The term cash in investments refers to the most liquid and widely accepted form of money, which is typically in the form of currency or readily accessible funds. In the context of investments, cash represents the immediate and available financial resources that can be used to purchase assets, securities, or other investment opportunities. It is a fundamental concept in finance, as it serves as a benchmark for assessing the liquidity and value of various investment instruments. Understanding the role of cash is crucial for investors, as it enables them to make informed decisions regarding their financial strategies, risk management, and the allocation of their investment portfolios.
What You'll Learn
- Cash as a liquid asset: Money readily available for immediate use
- Cash flow in investments: The movement of money in and out of investment accounts
- Cash equivalents: Short-term, highly liquid investments with minimal risk
- Cash management strategies: Techniques to optimize cash holdings and investment returns
- Cash dividends: Payments made by companies to shareholders from their profits

Cash as a liquid asset: Money readily available for immediate use
Cash, in the context of investments, refers to the most basic and essential form of capital: money. It is a liquid asset, meaning it can be quickly and easily converted into a usable form without significant loss of value. This liquidity is a critical aspect of cash's role in investments, as it provides investors with the flexibility to take advantage of opportunities or manage unexpected financial needs.
In the financial world, cash is often considered the most liquid asset due to its immediate convertibility into other forms of capital. It represents the funds that are readily available in a company's or an individual's account, ready to be used for various purposes. This includes paying bills, investing in new ventures, or simply maintaining a buffer for unexpected expenses. The term 'cash' in investments emphasizes the importance of having a substantial amount of this liquid asset to ensure financial stability and the ability to act swiftly when needed.
The concept of cash as a liquid asset is particularly crucial for businesses and investors who need to manage their finances effectively. It allows companies to cover short-term obligations, such as payroll, suppliers, and operational costs, ensuring smooth day-to-day operations. For investors, having a significant amount of cash provides the means to capitalize on investment opportunities, whether it's purchasing stocks, bonds, or other assets, or simply having a reserve for potential market downturns.
In personal finance, maintaining a healthy cash balance is essential for financial security. It enables individuals to build an emergency fund, providing a safety net for unforeseen circumstances like job loss or medical emergencies. Additionally, having cash on hand allows investors to take advantage of investment opportunities that may arise, ensuring they can act promptly without the need to liquidate other assets.
The term 'cash' in investments highlights the importance of having a substantial and readily available amount of money. It is a powerful tool for financial management, providing the means to navigate the complexities of the investment world and ensuring financial stability in various scenarios. Understanding the role of cash as a liquid asset is fundamental for anyone looking to build and maintain a robust financial portfolio.
Maximizing Wealth: Exploring Long-Term Investment Strategies for Financial Security
You may want to see also

Cash flow in investments: The movement of money in and out of investment accounts
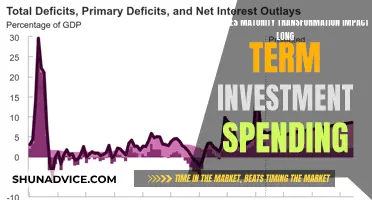
The term "cash" in investments refers to the actual currency or liquid assets that are used to purchase and sell investment vehicles. In the context of investments, cash flow is the movement of money in and out of investment accounts, representing the ebb and flow of funds that investors use to buy and sell assets. Understanding cash flow is crucial for investors as it provides insights into the liquidity and financial health of their investments.
Cash flow in investments can be analyzed through various metrics, such as the net cash flow, which is the total cash generated or spent by an investment over a specific period. This metric helps investors assess the profitability and sustainability of their investments. Positive net cash flow indicates that the investment is generating more cash than it is consuming, while negative net cash flow suggests the opposite. Investors should also consider the cash flow margin, which is the percentage of revenue that turns into cash, providing a clearer picture of the investment's efficiency in generating cash from its operations.
The movement of cash in and out of investment accounts is a dynamic process. Investors initiate cash flow by making initial investments, which can be in the form of purchasing stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments. When an investor buys an asset, they transfer cash from their account to the seller, thus increasing the cash outflow. Conversely, when an investor sells an asset, they receive cash, leading to a cash inflow. This simple yet fundamental concept underpins the very nature of investing.
In addition to buying and selling assets, cash flow in investments is influenced by other factors. Dividends and interest payments received from investments contribute to cash inflows, providing investors with regular returns on their capital. On the other hand, expenses such as management fees, transaction costs, or interest payments on borrowed funds can reduce cash flow, impacting the overall profitability of the investment strategy.
Effective management of cash flow is essential for investors to navigate the complexities of the financial markets. It involves monitoring cash positions, ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet financial obligations, and making strategic decisions to optimize returns. By understanding and analyzing cash flow, investors can make informed choices, adapt to market conditions, and build a robust investment portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Long-Term Investment Strategies: Navigating the Market's Future
You may want to see also

Cash equivalents: Short-term, highly liquid investments with minimal risk
The term "cash equivalents" refers to a specific category of short-term, highly liquid investments that are considered to have a very low risk of default. These investments are essentially a form of cash or very close to it in terms of liquidity and safety. Cash equivalents are crucial for investors who seek to maintain a highly liquid portfolio while also minimizing the risk associated with their investments.
These investments are typically used by investors and institutions to meet short-term financial goals, such as maintaining a reserve for upcoming expenses or taking advantage of immediate investment opportunities. They are often used as a bridge between cash and other long-term investments, providing a safe and accessible store of value.
The key characteristics of cash equivalents include their short-term nature, high liquidity, and minimal credit risk. Short-term investments are those with a maturity of less than one year, ensuring that the investor can access their funds quickly if needed. High liquidity means that these investments can be easily converted into cash without significant loss of value. Minimal credit risk indicates that the risk of the investment defaulting or failing to pay back the principal is very low, making them a safe haven for investors.
Examples of cash equivalents include money market funds, treasury bills, and commercial paper. Money market funds invest in a diversified portfolio of short-term debt instruments, providing investors with a safe and liquid option. Treasury bills are short-term debt securities issued by the government, offering a low-risk investment with a fixed maturity date. Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note issued by corporations, typically used for short-term financing needs.
In summary, cash equivalents are a critical component of investment portfolios, providing a safe, liquid, and low-risk option for investors. They are ideal for those who want to maintain a highly accessible store of value while also benefiting from the potential for capital growth. Understanding and utilizing cash equivalents can help investors achieve their financial goals, especially in times of market uncertainty or when immediate access to funds is required.
Navigating the Duality: Short-Term and Long-Term Investments Demystified
You may want to see also

Cash management strategies: Techniques to optimize cash holdings and investment returns
Effective cash management is a critical aspect of investment strategy, allowing investors to optimize their financial resources and enhance overall returns. When discussing cash in investments, it refers to the liquid assets or funds that an investor holds, which can be readily converted into cash with minimal impact on the investment's value. This includes cash on hand, bank deposits, and highly liquid investments like money market funds or short-term government securities. Efficient cash management involves a strategic approach to utilizing and growing these liquid assets.
One key strategy is to maintain a balanced cash reserve to ensure liquidity and meet financial obligations. This involves setting aside a portion of your cash holdings as a safety net for unexpected expenses or opportunities. A common rule of thumb is to keep three to six months' worth of living expenses in easily accessible cash or highly liquid investments. This reserve provides financial flexibility and ensures that investors can take advantage of investment opportunities without delay.
Another technique is to implement a disciplined approach to cash flow management. This entails regularly reviewing and analyzing cash inflows and outflows to identify patterns and potential areas for improvement. By understanding your cash flow, you can make informed decisions about spending, saving, and investing. For instance, you might allocate a specific portion of your cash inflows towards investments with higher returns while ensuring that essential expenses are covered.
Diversification is also a valuable cash management strategy. Instead of keeping all cash in one place, investors can distribute it across various investment vehicles. This could mean allocating funds to different asset classes like stocks, bonds, or real estate, each offering unique risk-return profiles. Diversification helps reduce the impact of market volatility on cash holdings, providing a more stable investment environment. Additionally, it allows investors to take advantage of growth opportunities in multiple sectors or markets.
Lastly, considering the time value of money is essential for optimizing cash holdings. This concept emphasizes that cash received or spent in the future is worth less than the same amount today due to its potential earning capacity. Investors can use this principle to make informed decisions about when to invest, spend, or save cash. For example, investing cash early can lead to compound growth, where returns are reinvested, generating even more returns over time. Understanding the time value of money enables investors to make strategic choices to maximize the growth of their cash resources.
Understanding Long-Term and Short-Term Investing: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Cash dividends: Payments made by companies to shareholders from their profits
Cash dividends are a fundamental concept in the world of investments, representing a crucial aspect of how companies distribute their profits to shareholders. When a company generates a profit, it has several options for utilizing those earnings, and one of the most common is to pay out a portion of the profit as dividends to its shareholders. This process is a direct way for companies to return value to their investors, providing a tangible benefit that can be particularly attractive to those seeking regular income from their investments.
In the context of investments, cash dividends refer to the monetary payments made by a corporation to its shareholders. These dividends are typically a result of the company's successful financial performance and are often a key indicator of a company's financial health and stability. Dividends are usually paid out of the company's retained earnings, which are the profits that the company has accumulated over time and decided to distribute to its shareholders instead of reinvesting them into the business.
The payment of cash dividends is a strategic decision made by the company's board of directors. They consider various factors, such as the company's financial position, future growth prospects, and the overall market conditions, to determine the amount and frequency of dividend payments. Shareholders are then entitled to receive a portion of these profits, which can be a significant source of income, especially for long-term investors who rely on a steady stream of cash flow from their investments.
Dividend payments can vary widely depending on the company's performance and the industry it operates in. Some companies may choose to pay dividends quarterly, while others may opt for annual payments. The amount of each dividend is typically calculated as a percentage of the shareholder's stockholding, ensuring that investors who have held the stock for longer periods receive a more substantial return. This system encourages long-term investment and provides a clear incentive for shareholders to maintain their holdings.
Understanding cash dividends is essential for investors as it allows them to assess the potential income they can generate from their investments. It also provides insights into the company's commitment to shareholder value and its financial stability. Investors often seek companies with a strong dividend track record as a sign of a well-managed business, indicating that the company has the financial strength to consistently return profits to its shareholders.
Secure Your Future: Long-Term Investment Strategies for Savvy Investors
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
In investments, cash refers to the physical currency or liquid assets that can be readily converted into cash with minimal impact on its value. This includes bank deposits, money market funds, and other highly liquid assets that can be quickly turned into cash without significant loss.
Cash is distinct from other investment instruments like stocks, bonds, or real estate, as it represents the most basic and liquid form of money. While other assets may appreciate or depreciate in value over time, cash itself does not fluctuate in value and can be easily exchanged for goods or services.
Cash is a critical component of investment portfolios as it provides liquidity and serves as a safety net. It allows investors to take advantage of immediate opportunities, cover unexpected expenses, or seize investment prospects without delay. Additionally, holding a portion of cash can help diversify the portfolio and reduce the impact of market volatility.
Holding cash offers several advantages. Firstly, it provides a hedge against market downturns, as cash is not subject to the same price fluctuations as other assets. Secondly, cash can be used to reinvest in other investment opportunities when market conditions are favorable, potentially maximizing returns. Lastly, cash ensures that investors have immediate access to their funds, providing flexibility and control over their investments.
While cash is generally considered a safe asset, there are some risks to consider. One risk is the potential loss of purchasing power due to inflation, especially if the cash is held in low-interest-bearing accounts. Another risk is the opportunity cost of not investing cash, which may result in missed potential gains. However, these risks can be managed by diversifying cash across different investment vehicles and regularly reviewing and adjusting the portfolio.