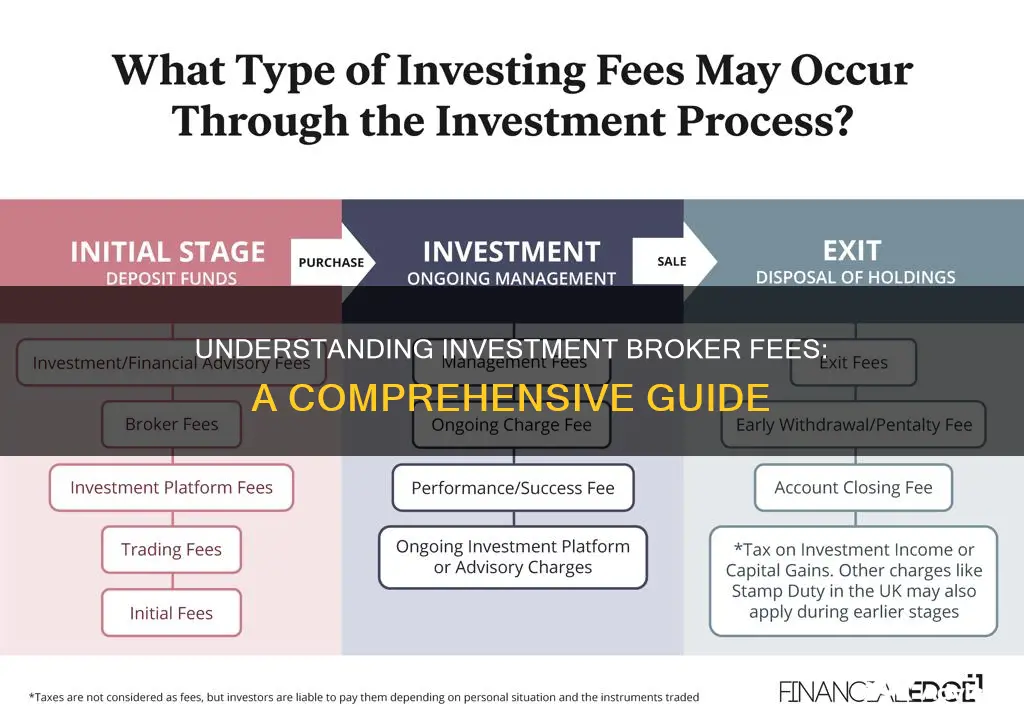
Understanding investment broker fees is crucial for anyone looking to invest in the financial markets. Broker fees are the charges incurred when an investor uses a brokerage firm to execute trades. These fees can vary widely depending on the type of account, the investment strategy, and the specific services provided. Common fee structures include commission-based fees, which are a percentage of the trade value, and flat fees, which are a set amount per transaction. Additionally, some brokers offer fee-free trading for certain assets or account types, which can significantly reduce costs for investors. This guide will delve into the various factors that influence these fees and provide insights into how investors can optimize their trading expenses.
What You'll Learn
- Fee Structure: Broker fees vary, often based on transaction volume, account type, and service level
- Commission-Based Fees: Common for stock trades, these fees are a percentage of the trade value
- Flat-Rate Fees: Fixed costs for specific services, e.g., account management or research reports
- Performance-Based Fees: Some brokers charge a percentage of profits or losses generated by the investor
- Hidden Fees: Additional costs may include inactivity fees, wire transfer fees, or account maintenance fees

Fee Structure: Broker fees vary, often based on transaction volume, account type, and service level
When it comes to investment brokerage fees, understanding the fee structure is crucial for investors. Broker fees can vary significantly, and several factors influence the cost of using a brokerage service. One of the primary determinants of broker fees is transaction volume. High-volume traders or investors who execute numerous trades within a given period often benefit from reduced per-transaction costs. Many brokers offer tiered fee structures, where the cost per trade decreases as the number of transactions increases. For example, a broker might charge a flat fee of $5 per trade for the first 100 transactions but then reduce the fee to $2.50 per trade for the next 100 transactions, and so on. This model incentivizes investors to trade more frequently, as the per-transaction cost decreases with higher volume.
Account type also plays a significant role in fee structures. Brokers often categorize accounts into different types, such as retail, institutional, or high-net-worth accounts. Each account type may have its own set of fees and minimum requirements. For instance, retail accounts, which are typically used by individual investors, might have lower minimum balance requirements but higher per-transaction fees compared to institutional accounts, which cater to large investors or financial institutions. High-net-worth accounts, designed for clients with substantial assets, often offer personalized services and lower fees as a premium for their exclusivity.
The level of service provided by a broker is another critical factor in fee determination. Brokers may offer various service packages, each with its own fee structure. Basic services might include trade execution and account management, while premium services could encompass additional features like research reports, portfolio management, and dedicated client support. Premium services typically come with higher fees, reflecting the increased value and expertise provided. Some brokers also offer commission-free trading for specific asset classes or account types, attracting investors who prioritize cost-effectiveness.
In addition to transaction fees, investors should be aware of other costs associated with brokerage services. These may include account maintenance fees, which are charged monthly or annually, and may vary based on account type and balance. Some brokers also impose inactivity fees if an account remains unused for a prolonged period. It is essential to review the fee schedule provided by the brokerage firm to understand all the associated costs.
Understanding the fee structure is vital for investors to make informed decisions. By considering transaction volume, account type, and service level, investors can choose a brokerage that aligns with their trading strategy and financial goals. Transparency in fee disclosure allows investors to compare different brokers and select the one that offers the best value for their investment needs.
Retirement Planning: Your Investment Mix
You may want to see also

Commission-Based Fees: Common for stock trades, these fees are a percentage of the trade value
When you buy or sell stocks through a broker, you often encounter commission-based fees, which are a common charge in the investment world. These fees are typically a small percentage of the total value of your trade. For example, if you purchase shares worth $1,000, the commission might be 0.5%, which equates to $5. This fee is charged by the broker to cover the costs associated with executing your trade, including market research, order processing, and the services provided by the brokerage firm.
The percentage of the trade value that you pay as a commission can vary depending on the brokerage and the type of account you have. Some brokers offer different commission structures, such as per-share fees or flat-rate commissions, especially for frequent traders or high-volume investors. These fees are designed to ensure that the broker can generate revenue from your trading activities, which is essential for their business model.
It's important to understand that commission-based fees are just one aspect of the overall cost of trading. Brokers may also charge other fees, such as account maintenance fees, inactivity fees, or even additional charges for certain types of trades. Therefore, it's crucial to review the fee structure of your chosen broker to ensure you are aware of all potential costs. Many online brokers now offer commission-free trading for certain assets, which can be a significant advantage for investors, especially those who engage in frequent trading.
For investors, it's wise to compare commission rates among different brokers to find the most cost-effective option. Lower commission rates can result in significant savings over time, especially for active traders who execute numerous trades. Additionally, some brokers may offer discounts or waive fees for specific account types or trading volumes, so it's worth exploring these options to optimize your investment strategy.
In summary, commission-based fees are a standard part of the investment process, especially for stock trades. Understanding how these fees are calculated and the factors that influence them can help investors make informed decisions and manage their trading costs effectively. By being aware of these charges, you can ensure that your investment strategy aligns with your financial goals and objectives.
Beyond the Desk: Investment Bankers' Extracurricular Engagements
You may want to see also

Flat-Rate Fees: Fixed costs for specific services, e.g., account management or research reports
When it comes to investment broker fees, one common structure is the flat-rate fee model. This approach involves a set, fixed cost for specific services, providing clients with a clear and transparent pricing structure. For instance, a brokerage firm might charge a flat fee for account management services, which could include regular portfolio reviews, performance updates, and personalized financial advice. This fee is typically agreed upon at the beginning of the service agreement and remains consistent, regardless of the number of transactions or the value of the investments.
The advantage of flat-rate fees is the predictability and simplicity it offers to investors. With this model, clients can easily budget for their investment-related expenses, as the cost is directly linked to the service provided. For example, a client might pay a fixed annual fee for comprehensive account management, ensuring they receive dedicated support and guidance throughout the year. This structure is particularly beneficial for investors who prefer a more personalized approach and value the ongoing relationship and expertise provided by the broker.
Research reports and analysis are another area where flat-rate fees can be applied. Investment firms may offer a subscription-based service, providing clients with access to a vast library of research reports, market insights, and economic forecasts for a set annual fee. This model ensures investors can stay informed and make data-driven decisions, all while benefiting from the broker's expertise and resources. The flat-rate structure here encourages investors to utilize the provided research, as the cost remains consistent, regardless of the frequency of report usage.
This fee structure also benefits brokers, as it provides a stable and predictable revenue stream. By offering flat-rate services, brokers can ensure a consistent income, which can be especially important for smaller firms or independent brokers who might rely on these fees as their primary source of revenue. Additionally, it allows brokers to focus on providing high-quality services, knowing that their fees are fair and transparent, which can enhance their reputation and attract more clients.
In summary, flat-rate fees for specific services offer a transparent and predictable pricing model for investment brokers and their clients. This approach ensures that investors can budget effectively while also benefiting from personalized services and research resources. For brokers, it provides a stable income and encourages a focus on delivering exceptional services, fostering a mutually beneficial relationship in the investment industry.
Recession-Proof Investments: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Performance-Based Fees: Some brokers charge a percentage of profits or losses generated by the investor
Performance-based fees are a unique and often controversial aspect of the investment brokerage industry. This fee structure is designed to directly link the broker's compensation to the investor's performance, creating a strong incentive for the broker to act in the best interest of the client. Here's how it works:
When an investor engages a broker to manage their investments, the broker typically charges a fee for their services. Traditionally, these fees have been structured as a flat rate or a percentage of the total assets under management. However, performance-based fees introduce a twist. In this model, the broker's fee is calculated as a percentage of the profits or losses generated by the investor's portfolio. For example, a broker might charge 20% of the net profit made on a trade or investment. If the investor incurs a loss, the broker may not charge anything, or they might charge a small fee to cover administrative costs.
This fee structure is particularly appealing to investors as it directly aligns the broker's interests with the investor's success. Brokers are motivated to provide superior performance because their earnings are directly tied to the outcomes of their clients' investments. As a result, investors can expect more personalized service and tailored strategies, knowing that the broker's compensation is performance-driven.
However, it's important to note that performance-based fees can also be complex and potentially risky. Investors should carefully consider the terms and conditions of such agreements, as they may have specific requirements or limitations. For instance, some brokers might set minimum performance thresholds, and if the portfolio underperforms, the investor may not incur any fees, but the broker also doesn't earn a commission. Additionally, investors should be aware that this fee structure can sometimes lead to conflicts of interest, especially if the broker's primary goal is to maximize fees rather than optimize investment returns.
In summary, performance-based fees offer a performance-linked compensation model for brokers, providing an incentive to deliver strong investment results. While it can be a powerful motivator for brokers, investors should approach this fee structure with caution, ensuring they fully understand the terms and potential risks involved.
Investing: Choosing Companies Wisely
You may want to see also

Hidden Fees: Additional costs may include inactivity fees, wire transfer fees, or account maintenance fees
When it comes to investment broker fees, it's important to be aware of the various costs that can accumulate, often without your knowledge. These hidden fees can significantly impact your overall investment experience and returns. Here's an overview of some common additional charges:
Inactivity Fees: Many brokers impose inactivity fees on accounts that have not been actively traded or managed for a certain period. This fee is typically charged monthly or annually and can be a surprise for investors who may have forgotten about an account or moved on to other investments. Inactivity fees are designed to encourage investors to keep their accounts active and engaged. It's crucial to review your account activity regularly and consider the frequency of your trading to avoid unexpected charges.
Wire Transfer Fees: International money transfers, often required for certain investment activities, can incur wire transfer fees. These fees are charged by both the sending and receiving institutions and can vary widely. When making or receiving international wire transfers, it's essential to understand the associated costs to manage your investment funds effectively. Some brokers may offer alternative methods of transferring funds, such as electronic funds transfers, which could be more cost-effective.
Account Maintenance Fees: Brokers may also charge account maintenance fees, which are typically associated with the ongoing management and administration of your investment account. These fees can include costs related to account monitoring, reporting, and compliance. While these charges might seem reasonable, they can add up over time, especially for investors with multiple accounts or those who require frequent account adjustments. It's advisable to inquire about these fees and understand the services they cover to ensure they align with your investment needs.
Being transparent about fees is essential for investors to make informed decisions. Brokers should provide clear and detailed fee structures, outlining all potential costs, including hidden fees. By understanding these additional charges, investors can better manage their investment expenses and ensure that their returns are not negatively impacted. Regularly reviewing your investment statements and fee schedules will help you stay on top of these costs and make necessary adjustments to your investment strategy.
Invest or Repay: The Car Conundrum
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Investment broker fees are charges incurred when you hire a broker to execute trades on your behalf. These fees can vary depending on the type of account, the broker, and the services provided.
Broker fees are often calculated as a percentage of the trade value or a flat fee per transaction. Some brokers may also charge additional fees for certain services, such as portfolio management or research reports.
No, different types of investment accounts have varying fee structures. For example, commission-based accounts charge a fee for each trade, while fee-based accounts charge a percentage of the assets under management. Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) also have their own fee structures, including management fees and distribution fees.
Yes, many brokers offer fee structures that can be negotiated. You can discuss fee reductions or waivers based on your trading volume, account size, or the frequency of your trades. Some brokers also provide fee-free trading for certain assets or during specific periods.
It's important to review the fee schedule provided by your broker to ensure transparency. Some brokers may have additional fees for services like wire transfers, early account closures, or certain types of investments. Understanding all associated costs is crucial to managing your investment expenses effectively.