Space investments are an emerging and exciting avenue for investors, offering the potential for significant returns while also contributing to the advancement of space exploration and technology. These investments typically involve funding startups and companies that are developing innovative technologies, such as satellite communications, space tourism, and space-based manufacturing. Understanding how these investments work is crucial for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and support the rapidly growing space industry. This paragraph will delve into the mechanics of space investments, exploring the various ways in which investors can participate in this burgeoning sector and the potential risks and rewards associated with these unique financial opportunities.
What You'll Learn
- Fundamentals: Understanding the core principles of space investment, including market dynamics and regulatory frameworks
- Technological Advancements: Exploring the impact of tech innovations on space investment opportunities and market trends
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with space ventures, such as launch delays and technological failures
- Return on Investment (ROI): Analyzing the financial returns and potential profits from space investment portfolios
- Industry Players: Examining the roles and contributions of key players in the space investment ecosystem

Fundamentals: Understanding the core principles of space investment, including market dynamics and regulatory frameworks
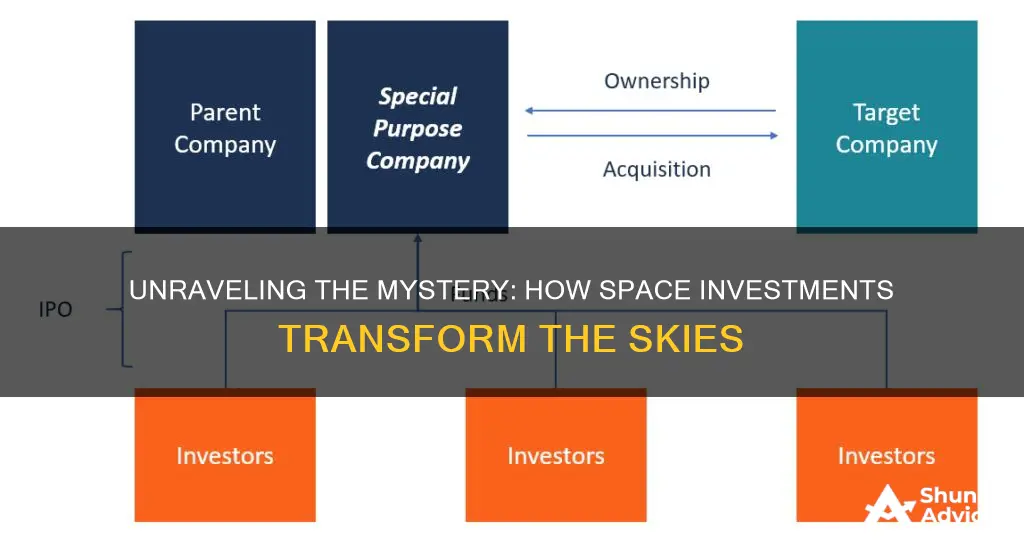
Space investment, often referred to as a Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC), is a unique and innovative approach to funding and acquiring space-related ventures. It involves a legal structure where a blank-check company, typically without an identified business, raises capital through an initial public offering (IPO) to invest in space startups or established companies. This concept has gained traction as a means to accelerate space exploration, satellite technology, and other space-based industries. Understanding the fundamentals of SPAC investments is crucial for investors and entrepreneurs alike.
The core principle of SPACs revolves around the idea of providing a rapid and efficient pathway to funding for space-focused companies. These companies often face challenges in accessing traditional capital markets due to their high-risk nature and the specialized nature of the industry. SPACs offer a solution by providing a pre-determined amount of capital, allowing space startups to focus on their core business objectives without the immediate pressure of raising funds through more conventional means. This structure essentially acts as a bridge between the capital market and the space industry.
Market dynamics play a significant role in SPAC investments. The space industry is characterized by rapid technological advancements, intense competition, and a high degree of uncertainty. Investors must carefully analyze the market potential, competitive landscape, and technological trends within the space sector. Due to the specialized nature of the industry, investors should also consider the unique risks associated with space ventures, such as technological failures, regulatory changes, and launch delays. A comprehensive understanding of these market dynamics is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Regulatory frameworks are another critical aspect of SPAC investments. The legal and regulatory environment for space activities varies across different regions and countries. Investors need to be well-versed in the specific regulations governing the space industry, including those related to satellite launches, space debris management, data privacy, and international space law. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure the long-term viability and success of space ventures. Additionally, understanding the regulatory landscape helps investors navigate potential legal challenges and ensure that the investments align with the evolving legal framework.
In summary, SPAC investments offer an exciting opportunity to participate in the growth of the space industry. By understanding the core principles, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks, investors can make informed decisions and contribute to the advancement of space-based technologies. This investment approach provides a unique and flexible way to support innovative space ventures, fostering growth and innovation in a rapidly evolving sector.
Zelle and Fidelity: Exploring Payment Options
You may want to see also

Technological Advancements: Exploring the impact of tech innovations on space investment opportunities and market trends
The rapid pace of technological advancements in the space industry has significantly influenced investment opportunities and market trends, creating a dynamic landscape for investors. One of the most prominent trends is the rise of Small Private Aerospace Companies (SPACs), which have revolutionized the way space ventures are funded and structured. SPACs, also known as "blank check" companies, are publicly traded entities that raise capital with the sole purpose of acquiring or merging with a private company, often in the space sector. This innovative funding model has enabled startups and established companies alike to access capital more efficiently, bypassing the traditional venture capital and initial public offering (IPO) processes.
Tech innovations have played a pivotal role in expanding the scope of space investments. Advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites and advanced alloys, are now being utilized to build lightweight and durable spacecraft, reducing costs and improving performance. Additionally, the development of 3D printing technology has opened up new possibilities for in-space manufacturing, allowing for the production of complex components and even entire structures in orbit, which can significantly reduce launch costs and time. These innovations have attracted investors seeking to capitalize on the potential of these cutting-edge technologies.
The impact of technological advancements is also evident in the growing interest in space tourism and commercial space travel. With the development of reusable launch systems, such as SpaceX's Falcon 9, the cost of space travel has decreased substantially, making it more accessible to a wider range of investors. This has led to a surge in investments in companies focused on space tourism, satellite-based services, and in-space transportation. As a result, the market is witnessing a shift towards more diverse and commercially viable space-related ventures.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms into space missions is transforming data analysis and decision-making processes. These technologies enable more efficient satellite operations, enhance weather forecasting, and improve the accuracy of space-based navigation systems. Investors are increasingly interested in companies that leverage AI and ML to provide innovative solutions, such as predictive maintenance for spacecraft or advanced data analytics for satellite imagery.
In summary, technological advancements have opened up a plethora of investment opportunities in the space industry. From SPACs providing alternative funding models to the development of advanced materials and in-space manufacturing, the market is witnessing a rapid evolution. Space tourism, commercial space travel, and the integration of AI/ML further diversify the investment landscape. As the space sector continues to innovate, investors are well-positioned to capitalize on these trends, driving the growth of the space economy and fostering further exploration and development.
Investments: Where Does the Money Go?
You may want to see also

Risk Assessment: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with space ventures, such as launch delays and technological failures
Space ventures, often referred to as 'SpaceTech' or 'SPAC' (Special Purpose Acquisition Company) investments, present a unique set of risks and challenges that investors must carefully navigate. These risks are multifaceted and can significantly impact the success and profitability of such ventures. Here's an overview of risk assessment and mitigation strategies for space investments:
Identifying Risks:
- Launch Delays: One of the most prominent risks in the space industry is launch delays. These can occur due to various factors such as weather conditions, technical issues, supply chain disruptions, or regulatory hurdles. Delays can lead to increased costs, missed market opportunities, and potential project failures. Investors should assess the launch vehicle provider's track record, contingency plans, and the overall project timeline to identify potential delays.
- Technological Failures: Space missions rely on advanced technology, and failures in spacecraft systems, instruments, or software can be catastrophic. These failures may result from design flaws, manufacturing defects, or unexpected environmental factors. Due diligence should include a thorough review of the technology being used, the manufacturer's reputation, and the testing and validation processes employed.
- Market and Competition: The space industry is rapidly evolving, with numerous private companies and startups entering the market. Investors must analyze the competitive landscape, market demand, and the uniqueness of the venture's offering. Understanding the target market and potential competitors is crucial to assessing the long-term viability of the investment.
- Regulatory and Legal Risks: Space ventures often operate in a highly regulated environment, with compliance requirements for launch permits, space debris mitigation, and international space law. Changes in regulations or legal challenges can impact project timelines and costs. A comprehensive review of the regulatory framework and potential legal risks is essential.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Diversification: Investors should consider diversifying their space portfolio to spread risk. This can include investing in multiple launch providers, different spacecraft technologies, or various space-related sectors like satellite communications, Earth observation, or space tourism. Diversification reduces the impact of a single event or technology failure.
- Contractual Agreements: Strong contractual agreements with launch providers and technology suppliers are vital. These contracts should outline performance metrics, liability clauses, and compensation mechanisms in case of delays or failures. Regular monitoring and auditing of these agreements can help identify potential issues early on.
- Contingency Planning: Developing comprehensive contingency plans is essential for risk management. This includes identifying alternative launch vehicles or suppliers, backup technologies, and strategies to mitigate the impact of delays or failures. Regularly updating and testing these plans ensures that the venture is prepared for various scenarios.
- Expertise and Due Diligence: Investors should engage experts in the space industry for due diligence. These experts can provide valuable insights into technology, market trends, and potential risks. A thorough technical and market analysis will help identify and assess risks more accurately.
- Insurance and Financial Safety Nets: Space ventures can consider obtaining specialized insurance coverage to protect against launch delays, technological failures, and other potential risks. Additionally, having a robust financial reserve and a well-defined exit strategy can provide a safety net during challenging times.
Unlocking NFT Investment: Strategies Beyond Buying
You may want to see also

Return on Investment (ROI): Analyzing the financial returns and potential profits from space investment portfolios
Return on Investment (ROI) is a critical metric for assessing the financial performance and profitability of any investment, including those in the emerging space industry. When evaluating Space Investment Companies (SPACs), understanding the potential ROI is essential for investors to gauge the financial returns and assess the viability of their investments. Here's a detailed breakdown of how to analyze ROI in the context of SPACs:
Defining ROI: ROI is a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency or profitability of an investment. It calculates the net profit or loss generated relative to the investment's cost. In the context of SPACs, ROI analysis involves assessing the financial gains or losses associated with the investment, considering both the initial investment and any subsequent returns or dividends.
Calculating ROI: The formula for ROI is straightforward: ROI = (Net Profit / Investment Cost) * 100. For SPACs, this calculation can be applied to the initial investment made by investors. Net profit is determined by subtracting the initial investment from the total returns received, including any capital gains, dividends, or other financial benefits. The investment cost represents the initial amount invested in the SPAC.
Assessing Financial Returns: When analyzing SPACs, investors should consider various financial indicators to gauge the potential returns. These may include revenue growth, profit margins, and the company's ability to generate consistent financial gains. Examining historical financial data, earnings reports, and industry trends can provide insights into the SPAC's performance and its potential for generating profits.
Risk Assessment and Diversification: ROI analysis should also incorporate risk assessment. Space investments are inherently risky due to the technological challenges, regulatory uncertainties, and market volatility associated with the industry. Investors should evaluate the SPAC's risk management strategies, including its ability to navigate technological advancements, comply with regulations, and adapt to market changes. Diversification is another crucial aspect, as spreading investments across multiple SPACs can mitigate risks and potentially enhance overall ROI.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term ROI: It is essential to consider both short-term and long-term ROI when investing in SPACs. Short-term gains might be attractive, but long-term profitability is often a more reliable indicator of a successful investment. Investors should assess the SPAC's potential for sustained growth, technological innovation, and market disruption over an extended period. This analysis can help in making informed decisions and managing expectations regarding the investment's financial returns.
By carefully analyzing ROI, investors can make more informed decisions about SPAC investments, considering both the financial gains and the inherent risks associated with the space industry. This approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the potential returns and helps investors navigate the complexities of the space investment landscape.
Retirement Planning: When Do People Start?
You may want to see also

Industry Players: Examining the roles and contributions of key players in the space investment ecosystem
The space investment ecosystem is a complex network of various players, each contributing uniquely to the process of funding and supporting space ventures. Here's an overview of the key roles and contributions of these industry players:
- Space Investment Firms: These are the primary financial backers in the space industry. Investment firms specializing in space ventures provide the necessary capital to fund projects, startups, and established companies. They assess the potential of space-related ideas and technologies, offering financial support in exchange for equity. These firms often have expertise in identifying high-growth opportunities and managing the risks associated with the space sector. By investing in space startups, they enable the development of innovative technologies, satellite launches, and space exploration missions.
- Venture Capitalists: Venture capitalists (VCs) play a crucial role in the early-stage funding of space companies. They invest in high-risk, high-reward ventures, often providing seed funding to startups with groundbreaking space-related concepts. VCs bring not only financial resources but also strategic guidance, industry connections, and mentorship. They help space startups navigate the challenges of scaling, product development, and market entry. Many successful space companies have been fueled by VC investments, which have accelerated their growth and enabled them to compete in the market.
- Space Agencies and Government Organizations: Government bodies and space agencies are significant players in the space investment landscape. They provide substantial funding for space research, development, and exploration. These organizations often have dedicated budgets for space-related projects, including satellite launches, space missions, and technological advancements. Space agencies collaborate with private companies, offering contracts and partnerships to support commercial space activities. Their involvement ensures the development of critical infrastructure, scientific research, and the overall growth of the space industry.
- Space Tech Startups and Innovators: Entrepreneurs and innovators are at the forefront of the space investment ecosystem. They bring fresh ideas, cutting-edge technologies, and disruptive solutions to the industry. These startups focus on various aspects of space, such as satellite manufacturing, space tourism, space data analytics, and space-based services. By attracting investments, these companies can develop and launch their products, challenge traditional space players, and drive innovation. Their contributions often lead to the creation of new markets and the evolution of space-related industries.
- Industry Experts and Consultants: Industry experts and consultants provide valuable insights, analysis, and strategic advice to space investors and companies. They offer technical expertise, market research, and due diligence services. These professionals help investors make informed decisions by evaluating investment opportunities, assessing risks, and providing industry-specific knowledge. Consultants also assist space companies in refining their business models, improving operations, and navigating regulatory frameworks. Their contributions ensure that investments are made strategically and that space ventures are well-positioned for success.
In the space investment ecosystem, these players work together, often forming partnerships and collaborations. Each player brings unique expertise and resources, contributing to the growth and development of the space industry. Understanding their roles and contributions is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and stakeholders to navigate the complex world of space investments effectively.
Classic Cars: Passion or Profit?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
SPAC investments, or Special Purpose Acquisition Companies, are a type of investment vehicle that combines elements of both private equity and public markets. A SPAC is a corporation formed for the purpose of acquiring or merging with an existing business, often with the goal of taking a private company public without going through the traditional initial public offering (IPO) process.
SPACs provide a unique way for investors to invest in private companies or startups. When a SPAC is formed, it raises capital from investors, typically through an initial public offering (IPO). This capital is then used to acquire or merge with a target company. The SPAC's investors become shareholders of the target company, and the SPAC itself is dissolved or merged with the acquired business. This process allows private companies to access public markets and provides investors with an opportunity to invest in these companies earlier in their lifecycle.
Investing in SPACs offers several advantages. Firstly, it provides access to private companies that might not be available through traditional public markets. This can be attractive to investors seeking early-stage growth opportunities. Secondly, SPACs often offer higher potential returns compared to more established public companies, as they are typically involved in high-growth sectors or innovative businesses. Additionally, SPACs provide a liquid investment option, as they trade on major stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy or sell their shares relatively easily.
While SPACs can be lucrative, they also carry certain risks. One significant risk is the potential for the SPAC to fail to find a suitable target company or for the acquisition to fall through. This could result in a loss of investment for shareholders. Additionally, SPACs may have higher fees and expenses compared to traditional investment vehicles, and the early-stage nature of the companies they invest in can make them more volatile and risky. It's crucial for investors to conduct thorough research and diversify their SPAC investments to manage these risks effectively.