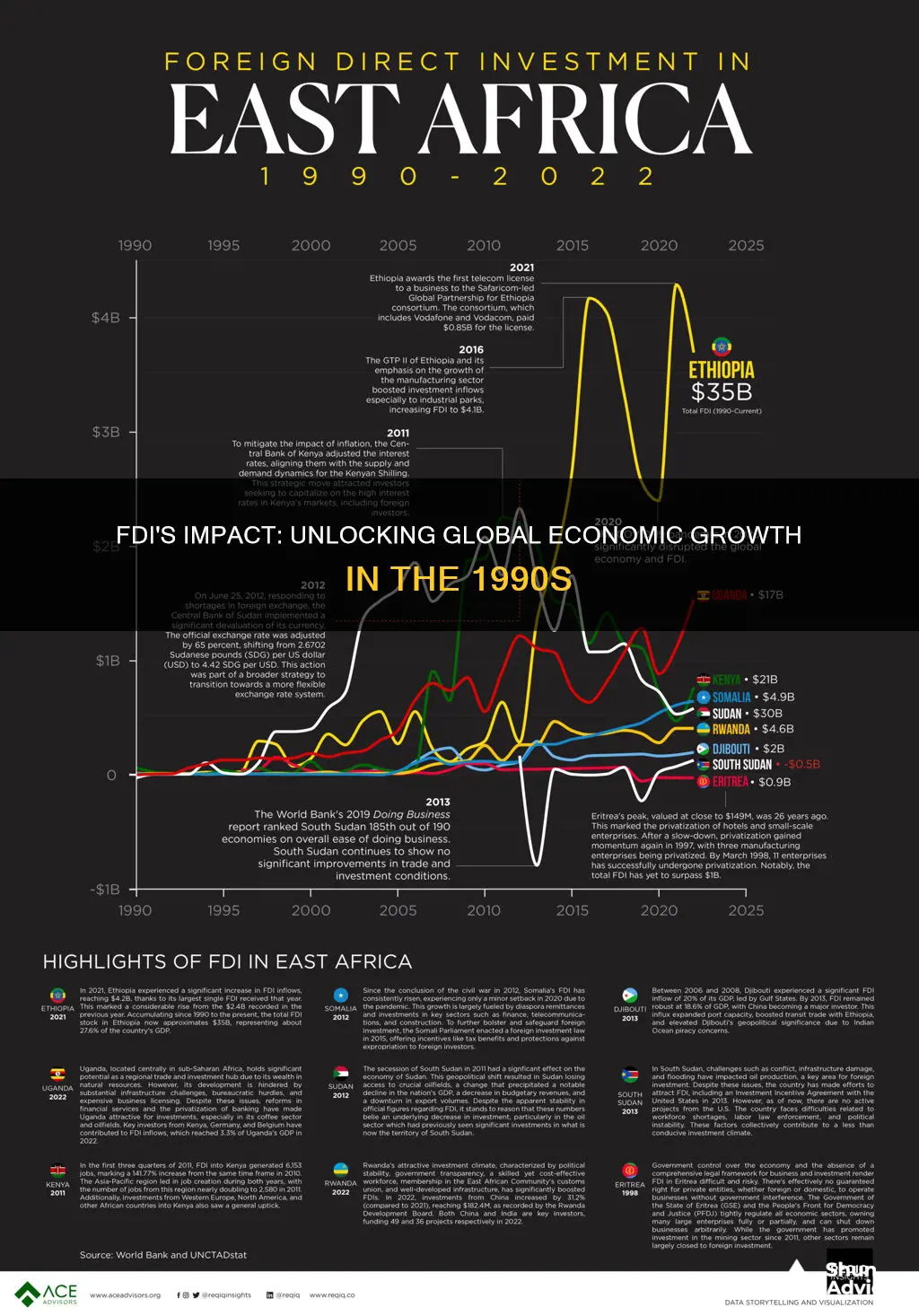
Foreign direct investment (FDI) has been a significant factor in the economic growth of many countries since the 1990s. This topic explores the impact of FDI on economic development, focusing on how it influences a country's growth and development. The analysis examines the various ways in which FDI can contribute to economic growth, including the transfer of technology, knowledge, and skills, as well as the creation of jobs and the development of infrastructure. It also considers the potential challenges and risks associated with FDI, such as the potential for environmental degradation and the impact on local industries. By understanding the complex relationship between FDI and economic growth, policymakers can make informed decisions to maximize the benefits of FDI while mitigating potential negative impacts.
What You'll Learn
- Impact on Domestic Investment: FDI can crowd in domestic investment, enhancing overall capital formation
- Technology Transfer: It facilitates the transfer of technology and knowledge, boosting productivity
- Employment Generation: FDI projects create jobs, reducing unemployment and improving labor market conditions
- Infrastructure Development: Foreign investment often leads to improved infrastructure, benefiting the local economy
- Market Access: It provides access to new markets, expanding export opportunities for host countries

Impact on Domestic Investment: FDI can crowd in domestic investment, enhancing overall capital formation
Foreign direct investment (FDI) has been a subject of extensive research and debate, particularly in understanding its impact on economic growth and development. When it comes to the relationship between FDI and domestic investment, there is a fascinating dynamic that can significantly influence a country's overall capital formation and economic growth.
The concept of 'crowding in' is crucial here. FDI can act as a catalyst, encouraging and stimulating additional domestic investment. This phenomenon occurs when foreign investors bring in capital, expertise, and technology, creating a ripple effect that attracts and supports local businesses and entrepreneurs. As FDI enters a market, it often leads to increased competition, which can drive domestic firms to invest in research and development, infrastructure, and innovation to remain competitive. This competitive environment can foster a culture of improvement and growth, where local businesses strive to enhance their productivity and efficiency.
One of the key mechanisms behind this impact is the demonstration effect. When foreign investors witness the potential and opportunities within a domestic market, they may be more inclined to invest, knowing that their presence will attract further attention and capital. This can create a positive feedback loop, where FDI attracts more FDI, and domestic investment flourishes as a result. Moreover, FDI often brings advanced technologies and management practices, which can be transferred to local businesses through joint ventures, partnerships, or knowledge-sharing agreements. This knowledge transfer can lead to improved productivity, better resource allocation, and the adoption of international standards, further boosting domestic investment.
Additionally, the entry of foreign investors can lead to the establishment of new industries or the expansion of existing ones, creating a more diverse and robust economic landscape. This diversification can attract a wider range of domestic investors, as they see the potential for growth and market opportunities. As a result, the overall capital formation increases, contributing to long-term economic development.
In summary, FDI has a powerful impact on domestic investment by creating a stimulating environment that encourages local businesses to invest and innovate. This 'crowding in' effect can lead to a positive cycle of economic growth, where foreign and domestic investments complement each other, driving the country's economic development and potentially reducing the reliance on foreign capital in the long run. Understanding this relationship is essential for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the importance of creating an environment that attracts FDI while also fostering a culture of domestic investment and entrepreneurship.
Investing Excess Cash: Strategies for Smart Financial Planning
You may want to see also

Technology Transfer: It facilitates the transfer of technology and knowledge, boosting productivity
Foreign direct investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in fostering economic growth, and one of its most significant impacts is the facilitation of technology transfer. When foreign investors establish a presence in a host country, they bring with them advanced technologies, expertise, and knowledge that can significantly enhance the recipient nation's productivity and competitiveness.
Technology transfer through FDI occurs in several ways. Firstly, multinational corporations (MNCs) often transfer their proprietary technologies and processes to local subsidiaries or partners. This transfer can involve licensing agreements, where the MNC grants the host country's company the right to use their technology, or it can be through the establishment of joint ventures, where both parties collaborate to develop and implement new technologies. By sharing their technological capabilities, MNCs enable local firms to improve their production methods, increase efficiency, and enhance the quality of their products.
Secondly, FDI often leads to the creation of new industries or the expansion of existing ones. Foreign investors may identify gaps in the host country's market and introduce new technologies to meet those demands. For example, a foreign auto manufacturer might set up a plant in a developing nation, bringing with it advanced manufacturing techniques and assembly lines, which then get adopted by local competitors. This transfer of technology can lead to a rapid improvement in the overall quality and standards of local industries, making them more attractive to both domestic and international consumers.
Moreover, technology transfer through FDI can have a multiplier effect on the economy. As local firms adopt new technologies, they may become more efficient, which can lead to cost savings. These savings can then be reinvested into the business, allowing for further expansion and the creation of additional jobs. This process can stimulate economic growth, not only in the immediate sector but also in related industries, creating a positive feedback loop.
In summary, foreign direct investment serves as a powerful catalyst for technology transfer, which, in turn, drives productivity gains. By sharing advanced technologies and knowledge, foreign investors enable local businesses to modernize, improve their competitiveness, and contribute to the overall economic development of the host country. This aspect of FDI is particularly important in today's globalized world, where technology is a key driver of economic success.
Foreign Investment: A Blessing or Curse for the American Economy?
You may want to see also

Employment Generation: FDI projects create jobs, reducing unemployment and improving labor market conditions
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has been widely recognized as a powerful catalyst for economic growth and development, particularly in the context of job creation and labor market improvements. When foreign investors establish projects or acquire local businesses, they bring with them not only capital but also a range of skills, technologies, and management practices that can significantly enhance the host country's economy. One of the most tangible benefits of FDI is its ability to generate employment opportunities, which can have a profound impact on the local population.
FDI projects often require a diverse workforce, including skilled and unskilled labor, to operate effectively. This leads to the creation of numerous job openings, which can help reduce unemployment rates, especially among the youth and less-educated segments of the population. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, FDI can lead to the establishment of factories, which not only produce goods but also employ a significant number of workers, often providing stable and long-term employment. This is particularly beneficial in regions where unemployment is a pressing issue, as it can help alleviate poverty and improve the overall standard of living.
The positive impact of FDI on employment is not limited to the direct jobs created by the investment. As FDI projects expand and become more established, they often stimulate the growth of ancillary businesses and services, further increasing the demand for labor. This multiplier effect can lead to a significant rise in employment opportunities, not only in the immediate vicinity of the FDI project but also in related industries and sectors. Moreover, FDI can attract local entrepreneurs and businesses, fostering a more dynamic and competitive business environment, which further contributes to job creation.
In addition to direct job creation, FDI can also improve labor market conditions by introducing new skills and training programs. Foreign investors often bring advanced technical knowledge and management techniques, which can be transferred to local employees through training and development initiatives. This not only enhances the skill set of the workforce but also increases productivity and efficiency, making the labor market more competitive and adaptable. As a result, the host country's workforce becomes more attractive to investors, creating a positive feedback loop that encourages further FDI.
The employment generation aspect of FDI is a crucial factor in its overall impact on economic growth. By reducing unemployment and improving labor market conditions, FDI can contribute to a more stable and prosperous society. This, in turn, can lead to increased consumer spending, higher tax revenues, and improved social indicators, all of which are essential for sustainable economic development. Therefore, policymakers and investors should recognize the importance of FDI in creating jobs and should work towards creating an environment that encourages and supports such investments.
Default Investment Option: Should You Take the Easy Route?
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Foreign investment often leads to improved infrastructure, benefiting the local economy
Foreign direct investment (FDI) has been a significant catalyst for economic growth and development, particularly in the context of infrastructure improvements. When foreign investors enter a country, they often bring with them not only capital but also advanced technologies, expertise, and best practices. This influx of resources can have a transformative effect on the local infrastructure sector.
One of the most notable impacts of FDI on infrastructure is the development of transportation networks. Foreign investors may establish or upgrade roads, railways, and ports, connecting previously isolated regions to major trade routes. These improvements facilitate the movement of goods and people, reducing transportation costs and increasing efficiency. For instance, in many developing countries, foreign-funded projects have led to the construction of modern highways, bridges, and tunnels, which have not only boosted local economies but also improved the overall connectivity and accessibility of the region.
In addition to transportation, FDI can significantly enhance communication infrastructure. Foreign companies often invest in the expansion of telecommunications networks, including the installation of fiber-optic cables, cell towers, and internet infrastructure. This development is crucial for the digital transformation of a country, enabling faster and more reliable communication, which is essential for economic activities, education, and social development. Improved internet connectivity can also attract further FDI, creating a positive feedback loop that accelerates economic growth.
The impact of foreign investment on energy infrastructure is another critical aspect. Foreign companies may invest in power plants, renewable energy projects, and energy distribution networks. These investments can address the growing energy demands of a developing economy, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. For example, in regions with abundant renewable resources, foreign investors might establish wind farms or solar power plants, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy sector.
Furthermore, FDI in infrastructure can have a ripple effect on the local economy. Improved infrastructure attracts more businesses, both domestic and international, leading to increased economic activity and job creation. The development of industrial parks, special economic zones, and modern business hubs can further stimulate economic growth, as these areas provide the necessary infrastructure for businesses to operate efficiently. This, in turn, generates tax revenues for the government, which can be reinvested in further infrastructure development and social programs.
ETFs: A Passive Investor's Best Friend?
You may want to see also

Market Access: It provides access to new markets, expanding export opportunities for host countries
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in facilitating market access for host countries, which in turn significantly impacts economic growth. When a foreign investor establishes a business or acquires assets in a host country, it often leads to the creation of new export opportunities. This is particularly beneficial for developing nations, as it can help them integrate into the global economy and tap into international markets.
One of the primary advantages of FDI in this context is the establishment of production facilities or subsidiaries in the host country. These new operations can produce goods and services that were previously unavailable or limited in the local market. By doing so, FDI introduces new products and services to the host country's economy, making them more competitive and attractive to both domestic and international consumers. This increased competition can drive down prices, improve product quality, and create a more dynamic business environment.
Moreover, FDI often leads to the transfer of technology, knowledge, and skills from the foreign investor to the host country. This knowledge transfer can enhance the productivity and efficiency of local businesses, enabling them to produce goods that are more competitive in both domestic and international markets. As a result, host countries can experience a boost in exports, as their products become more desirable and accessible to foreign buyers.
The expansion of export opportunities through FDI has a positive ripple effect on the host country's economy. Increased exports can lead to higher foreign exchange reserves, which can be used to stabilize the local currency and support further economic growth. Additionally, the revenue generated from exports can contribute to government revenue, enabling investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, which are essential for long-term economic development.
In summary, FDI provides a gateway to new markets by establishing a presence in host countries, offering export opportunities, and facilitating the transfer of valuable resources. This market access is a powerful catalyst for economic growth, as it encourages international trade, enhances productivity, and contributes to the overall development of the host nation. Understanding the impact of FDI on market access is essential for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the potential for FDI to drive positive economic transformations.
A Beginner's Guide to Investing with Upstox
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Foreign direct investment has been a significant factor in promoting economic growth and development, especially in developing countries. FDI involves the purchase of assets or the establishment of operations in a foreign country, often leading to the transfer of capital, technology, and expertise. This influx of investment can stimulate local economies by creating jobs, improving infrastructure, and fostering innovation. Research from the early 1990s suggests that FDI can contribute to higher productivity, increased competition, and improved resource allocation, ultimately leading to economic growth.
In the context of industrialization, FDI can play a crucial role in accelerating a country's development. It provides access to advanced technologies and management practices, enabling local industries to modernize and enhance their productivity. Foreign investors often bring specialized skills and knowledge, which can help local businesses improve their production processes, product quality, and overall efficiency. This, in turn, can lead to a more competitive business environment and contribute to the country's industrialization goals.
While FDI is generally considered beneficial, there are some potential challenges. One concern is the risk of environmental degradation, especially when foreign investors prioritize short-term profits over sustainable practices. Additionally, there might be cultural and social impacts, as FDI can lead to changes in local labor markets and community dynamics. Host countries need to ensure that FDI is managed carefully to minimize negative externalities and promote equitable growth.
The understanding of FDI's impact on economic growth has evolved over the years. Initially, FDI was often seen as a panacea for developing economies, but later studies revealed more nuanced effects. Researchers now emphasize the importance of context, such as the host country's institutional quality, policy environment, and existing infrastructure. It is now widely recognized that FDI's benefits are maximized when it is accompanied by sound domestic policies, regulatory frameworks, and strategic planning.







