China's investment in US dollars is a significant aspect of its foreign exchange reserves and international financial strategy. The country has been a major holder of US Treasury securities, which are denominated in dollars, for many years. This investment is driven by the need to diversify its reserves, maintain liquidity, and support the stability of the US dollar as a global reserve currency. China's approach to investing in US dollars involves a combination of short-term and long-term strategies, including direct purchases of Treasury securities, participation in the secondary market, and various other financial instruments. Understanding these investment patterns is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the global financial market and the complex relationship between China and the United States.
What You'll Learn
- China's Dollar Reserves: A Deep Dive into US Treasury Holdings
- Currency Manipulation: China's Influence on the Dollar's Value
- Trade Balances: Impact of Dollar Investments on China's Trade Surplus
- Financial Market Access: China's Investment in US Stocks and Bonds
- Geopolitical Implications: Dollar Investments and China's Global Influence

China's Dollar Reserves: A Deep Dive into US Treasury Holdings
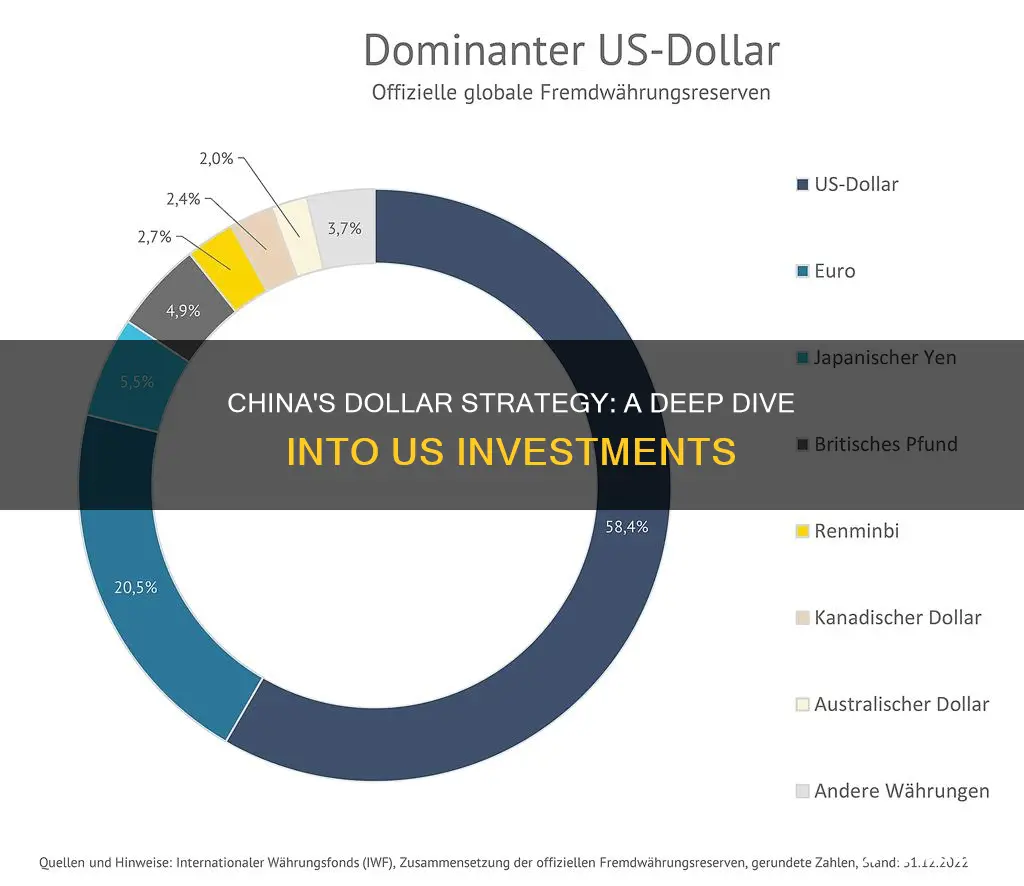
China's foreign exchange reserves are substantial, and a significant portion of these reserves is held in US dollars, making it one of the largest holders of US Treasury securities. This investment strategy has been a cornerstone of China's financial policy for decades, offering both stability and potential risks. The country's approach to managing these reserves is a complex interplay of economic strategy, geopolitical considerations, and financial market dynamics.
The primary reason for China's significant investment in US dollars is the perceived stability and liquidity of the US financial market. The US Treasury market is the largest and most liquid in the world, providing China with a safe haven for its reserves. By holding US Treasury securities, China can easily convert its dollars into other currencies or assets when needed, ensuring flexibility in its investment portfolio. This liquidity is particularly important for a country with vast reserves, as it allows for quick adjustments to market conditions and potential economic shocks.
Over the years, China's US Treasury holdings have grown significantly, often surpassing other major investors. This growth is a result of various factors, including the historical low-interest rates in the US, which made US Treasury securities an attractive, low-risk investment. Additionally, China's trade surplus with the United States has contributed to its dollar reserves, as the surplus generates a steady stream of US dollars that can be invested. The country's strategic decision to diversify its reserves into US assets also played a role in this expansion.
However, this heavy investment in US dollars and US Treasury securities also carries risks. One of the primary concerns is the potential for a decline in the value of the US dollar, which could erode China's reserves. The US-China trade tensions and the possibility of a trade war have also raised questions about the safety of Chinese investments in the US. As a result, China has been diversifying its reserve portfolio, reducing its reliance on US assets. This diversification strategy aims to mitigate risks and ensure the long-term stability of China's foreign exchange reserves.
In summary, China's investment in US dollars, particularly through US Treasury securities, is a strategic move driven by the need for stability and liquidity. While this approach has served China well in the past, the country is now taking steps to balance its risks by diversifying its reserve portfolio. Understanding China's reserve management strategies provides valuable insights into the global financial landscape and the complex relationship between major economies and their investment choices.
AI Investing: Unlocking the Future of Financial Markets
You may want to see also

Currency Manipulation: China's Influence on the Dollar's Value
China's investment in US dollars is a significant aspect of its economic strategy, and it has a profound impact on global financial markets, especially in the context of currency manipulation. The Chinese government and state-owned enterprises have been major holders of US Treasury securities, which are primarily denominated in US dollars. This investment strategy serves multiple purposes, including diversifying China's foreign exchange reserves, supporting the US economy, and potentially influencing the value of the US dollar.
When China invests in US dollars, it typically purchases US Treasury bonds, notes, and bills, which are considered low-risk assets. These investments are a significant portion of China's vast foreign exchange reserves, which are among the largest globally. By holding these securities, China contributes to the demand for US dollars, which can have a direct effect on its value. The more US dollars China holds, the more it can influence the market and potentially manipulate the currency's value.
Currency manipulation is a strategy where a country intervenes in the foreign exchange market to affect the value of its currency relative to others. China has been accused of this practice, as its massive foreign exchange reserves and strategic investments can be used to keep the yuan (Chinese currency) artificially low. By maintaining a weak yuan, China can make its exports more competitive globally, which is essential for its large trade surplus. This strategy, however, has sparked debates and tensions with other major economies, particularly the United States, as it can distort global trade and investment patterns.
The relationship between China's investments and the US dollar's value is complex. While China's purchases of US Treasury securities provide liquidity to the US financial system and support the dollar's role as the global reserve currency, it also has the potential to influence exchange rates. If China were to sell a significant portion of its US dollar assets, it could lead to a decrease in demand for the dollar, causing its value to drop. This scenario highlights the delicate balance China must maintain in its investment strategy to avoid triggering currency wars and potential economic repercussions.
In summary, China's investment in US dollars is a strategic move with far-reaching implications. It not only contributes to the stability of the global financial system but also provides China with a tool to manage its currency. However, the potential for currency manipulation and the associated economic risks have led to international scrutiny and discussions on the appropriate use of such influence. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for investors, policymakers, and economists alike, as it shapes global financial markets and international trade relationships.
Energy Investment: Now or Never?
You may want to see also

Trade Balances: Impact of Dollar Investments on China's Trade Surplus
China's extensive investment in US dollars has had a significant impact on its trade balances and overall economic landscape. The country's strategic decision to accumulate vast amounts of foreign exchange reserves, primarily in the form of dollars, has both advantages and challenges.
One of the primary effects is the substantial trade surplus China has consistently maintained. By investing heavily in US assets, including government bonds, China has become a major holder of US debt. This investment strategy allows China to purchase US goods and services, contributing to a consistent trade surplus. The surplus arises as China's exports to the United States exceed its imports from the country. As a result, China's foreign exchange reserves, largely denominated in dollars, continue to grow, providing the nation with significant economic leverage.
However, this investment approach also has implications for China's trade balance. The country's large-scale dollar investments can influence the value of the Chinese yuan. When China buys US assets, it increases demand for the dollar, which can lead to a stronger yuan. A stronger currency can make Chinese exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially impacting the country's export-oriented industries. To maintain its trade surplus, China might need to carefully manage its currency value, ensuring it remains competitive in the global market.
Moreover, the investment in US dollars can also affect China's domestic economy. The influx of dollars can impact interest rates and credit availability within China, potentially influencing investment and consumption patterns. A significant portion of China's foreign exchange reserves is held in low-risk, low-yield assets, which may limit the potential for higher returns. This could encourage China to diversify its investment portfolio, further impacting its trade relationships and economic strategies.
In summary, China's investment in US dollars has a direct correlation with its trade balances and economic policies. While it contributes to a trade surplus and foreign exchange reserves, it also presents challenges related to currency management and economic diversification. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending China's global economic influence and its strategies to maintain a balanced trade position.
Invest Wisely in People, Shape Your Legacy
You may want to see also

Financial Market Access: China's Investment in US Stocks and Bonds
China's investment in US financial markets is a significant aspect of its strategy to diversify its foreign exchange reserves and gain access to global financial assets. The country's approach to investing in US dollars and financial instruments is multifaceted and has evolved over time.
One of the primary methods China employs is through the purchase of US Treasury securities, which are considered a safe-haven asset. These securities are highly liquid and are often sought after by investors during times of economic uncertainty. By investing in US Treasuries, China not only diversifies its reserve portfolio but also contributes to the stability of the US financial system. The Chinese government and various state-owned entities have been significant buyers of these securities, often in the form of long-term bonds, to ensure a steady and substantial investment.
In addition to Treasury securities, China has been increasingly investing in US stocks and corporate bonds. This strategy allows China to gain exposure to the US equity markets and benefit from the potential growth and dividends associated with these investments. Chinese investors, including state-owned funds and private equity firms, have been actively participating in the US stock market, particularly in sectors like technology, healthcare, and energy. The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ have seen a surge in Chinese investment, with some companies even choosing to list their shares in the US, providing Chinese investors with direct access to these markets.
The investment in US corporate bonds is another way China accesses the US financial market. These bonds offer higher yields compared to US Treasuries, attracting Chinese investors seeking more attractive returns. Chinese insurance companies and asset management firms have been particularly active in this segment, allowing them to diversify their portfolios and potentially increase their returns.
Furthermore, China's investment in US financial markets is not limited to direct purchases. The country has also been utilizing various financial instruments and derivatives to manage its exposure. For instance, China has been known to employ currency swaps and forward contracts to hedge its currency risks and protect its investments. These tools enable China to maintain its investment position while managing potential fluctuations in the value of the US dollar.
In summary, China's investment in US dollars and financial markets is a strategic move to diversify its reserves, gain market access, and potentially earn higher returns. Through a combination of Treasury securities, US stocks, corporate bonds, and sophisticated financial instruments, China has been able to navigate the US financial system, contributing to the global economy and its own financial stability. This approach also highlights China's growing influence in international financial markets and its ability to adapt to changing economic landscapes.
Fear of Losing Money Keeps People from Investing
You may want to see also

Geopolitical Implications: Dollar Investments and China's Global Influence
The Chinese government's investment in US dollars carries significant geopolitical implications, shaping China's global influence and its relationship with the United States. This investment strategy is a strategic move to secure financial stability and gain economic leverage on the world stage. By holding a substantial portion of its foreign exchange reserves in US dollars, China gains a degree of control over its financial assets and can influence global markets. This investment also provides China with a powerful tool to potentially sway US economic policies and decisions.
One key geopolitical implication is the potential for China to use its dollar investments to exert pressure on the US. With a large portion of its reserves in US assets, China can influence the value of the dollar and, by extension, the global economy. This power can be wielded in times of economic tension or political disagreements, allowing China to potentially gain concessions or favorable outcomes in international negotiations. For instance, China could adjust its dollar investments to impact the US stock market, potentially influencing policy decisions or creating economic challenges for the US government.
Moreover, China's investment in US dollars can be seen as a strategic move to diversify its own economy and reduce reliance on the Chinese yuan. By holding a significant portion of its reserves in a stable and widely accepted currency, China can protect its financial assets from potential domestic economic fluctuations. This strategy also allows China to maintain a strong position in the global financial system, ensuring its currency's stability and acceptance as a reserve currency.
The geopolitical implications extend beyond direct economic influence. China's investment in US dollars can also shape its relationships with other countries. As China's dollar investments grow, it can use these assets to provide financial support or loans to developing nations, potentially gaining strategic allies and influence in international affairs. This strategy can be particularly effective in regions where China has historical or cultural ties, allowing it to exert a subtle yet powerful form of soft power.
In summary, China's investment in US dollars is a strategic geopolitical move with far-reaching consequences. It provides China with economic leverage, the potential to influence global markets, and a tool to shape its relationships with other nations. As China continues to invest in US assets, the geopolitical dynamics between the two countries will likely evolve, impacting international trade, financial stability, and global power dynamics. Understanding these implications is crucial for policymakers and economists alike as they navigate the complex interplay between finance, politics, and international relations.
Ford: A Smart Investment Move
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
China's investment in US Treasury securities and other dollar-denominated assets significantly influences the American financial landscape. These investments provide a stable source of funding for the US government and help keep interest rates low, stimulating economic growth. However, it also means China has a substantial amount of influence over US monetary policy, as it can sell these assets and potentially impact the value of the US dollar.
China's investment in US dollars primarily occurs through the purchase of US Treasury bonds, notes, and bills, as well as other government securities. The Chinese government and state-owned enterprises also invest in US stocks, real estate, and various financial instruments. Additionally, China's foreign exchange reserves, which are predominantly held in dollars, contribute to this investment strategy.
China's investment in US dollars allows it to diversify its foreign exchange reserves, reducing risk by not holding a single currency. This strategy also provides China with a stable store of value and a means to finance its trade deficit with the US. By investing in US assets, China can earn interest and capital gains, contributing to its overall economic growth and financial stability.
While China's investment in US dollars offers numerous benefits, it also carries certain risks. The US economy's performance directly impacts the value of these investments. A recession or significant economic downturn could lead to capital losses for China. Additionally, geopolitical tensions or changes in US monetary policy might affect the attractiveness of US assets, potentially causing China to reevaluate its investment strategy.