill Development: Foreign investors often bring advanced technologies, management practices, and skills that can be transferred to local workers. Through training programs, mentorship, and on-the-job experience, local employees can acquire new skills, making them more employable not only within the FDI project but also in other sectors of the economy. This knowledge transfer can lead to a more skilled workforce, which is essential for long-term economic growth and development.
Infrastructure Development: FDI projects often go hand in hand with infrastructure development. Foreign investors may invest in transportation, energy, telecommunications, or other critical infrastructure, which, in turn, creates jobs during construction and operation. These infrastructure projects can have a wide-ranging impact, improving connectivity, facilitating trade, and attracting further investment, all of which contribute to economic growth and job creation.
In summary, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) serves as a powerful catalyst for job creation in developing countries. It stimulates economic growth, develops new industries, and provides direct employment opportunities. The impact of FDI on job creation can be far-reaching, benefiting not only the immediate workforce but also the broader local economy through induced investment and skill development. Understanding and promoting FDI as a tool for economic transformation is essential for policymakers and development organizations aiming to reduce unemployment and improve the standard of living in developing nations.
Warren Buffet's Strategy for Investing Berkshire's Cash Reserves
You may want to see also

Impact of portfolio investments on local businesses and infrastructure
Foreign portfolio investments can have a significant impact on local businesses and infrastructure in developing countries, often leading to both positive and negative outcomes. These investments typically involve the purchase of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, by international investors, and can influence various aspects of the local economy.
One of the primary effects is the potential for economic growth and development. When foreign investors inject capital into local businesses, it can stimulate economic activity and create opportunities for expansion. For instance, portfolio investments might lead to the establishment of new ventures, the modernization of existing industries, or the diversification of the local economy. This increased investment can result in job creation, higher income levels, and improved standards of living for the local population.
In the context of infrastructure, foreign portfolio investments can bring much-needed capital for development. These investments may be directed towards improving transportation networks, energy systems, water supply, or telecommunications. For example, a foreign investor might acquire a local utility company, leading to the modernization of aging infrastructure and improved access to essential services for the community. This can enhance the overall productivity and competitiveness of the country in the global market.
However, there are potential challenges and risks associated with these investments. Local businesses might face increased competition from foreign-owned enterprises, which could lead to market disruptions and potential job losses if not managed carefully. Additionally, the influx of foreign capital might cause a rapid appreciation of the local currency, making exports more expensive and potentially harming the country's manufacturing sector.
To maximize the benefits and mitigate the risks, developing countries often implement strategic policies. These may include setting clear investment guidelines, ensuring fair competition, providing incentives for local businesses, and establishing regulatory frameworks that protect the interests of both foreign investors and the local population. Balancing the benefits of foreign portfolio investments with sustainable development goals is crucial for long-term economic prosperity.
Schwab's Cash Investment Options: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

How remittances from abroad influence economic growth and poverty reduction
Remittances from abroad, often referred to as international remittances, play a significant role in shaping the economic landscape of developing countries. These financial inflows, primarily in the form of money sent by migrants working in other countries, have a profound impact on economic growth and poverty reduction. Here's a detailed breakdown of their influence:
Economic Growth Catalyst: Remittances act as a vital source of external finance for developing nations, often surpassing foreign direct investment and official development assistance. This influx of funds contributes to the overall economic growth of the country. When migrants send money back home, it increases the disposable income of recipients, which can then be spent on various economic activities. This spending stimulates local businesses, encourages entrepreneurship, and boosts consumption, all of which are essential drivers of economic growth. Moreover, remittances can help bridge the savings gap in developing countries, providing much-needed capital for investment in businesses, infrastructure, and other productive sectors.
Poverty Alleviation: The impact of remittances on poverty reduction is particularly noteworthy. Migrants often send money back to their families, which can significantly improve the standard of living for the recipients. This is especially true in rural areas where remittances can provide a safety net for families, helping them afford basic necessities, healthcare, and education. Over time, this can lead to improved health and education outcomes, which are fundamental to breaking the cycle of poverty. Remittances also empower individuals and communities to invest in income-generating activities, such as starting small businesses or purchasing agricultural equipment, further reducing poverty and enhancing economic resilience.
Infrastructure and Development: The financial resources provided by remittances can be channeled into critical infrastructure projects, such as building roads, bridges, and utilities. This not only improves the overall quality of life but also enhances the country's connectivity and accessibility, making it more attractive for further investment. Additionally, remittances can contribute to the development of social sectors, including healthcare and education, which are essential for long-term economic growth and poverty reduction.
Financial Stability and Risk Mitigation: Regular remittances can provide a stable source of foreign currency, helping to maintain a country's external balance and financial stability. This stability is crucial for managing economic shocks and reducing the vulnerability of developing countries to external financial crises. Furthermore, remittances can serve as a form of risk mitigation, as they provide a reliable source of income even during economic downturns or natural disasters, which are common challenges faced by these countries.
In summary, remittances from abroad are a powerful tool for economic development and poverty alleviation in developing countries. They contribute to economic growth by stimulating local businesses and investment, while also directly improving the lives of recipients, especially in rural areas. The impact of remittances extends beyond individual families, fostering community development and overall economic resilience. Understanding and effectively utilizing these financial flows can be a key strategy for policymakers to address the unique challenges faced by developing nations.
Should I Withdraw My Vanguard Investments?
You may want to see also

The role of international aid in fostering economic development
International aid plays a crucial role in fostering economic development in developing countries, often serving as a catalyst for growth and a means to address specific challenges these nations face. It provides a vital source of funding and technical assistance, enabling recipient countries to invest in infrastructure, education, healthcare, and other sectors that are essential for long-term development. By offering grants, loans, and technical expertise, international aid organizations can help developing nations build the necessary foundations for sustainable economic growth.
One of the primary benefits of international aid is its ability to stimulate economic activity and create a more favorable investment climate. When aid is directed towards improving infrastructure, such as building roads, bridges, and power grids, it enhances connectivity and facilitates trade. This, in turn, attracts foreign direct investment (FDI), as businesses seek reliable transportation and communication networks to establish a presence in the region. FDI brings capital, technology, and expertise, contributing to the development of local industries and the creation of jobs, which are vital for reducing poverty and improving living standards.
Moreover, international aid can be strategically targeted to address specific economic challenges. For instance, in sectors like agriculture and manufacturing, aid can provide the necessary resources and training to improve productivity and efficiency. This can lead to increased food production, higher-quality goods, and a more competitive business environment. By supporting local industries, aid can help developing countries diversify their economies, reducing reliance on a few primary exports and making them more resilient to global market fluctuations.
The impact of international aid extends beyond immediate economic gains. It also contributes to institutional development and governance. Aid programs often include capacity-building initiatives, helping local governments and institutions strengthen their ability to manage resources, implement policies, and regulate economic activities effectively. Improved governance is essential for creating a stable and predictable business environment, which encourages both domestic and foreign investment.
However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of international aid in fostering economic development depends on various factors. These include the quality and design of aid programs, the recipient country's policy environment, and the alignment of aid with local priorities and needs. Successful aid strategies often involve a combination of grants, loans, and technical assistance, tailored to the specific circumstances of the developing country. Additionally, ensuring transparency, accountability, and local ownership in aid projects is crucial to maximize their positive impact.
Where to Park Cash: TD Ameritrade Options
You may want to see also

Foreign investment's effect on the balance of payments and currency stability
Foreign investments can have a significant impact on the balance of payments and currency stability in developing countries. When foreign investors enter a country, they bring capital that can be invested in various sectors, such as infrastructure, manufacturing, or services. This influx of capital can lead to several economic effects.
Firstly, foreign investment often results in an increase in the country's exports. As foreign investors bring their own capital and expertise, they may establish new businesses or expand existing ones, producing goods and services that can be sold both domestically and internationally. This boost in production capacity can lead to a trade surplus, where the value of exports exceeds the value of imports. A trade surplus improves the country's balance of payments, as it receives more foreign exchange from exports than it pays out for imports.
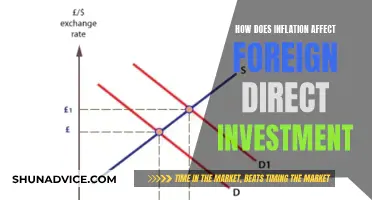
Secondly, foreign investments can directly impact the balance of payments through capital inflows. When foreign investors invest in a country, they transfer funds, often in the form of direct investment, portfolio investment, or loans. These capital inflows can strengthen the country's currency, as the demand for the local currency increases to facilitate transactions. A stronger currency can make imports cheaper, potentially leading to a trade deficit if not managed carefully. However, it also makes the country's exports more expensive for foreign buyers, which might reduce their competitiveness in international markets.
The stability of the currency is another critical aspect influenced by foreign investments. A consistent and positive flow of foreign investment can provide a stable foundation for the local currency. As investors believe in the country's economic prospects, they are more likely to hold and invest in the local currency, increasing its demand and value. This stability can encourage further investment, as a strong currency reduces the risk associated with doing business in the country. Moreover, a stable currency can help control inflation, making the country's exports more competitive and attracting even more foreign investment.
However, it is essential to manage these effects carefully. While foreign investments can bring benefits, they can also lead to challenges. For instance, a sudden influx of capital can cause the local currency to appreciate rapidly, making exports less competitive in the short term. Additionally, if foreign investments are not well-regulated, they might lead to environmental degradation or social issues, which could have long-term negative consequences. Therefore, developing countries should implement policies that encourage sustainable and balanced foreign investments, ensuring that the benefits are distributed equitably across the population.
Unequal Annual Cash Flows: Navigating Investment Challenges
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Foreign investments can significantly boost the economic growth of developing countries by providing much-needed capital, technology, and expertise. These investments often lead to the establishment of new businesses, the expansion of existing ones, and the creation of job opportunities, all of which contribute to increased productivity and higher income levels. Additionally, foreign investment can attract local investment, as investors may be more inclined to invest in a country with a supportive foreign investment environment.
FDI brings several advantages to developing countries. Firstly, it can lead to the transfer of advanced technologies and management practices, enabling local industries to modernize and become more competitive. Secondly, FDI projects often create jobs, reduce unemployment, and improve the standard of living for local communities. Moreover, foreign investors may bring access to international markets, facilitating the export of goods and services, and thus contributing to a country's overall economic diversification.
While foreign investments offer numerous benefits, there are also potential challenges. One concern is the risk of environmental degradation, especially when investments are made in resource-rich sectors. Additionally, there might be a loss of local cultural heritage and traditional practices due to rapid industrialization and globalization. Another challenge is the potential for exploitation, where local resources are extracted or labor is exploited for profit. Balancing the benefits of FDI with sustainable development and social welfare is crucial for the long-term success of these investments.