Budget surplus plays a significant role in influencing interest rates and investment decisions. When a government runs a budget surplus, it means it is collecting more revenue than it spends, often through increased tax revenues or reduced expenditures. This surplus can have a direct impact on interest rates as it affects the supply of funds in the financial market. With a surplus, the government can borrow less from the market, reducing the demand for loans and, consequently, lowering interest rates. Lower interest rates can then stimulate investment as businesses and individuals find borrowing more attractive, leading to increased capital spending and economic growth. This relationship between budget surplus, interest rates, and investments is a crucial aspect of macroeconomic policy and financial market dynamics.
What You'll Learn
- Fiscal Policy: Budget surplus reduces government borrowing, leading to lower interest rates and increased investment
- Monetary Policy: Surplus can signal economic stability, encouraging central banks to lower rates and stimulate investment
- Market Sentiment: Investors perceive surplus as positive, boosting confidence and driving up investment demand
- Government Spending: Reduced spending on public services can lead to lower interest rates and increased private investment
- Economic Growth: Surplus indicates strong economic fundamentals, attracting foreign investment and driving up local investment

Fiscal Policy: Budget surplus reduces government borrowing, leading to lower interest rates and increased investment
A budget surplus is a financial concept that occurs when a government's revenue exceeds its spending over a specific period. This surplus has significant implications for a country's economy, particularly in the context of fiscal policy. When a government runs a budget surplus, it means it is not relying on borrowing to fund its operations, which can have a direct impact on interest rates and investment.
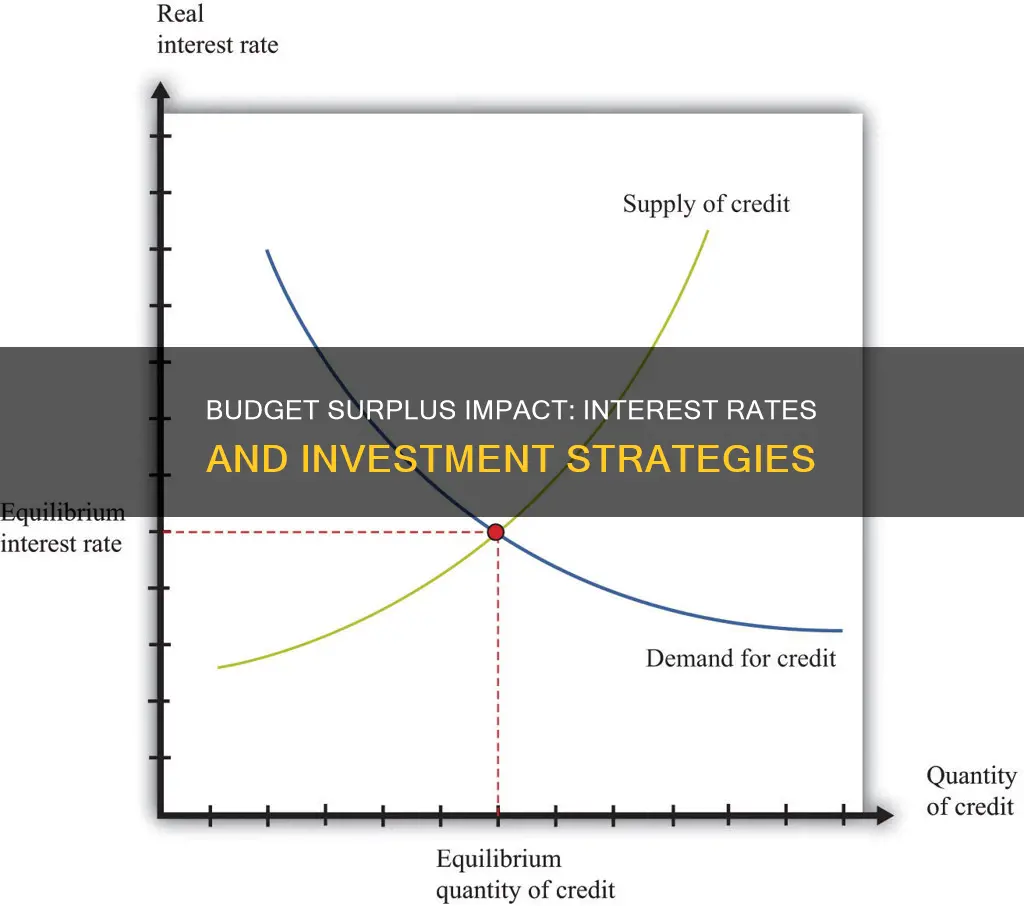
One of the key effects of a budget surplus is its influence on government borrowing. When a government has a surplus, it has already generated more revenue than it needs to spend, leaving a portion of the funds unutilized. This surplus can be used to reduce or eliminate the need for borrowing, as the government has the financial capacity to cover its expenses without relying on external sources of credit. By reducing borrowing, the government can lower its debt burden and the associated costs of servicing that debt.
Lower interest rates are often a direct consequence of a budget surplus. When the government is not borrowing extensively, it reduces the demand for loans in the financial market. As a result, lenders may lower their interest rates to attract borrowers, making borrowing more affordable for individuals and businesses. Lower interest rates can stimulate investment as businesses may find it cheaper to finance their operations, expansion, or new projects. This increased investment can further boost economic growth and create a positive feedback loop, where the economy benefits from the initial surplus.
Additionally, a budget surplus can signal economic stability and responsibility to investors. This stability can attract foreign investment, as investors are more inclined to invest in countries with a strong financial position and low debt. The influx of investment can lead to increased economic activity, job creation, and overall growth. Moreover, with a surplus, the government can allocate more funds towards infrastructure, education, and other long-term projects, which can have a positive impact on the country's development and productivity.
In summary, a budget surplus is a powerful tool in fiscal policy. It reduces government borrowing, which in turn leads to lower interest rates, making borrowing more accessible and affordable. This environment encourages increased investment, both domestically and internationally, fostering economic growth and development. By managing its finances effectively, a government can create a stable and attractive economic climate, benefiting various sectors and the population as a whole.
Foreign Investment and Interest Rates: A Global Economic Relationship
You may want to see also

Monetary Policy: Surplus can signal economic stability, encouraging central banks to lower rates and stimulate investment
A budget surplus, where government revenue exceeds expenditures, can have a significant impact on monetary policy and the economy as a whole. When a government runs a surplus, it often indicates a healthy and stable economic environment, which can influence central banks' decisions regarding interest rates and investment strategies. This surplus signals to the market that the government has a strong financial position, which can have a ripple effect on various economic indicators.
In the context of monetary policy, a budget surplus can be a powerful tool for central banks. When a government consistently runs a surplus, it demonstrates fiscal discipline and a commitment to long-term economic stability. This stability is attractive to investors, as it suggests a lower risk environment for their investments. As a result, the demand for the country's currency and government securities may increase, leading to a potential decrease in interest rates. Lower interest rates can stimulate investment as borrowing becomes more affordable, encouraging businesses to expand and individuals to make purchases.
Central banks often use interest rates as a lever to control the money supply and manage economic growth. When a budget surplus is present, it provides a positive signal to the central bank, suggesting that the economy is on a solid footing. This encourages the central bank to adopt a more accommodative monetary policy, where lowering interest rates becomes a viable option. By reducing interest rates, central banks aim to encourage borrowing and investment, which can further boost economic activity.
The relationship between a budget surplus and interest rates is particularly important for investment decisions. Investors often view a budget surplus as a sign of a robust economy, which can lead to increased confidence in the financial markets. This confidence may prompt investors to allocate more capital to the country, seeking higher returns. As a result, the increased investment demand can drive up asset prices and further lower interest rates, creating a positive feedback loop.
In summary, a budget surplus can have a profound effect on monetary policy and investment strategies. It signals economic stability, which encourages central banks to take a more relaxed approach to interest rates, potentially lowering them to stimulate investment. This, in turn, can attract more investment, further strengthening the economy. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the interconnectedness of fiscal and monetary policies in driving economic growth and stability.
Understanding Investment Interest: A Comprehensive Guide for Investors
You may want to see also

Market Sentiment: Investors perceive surplus as positive, boosting confidence and driving up investment demand
Budget surpluses are often seen as a positive sign by investors and can significantly impact market sentiment and investment behavior. When a government runs a budget surplus, it means that its revenue exceeds its spending over a specific period, typically a fiscal year. This surplus is a result of careful financial management and can have several effects on the economy, particularly in the context of interest rates and investments.
Investors generally view budget surpluses as a sign of fiscal responsibility and economic stability. A surplus indicates that the government is not overspending and is instead managing its finances effectively. This perception of fiscal discipline can boost investor confidence, especially in uncertain economic times. When investors believe that the government has a strong handle on its finances, they are more likely to feel secure in their investments, as they perceive a lower risk of financial mismanagement or economic downturn.
As a result of this positive sentiment, investors may become more willing to invest in various financial instruments, such as government bonds, stocks, and other assets. The increased demand for investments can lead to a rise in asset prices and a decrease in interest rates. Here's why: when the government has a surplus, it often has the option to borrow less or not at all, reducing the supply of government debt in the market. This shift in the supply and demand dynamics for bonds can lead to lower interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and individuals.
Lower interest rates can further stimulate investment as borrowing becomes more affordable. Businesses may be more inclined to invest in expansion projects, research, and development, or hire more employees, knowing that the cost of capital is reduced. This increased investment can drive economic growth and potentially lead to higher returns on investments, attracting even more capital into the market.
In summary, budget surpluses can create a positive feedback loop in the market. The initial boost in investor confidence can lead to higher investment demand, which, in turn, drives up asset prices and lowers interest rates. This environment can be particularly attractive to investors seeking stable and secure investment opportunities, as it suggests a healthy and responsible economic outlook. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for investors and policymakers alike, as it highlights the potential benefits of fiscal discipline and its impact on the broader financial markets.
Trump's Dakota Pipeline Stake: A Conflict of Interest?
You may want to see also

Government Spending: Reduced spending on public services can lead to lower interest rates and increased private investment
A budget surplus, when the government's revenue exceeds its spending, can have significant implications for interest rates and private investments. One key aspect to consider is the impact of reduced government spending on public services. When a government runs a surplus, it often indicates a healthy financial position, which can lead to a decrease in interest rates. This is because a surplus suggests that the government has ample funds available, reducing the need for borrowing from the market. As a result, the demand for loans and bonds decreases, causing interest rates to fall. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper for both the government and private entities, encouraging increased investment.
In the context of public services, reduced government spending can have a direct effect on interest rates. When the government allocates less money to healthcare, education, or infrastructure, it may need to borrow less to meet its financial obligations. This reduced borrowing requirement can lead to a surplus in the financial markets, where excess funds are available. As a result, lenders become more willing to offer loans at lower rates, further decreasing interest rates across the economy.
The relationship between government spending and private investment is also crucial. When the government reduces its spending on public services, it can create a ripple effect in the economy. Lower interest rates make it more attractive for businesses to invest in expansion, research, and development. With reduced government competition for funds, private investors can find more opportunities to channel their capital into productive ventures. This increased private investment can stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and contribute to overall prosperity.
Additionally, a budget surplus and reduced spending on public services can signal economic stability and responsible financial management to investors. This stability can attract foreign investments, as it indicates a lower risk of government default or sudden economic shifts. As a result, the country's currency may strengthen, further lowering interest rates and encouraging more private investments.
In summary, a budget surplus, coupled with reduced government spending on public services, can create an environment conducive to lower interest rates and increased private investment. This dynamic can have a positive impact on the economy, fostering growth and potentially improving the overall investment climate. Understanding these relationships is essential for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the interconnectedness of government finances, interest rates, and private sector activities.
Navigating the Low-Interest Rate Landscape: Why People Still Invest in CDs
You may want to see also

Economic Growth: Surplus indicates strong economic fundamentals, attracting foreign investment and driving up local investment
A budget surplus, which occurs when a government's revenue exceeds its spending, has significant implications for the economy, particularly in terms of interest rates and investment. Firstly, a surplus signals that the government is managing its finances effectively, which can boost investor confidence. This confidence often translates into lower interest rates, as investors perceive the government as a stable and reliable borrower. Lower interest rates then encourage businesses and individuals to borrow more, stimulating investment and consumption.
In the context of economic growth, a budget surplus is a positive indicator of a country's economic health. It suggests that the government has a strong fiscal position, which is attractive to foreign investors. These investors are more likely to invest in the country's financial markets, driving up the demand for the local currency and potentially leading to a stronger exchange rate. A stronger currency can further reduce the cost of borrowing for businesses and individuals, making investments more attractive.
The impact of a budget surplus on interest rates and investments can be twofold. Firstly, it can lead to a decrease in government borrowing, as the surplus reduces the need for additional funding. This, in turn, can lead to lower interest rates on government bonds, making them less attractive to investors. However, this also means that the government has more fiscal space to stimulate the economy through other means, such as tax cuts or increased spending on infrastructure.
Secondly, a budget surplus often indicates a stable and predictable economic environment, which is crucial for long-term investments. Foreign investors are more likely to commit capital to a country with a strong fiscal position, as it reduces the risk of economic instability. This influx of foreign investment can further drive up local investment, as businesses and individuals benefit from increased competition for capital. The result is a more vibrant and dynamic investment climate, fostering economic growth and development.
In summary, a budget surplus is a powerful catalyst for economic growth. It attracts foreign investment by demonstrating strong economic fundamentals, and it encourages local investment by creating a favorable environment for borrowing and spending. The surplus's impact on interest rates and the overall investment climate can lead to increased economic activity, higher employment, and improved living standards. Understanding these effects is essential for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced budget and promoting sustainable economic growth.
Uncover the Interest-Earning Potential of Your Investments
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A budget surplus, when a government's revenue exceeds its spending, often leads to lower interest rates. This is because a surplus indicates that the government is not relying heavily on borrowing, which can reduce the demand for loans in the market. As a result, lenders may offer lower interest rates to attract investors, and this can subsequently lower the overall cost of borrowing for businesses and individuals.
A budget surplus can stimulate investment in several ways. Firstly, lower interest rates resulting from a surplus encourage businesses to borrow and invest in expansion projects. Secondly, a surplus may lead to increased government spending on infrastructure or other initiatives, creating a positive economic environment that attracts private investments. Additionally, a surplus can signal economic stability and growth, making it an attractive prospect for investors.
Yes, a budget surplus can potentially contribute to higher investment returns. With a surplus, the government may have more financial resources to invest in productive assets, infrastructure, or other ventures that can drive economic growth. This can lead to increased productivity, higher demand for goods and services, and ultimately, improved investment opportunities. As a result, investors may benefit from a more favorable market environment, potentially leading to better returns on their investments.