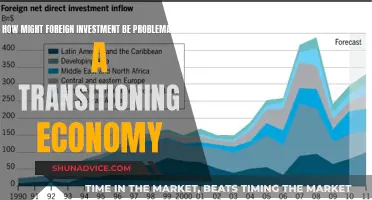
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in the global economy, and understanding its distribution is essential for businesses and policymakers alike. This paragraph introduces the topic by highlighting the significant impact of foreign investment on various sectors and regions worldwide. It emphasizes that while some countries attract substantial foreign investment, others may face challenges in this regard. The discussion will explore the factors influencing the geographical distribution of foreign investment, including economic stability, market size, political environment, and regulatory frameworks. By examining these aspects, we can gain insights into why certain regions become more attractive destinations for foreign investors, shaping global trade and development.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Top Countries | United States, China, Hong Kong, Singapore, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Japan, Canada, South Korea |
| Investment Sectors | Technology, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Real Estate, Infrastructure, Energy, Telecommunications, Financial Services |
| Investment Trends | Rising global trade tensions, Shifts towards developing economies, Increased focus on sustainable and green investments |
| Regional Distribution | Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, Latin America, Africa, Middle East |
| Investment Flows | Inward FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) is more common in developed countries, Outward FDI is driven by multinational corporations |
| Key Factors | Political stability, Economic growth, Market size, Infrastructure, Skilled workforce, Government policies and incentives |
| Recent Developments | Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, Geopolitical tensions affecting investment patterns, Rise of digital and tech-based investments |
What You'll Learn
- Economic Development Zones: Foreign investment often targets designated areas for infrastructure and job creation
- Natural Resources: Countries rich in oil, gas, minerals attract significant foreign investment for extraction
- Manufacturing Hubs: Industrial parks and factories are common destinations for foreign capital to boost production
- Technology and Innovation: Startups and tech giants draw investment to foster innovation and market expansion
- Infrastructure Projects: Transportation, energy, and telecommunications attract foreign capital to improve national infrastructure

Economic Development Zones: Foreign investment often targets designated areas for infrastructure and job creation
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in economic development, and one of the key strategies employed by governments and international organizations is the establishment of Economic Development Zones (EDZs). These zones are specifically designated areas that offer a range of incentives and benefits to attract foreign investors and promote economic growth. The primary focus of EDZs is to create an environment conducive to investment, often targeting industries that can drive significant economic impact.
In many countries, EDZs are established in regions that may have previously been economically disadvantaged or underdeveloped. These areas are chosen for their potential to attract foreign capital and create a ripple effect of positive economic changes. The primary goal is to stimulate local economies, generate employment opportunities, and improve the overall standard of living for the local population. By targeting these specific zones, governments aim to showcase the benefits of foreign investment and encourage further development.
Foreign investors are often drawn to EDZs due to the various advantages and support systems in place. These zones typically offer tax incentives, streamlined regulations, and improved infrastructure. Investors can benefit from reduced tax rates, simplified business registration processes, and access to specialized support services. Additionally, EDZs often provide infrastructure such as industrial parks, transportation networks, and utility systems, ensuring that businesses have the necessary resources to operate efficiently.
The impact of foreign investment in these zones can be far-reaching. It not only leads to the establishment of new businesses and industries but also contributes to the transfer of knowledge and technology. Foreign investors bring expertise, management skills, and access to global markets, which can enhance the local business environment. As a result, local companies can improve their productivity, adopt advanced technologies, and potentially expand their operations.
Moreover, the creation of jobs is a significant outcome of foreign investment in EDZs. As businesses set up and expand, they require a skilled workforce, which can lead to increased local employment. This, in turn, can reduce unemployment rates and improve the financial stability of the region. The positive economic effects of EDZs can create a cycle of development, encouraging further investment and fostering long-term economic growth.
Ally Invest App: A User's Guide to Trading
You may want to see also

Natural Resources: Countries rich in oil, gas, minerals attract significant foreign investment for extraction
The global economy is heavily reliant on natural resources, and countries endowed with abundant oil, gas, and mineral deposits have long been magnets for foreign investment. These resources are the lifeblood of many industries and are essential for energy production, manufacturing, and technological advancements. As a result, nations with significant natural resource endowments often find themselves at the center of international investment strategies.
Oil-rich countries, in particular, have historically attracted substantial foreign direct investment (FDI) due to the high demand for this vital energy source. The Middle East, for example, is home to some of the world's largest oil reserves, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) being prominent recipients of foreign investment in the energy sector. These nations have established robust infrastructure and have been proactive in attracting international oil companies to develop their vast oil fields. The revenue generated from these investments contributes significantly to the host country's economy, enabling infrastructure development and social welfare programs.
Similarly, natural gas-rich countries have also become attractive destinations for foreign investors. Countries like Russia, with its vast natural gas reserves, have leveraged their resources to secure substantial investment in the energy sector. The development of natural gas infrastructure, including pipelines and processing facilities, has been a key focus for these nations, as it enables the export of this valuable resource to global markets. Foreign investors are drawn to the potential for long-term revenue streams and the opportunity to participate in the growing demand for natural gas worldwide.
Mineral-rich countries also play a crucial role in attracting foreign investment. Countries like South Africa, with its diverse mineral resources, have a long history of mining-related FDI. Investors are drawn to the country's extensive mineral deposits, including gold, diamonds, and platinum, which are essential for various industries. The establishment of mining operations not only generates significant revenue for the host country but also creates numerous job opportunities and contributes to economic growth.
In summary, countries rich in natural resources, particularly oil, gas, and minerals, have a unique advantage in attracting foreign investment. These resources are highly sought-after commodities, driving economic growth and development in the host countries. Foreign investors are keen to capitalize on the potential for revenue generation and the establishment of long-term partnerships in these sectors. As the global demand for energy and raw materials continues to rise, the importance of these natural resource-rich countries in the global investment landscape is likely to persist and even grow.
CAPM: Should You Invest?
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Hubs: Industrial parks and factories are common destinations for foreign capital to boost production
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in global economic development, and understanding its flow is essential for businesses and policymakers alike. When it comes to where most foreign investment occurs, the manufacturing sector stands out as a significant recipient of this capital. Industrial parks and factories have become prime destinations for foreign capital, offering a strategic advantage to both investors and host countries.
The allure of manufacturing hubs lies in their ability to provide a comprehensive ecosystem for production. These hubs often offer a range of benefits, including access to skilled labor, advanced infrastructure, and favorable tax incentives. Many countries have strategically developed industrial parks to attract foreign investors, creating a conducive environment for manufacturing operations. These parks typically provide state-of-the-art facilities, efficient logistics, and streamlined regulatory processes, making them an attractive choice for companies looking to expand their global footprint.
Foreign investment in manufacturing hubs can take various forms, such as greenfield investments, where companies build new facilities from scratch, or brownfield investments, which involve acquiring and upgrading existing factories. Greenfield investments are common in emerging markets, where companies can establish a strong presence and tap into new consumer markets. For instance, the development of special economic zones (SEZs) in countries like China, Singapore, and South Korea has attracted numerous foreign investors, leading to the establishment of cutting-edge manufacturing facilities.
Brownfield investments, on the other hand, are prevalent in more mature markets where companies seek to optimize their production capabilities. This approach involves acquiring underutilized or distressed factories and revitalizing them with modern technology and management practices. By doing so, investors can quickly scale up production and gain a competitive edge in the local market. For example, the acquisition of local factories by multinational corporations in Europe and North America has led to increased efficiency and the introduction of innovative production techniques.
The benefits of foreign investment in manufacturing hubs extend beyond the immediate economic impact. These investments often create a ripple effect, stimulating local economies and fostering technological advancements. As foreign capital flows into industrial parks, it generates employment opportunities, encourages the transfer of knowledge and skills, and promotes the adoption of best practices in manufacturing. This, in turn, can lead to the development of a robust domestic supply chain and enhance the overall competitiveness of the host country.
In summary, manufacturing hubs, characterized by industrial parks and factories, are prime destinations for foreign investment. These hubs offer a comprehensive package of advantages, including skilled labor, infrastructure, and incentives, making them an attractive choice for investors. The strategic development of such hubs can drive economic growth, create jobs, and foster technological progress, ultimately benefiting both the investors and the host nations. Understanding these investment patterns is vital for businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions and capitalize on the opportunities presented by foreign capital.
What Investment Criterion Methods Do Firms Favor?
You may want to see also

Technology and Innovation: Startups and tech giants draw investment to foster innovation and market expansion
The global landscape of foreign investment is a dynamic arena, with technology and innovation at the forefront of attracting capital and driving economic growth. Startups and tech giants alike are pivotal players in this ecosystem, each contributing uniquely to the expansion of markets and the fostering of innovation.
Startups, often brimming with cutting-edge ideas and disruptive potential, have become a significant draw for foreign investment. These early-stage companies are typically characterized by their ability to innovate rapidly and adapt to changing market conditions. Investors are drawn to startups that demonstrate a unique value proposition, a strong team, and a clear path to market success. Many startups leverage foreign investment to fuel their growth, enabling them to scale operations, enhance product development, and expand into new markets. This investment often provides the necessary capital to navigate the initial stages of business, where resources can be scarce and the risk of failure is high.
Tech giants, on the other hand, have established themselves as powerhouses in the global economy. These large corporations possess substantial market share, brand recognition, and a proven track record of innovation. Foreign investment in tech giants often focuses on expanding their global footprint, acquiring complementary businesses, and diversifying their product portfolios. By attracting investment, these companies can accelerate their international expansion, enter new markets, and strengthen their competitive advantage. For instance, a tech giant might secure funding to develop and launch a new product line, enter a foreign market, or acquire a smaller, innovative company to bolster its capabilities.
The appeal of technology and innovation as investment drivers lies in their potential for high returns and long-term value creation. Investors recognize that these sectors can drive significant economic growth, create jobs, and foster technological advancements. Startups and tech giants alike contribute to the overall innovation ecosystem, creating a positive feedback loop where investment leads to growth, which in turn attracts more capital. This cycle is particularly evident in the tech industry, where rapid advancements and disruptive technologies can quickly become obsolete, requiring constant innovation and investment to stay ahead.
Foreign investment in technology and innovation also plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between developed and developing nations. Startups and tech giants can leverage their expertise and resources to help less-developed countries leapfrog traditional infrastructure, adopting cutting-edge solutions directly. This not only accelerates economic growth in these regions but also positions the investors as leaders in sustainable and innovative development.
In summary, the convergence of startups and tech giants in the realm of foreign investment is a powerful force driving technological advancement and market expansion. This dynamic relationship between investors and innovative companies is essential for economic growth, job creation, and the overall development of both individual nations and the global economy. Understanding these investment patterns can provide valuable insights for policymakers, investors, and entrepreneurs alike, shaping strategies for fostering innovation and market growth.
Webull's User Age Limit: Who Can Invest?
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Projects: Transportation, energy, and telecommunications attract foreign capital to improve national infrastructure
Infrastructure projects, particularly in the sectors of transportation, energy, and telecommunications, are significant drivers of foreign investment globally. These sectors play a crucial role in the development and modernization of a country's infrastructure, which is essential for economic growth and improved quality of life. Foreign investors are often attracted to these areas due to the potential for substantial returns on investment and the long-term benefits that can be derived from such projects.
Transportation infrastructure, including roads, railways, and airports, is a key area of interest. Well-developed transportation networks facilitate the movement of goods and people, fostering trade and economic activity. Foreign investors often contribute capital to upgrade and expand these networks, ensuring efficient connectivity within a country and beyond. For instance, the construction of high-speed rail lines or the development of international airports can significantly enhance a nation's attractiveness to international businesses and tourists.
Energy projects also attract a substantial amount of foreign investment. The development of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is a growing trend globally. Foreign investors are increasingly interested in funding these projects to promote sustainable energy practices and reduce environmental impacts. Additionally, traditional energy sectors, such as oil and gas, continue to draw investment, especially in regions with abundant natural resources. These energy projects not only contribute to a country's energy security but also create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
Telecommunications infrastructure is another critical sector that attracts foreign capital. Modern and reliable communication networks are essential for businesses to operate efficiently and for individuals to stay connected. Foreign investors often invest in the expansion of broadband networks, mobile infrastructure, and data centers. This investment enables the adoption of advanced technologies, such as 5G, which can drive innovation, improve productivity, and support the growth of digital industries.
The impact of these infrastructure projects extends beyond the immediate economic benefits. Improved transportation networks can lead to better access to remote areas, fostering social and economic development. Energy projects can provide reliable power to communities, supporting local industries and improving living standards. Telecommunications advancements enable better connectivity, facilitating education, healthcare, and government services, especially in rural or underserved regions.
In summary, infrastructure projects, particularly in transportation, energy, and telecommunications, are powerful magnets for foreign investment. These investments not only improve a country's infrastructure but also contribute to economic growth, job creation, and the overall development of the nation. As countries continue to prioritize infrastructure development, foreign investors will likely play a significant role in shaping the future of these essential sectors.
Investing Surplus Cash: Strategies for Long-Term Financial Growth
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The majority of FDI is concentrated in developed countries, particularly in North America, Europe, and East Asia. These regions have a strong economic infrastructure, political stability, and favorable business environments, making them attractive destinations for foreign investors.
Yes, certain sectors often attract significant foreign investment. Manufacturing, particularly in industries like automobiles, electronics, and chemicals, is a major recipient. Other key areas include technology and telecommunications, financial services, healthcare, and renewable energy. These industries offer high growth potential and often benefit from the expertise and resources of foreign investors.
While developed countries dominate in terms of the overall volume of FDI, developing nations have been increasingly attracting foreign capital. Many developing countries offer low-cost labor, natural resources, and emerging markets, making them appealing for manufacturing, agriculture, and infrastructure projects. However, the distribution of FDI can vary widely across different regions and countries within the developing world.
Regional trade agreements (RTAs) play a crucial role in facilitating foreign investment. These agreements often include provisions that reduce barriers to trade and investment, providing a more favorable environment for businesses. By establishing common rules and standards, RTAs can encourage FDI by reducing risks and providing market access. Examples include the European Union's internal market, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and various African regional blocs.
Several factors influence the choice of location for foreign investors. These include political and economic stability, the availability of skilled labor, infrastructure development, tax incentives, and the overall business climate. Additionally, proximity to existing supply chains, market access, and the presence of complementary industries can also be significant considerations when deciding where to invest.